Page 69
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 3 (Suppl)
Mod Chem Appl, an open access journal
ISSN: 2329-6798
Global Chemistry 2017
September 04-06, 2017
September 04-06, 2017 | London, UK
5
th
Global Chemistry Congress
Multifunctional nanoparticles composed of a mixed ferrite core and a mesoporous silica shell for
RGD peptide to target alpha (v) beta (3) integrin in cancer therapy and diagnosis
Susel Del Sol Fernandez
1
, Herlys Viltres Cobas
1
, Ricardo García Salcedo
1
, Oscar F Odio Chacon
2
and
Edilso Reguera Ruiz
1
1
CICATA-IPN, Mexico
2
IMRE, Cuba
T
he integrin αvβ3 plays an important role in angiogenesis. It is expressed on tumoral endothelial cells as well as on some
tumor cells. RGD peptides are well-known to bind preferentially to the αvβ3 integrin. In this context, targeting tumor
cells or tumor vasculature by RGD-based strategies is a promising approach for delivering anticancer drugs or contrast
agents for cancer therapy and diagnosis. A key challenge in developing theranostic nano platform is to achieve an optimal
pharmacokinetic profile to allow sufficient targeting and to avoid rapid clearance by the reticuloendothelial system (RES).
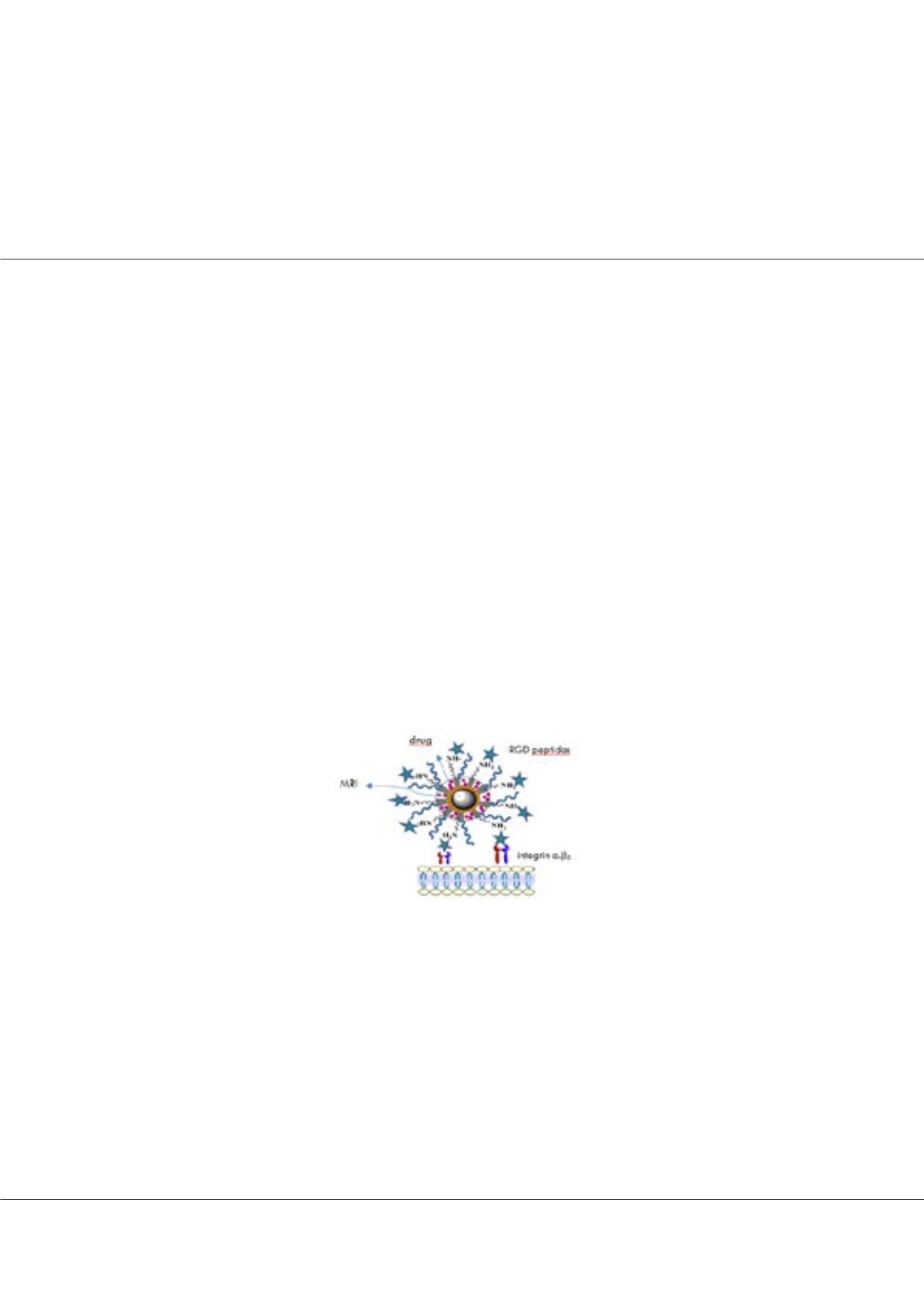
Recently, multifunctional nanostructured materials have been applied to multimodal imaging and simultaneous diagnosis
and therapy. In this context, the integration of mesoporous silica with superparamagnetic monodisperse nanocrystals to form
uniform core–shell composite particles has great potential for simultaneous bio imaging and drug delivery. In the present study,
mixed ferrite (MnFe
2
O
4
) were coated with a mesoporous silica and polyethylene glycol (PEG), making them water soluble
and function-extendable for future bio-conjugation with RGD peptide. MnFe
2
O
4
@mSiO
2
-PEG particles were characterized
by DRX, TEM, DLS and VMS. Results showed that a spherical, highly-ordered MnFe2O4 nanoparticles with a diameter of
around 10 nm, and a narrow size distribution. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis revealed that such MnFe
2
O
4
@mSiO
2
-
PEG has a hydrodynamic size of ˜20 nm in aqueous solution. The field dependent magnetism of at 300 K shows no hysteresis,
demonstrating a superparamagnetic behavior, which is a desirable characteristic for T2 MR contrast agents. The integrated
capability of the core–shell NPs to be used as MR and fluorescence imaging agents, along with their potential use as a drug
delivery vehicle, make them a novel candidate for future cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Biography
Susel Del Sol Fernandez has expertise in the synthesis and characterization of nanomaterials and Medical Physics. She has completed her Master's degree at
Center for Research in Applied Science and Advanced Technology (CICATA), Legaria Unit, National Polytechnic Institute, Mexico City, Mexico. Currently, she is a
PhD student at CICATA, Legaria Unit. She worked on the synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles (magnetite and mixed ferrites) for delivering
anticancer drugs or contrast agents for cancer therapy and diagnosis.
susel2489@gmail.comSusel Del Sol Fernandez et al., Mod Chem Appl 2017, 5:3(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2329-6798-C1-006