Page 65
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 3 (Suppl)
Mod Chem Appl, an open access journal
ISSN: 2329-6798
Global Chemistry 2017
September 04-06, 2017
September 04-06, 2017 | London, UK
5
th
Global Chemistry Congress
Synthesis of triazole-linked morpholine oligonucleotides via CuI catalysed cycloaddition
Rima D Alharthy
1
, Matthew J Palframan
2
, Paulina K Powalowska
2
and
Christopher J Hayes
2
1
King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia
2
University of Nottingham-University Park, UK
T
he Cu
I
catalysed (3+2) azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) has been used to construct modified inter nucleotide linkages,
to prepare nucleic acid conjugates, and as a strand ligation tool. In particular, the artificial triazole-linked DNA
TL
DNA 1
retains good aqueous solubility, is stable towards enzymatic degradation, and can be read by polymerases. As part of our own
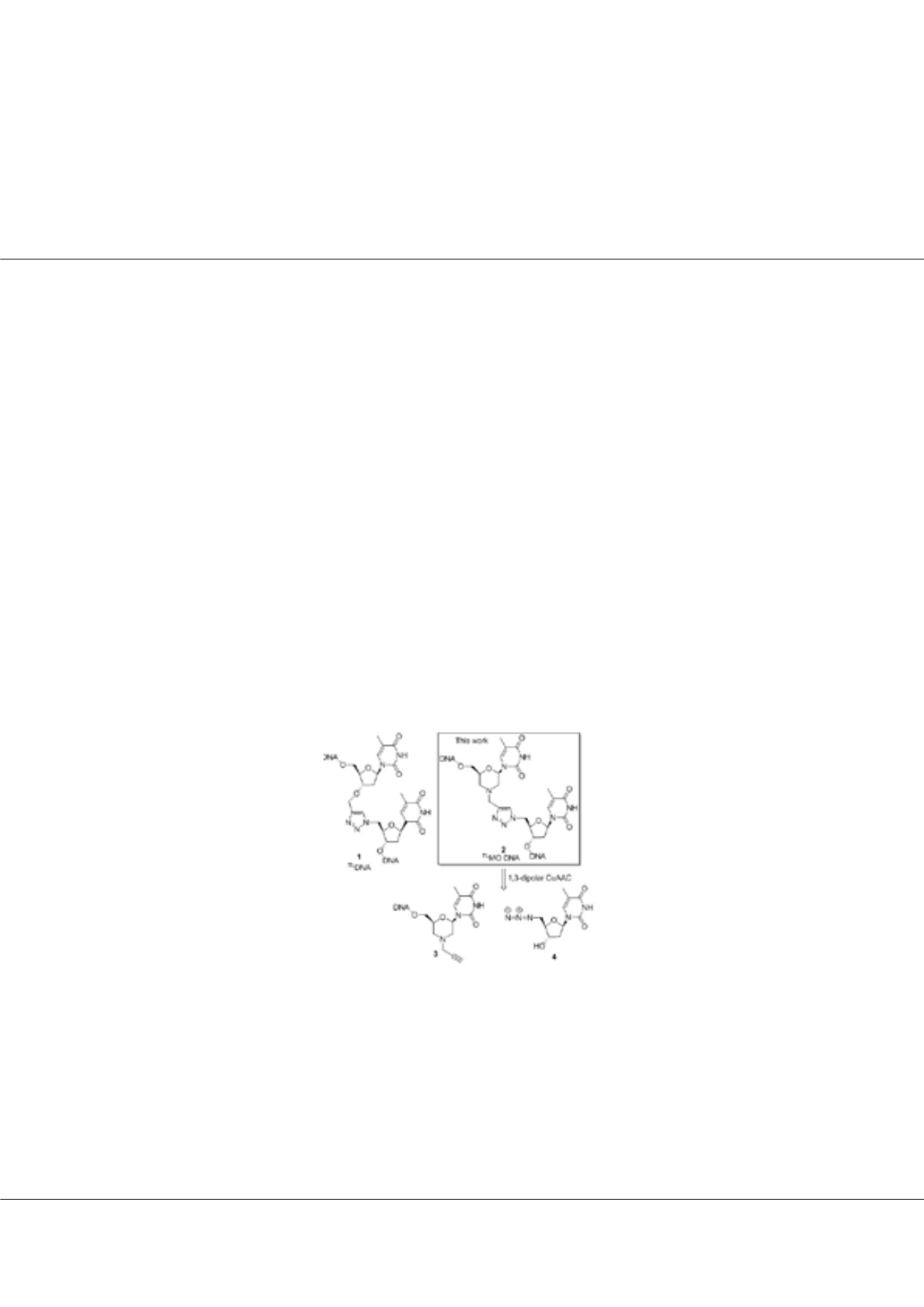
research aimed at developing therapeutic nucleic acids, we decided to examine triazole-linked morpholino (
TL
MO) hybrid
structures 2 (Fig. 1) as they could combine the ease of synthesis of the
TL
DNAs 1 with the increased melting temperatures
associated with morpholino drug candidates. Thus, triazole-linked morpholino (
TL
MO) oligonucleic acids were synthesized
using the CuAAC reaction. The
TL
MO hybrid 2 can be disconnected to reveal the azide 4 and the alkyne-substituted morpholine
3 as potential precursors for the proposed CuAAC reaction (Fig. 1). Synthesis strategy involved oxidative cleavage of ribose,
reductive amination treatment with sodium cyanoborohydride/AcOH to build the propargylamine partner. The azido
thymidine building block was accessed via a two-step sequence involving mesylate formation and displacement with sodium
azide. Next, CuAAC was successfully applicable to obtain
TL
MO. A range of catalysts and solvents were initially screened, and
it was quickly found that the use of copper(I) iodide in THF:tBuOH:H2O (3:2:1) with microwave heating (80°C) was optimal.
Under these conditions, cycloaddition of the acetylene with the TBS-protected azide gave the
TL
MO dimer in good yield, and
TBAF de-protection gave the desired alcohol in good yield. The modified DNA analogues were incorporated into 13-mer
sequences via solid phase synthesis. UV melting experiments showed that the
TL
MO modification gives higher Tm values
than the corresponding
TL
DNA modification. Thus, addition of the morpholine modification can regain half of the Tm lost by
incorporating the triazole inter nucleotide linkage.
Biography
Rima D Alharthy is an Organic Synthetic Chemist. During her Post-doctoral research, she was working on the synthesis of attractive bioactive compounds and
consequently evaluating their activity. This includes the synthesis of hetrocycles such as Pyrido[2,3-b]pyrazines, polyphenols, pyrazolo pyrimidine scaffolds and
hybrid acridine-HSP90 ligand conjugates.
iaaalharte@kau.edu.saRima D Alharthy et al., Mod Chem Appl 2017, 5:3(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2329-6798-C1-006