Page 52
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
Journal of Biotechnology & Biomaterials
ISSN: 2155-952X
Biotech Congress 2018 & Enzymology 2018
March 05-07, 2018
JOINT EVENT
20
th
Global Congress on
Biotechnology
3
rd
International Conference on
Enzymology and Molecular Biology
&
March 05-07, 2018 London, UK
Lysyl oxidase: A versatile and elusive enzyme
Karlo M Lopez
California State University-Bakersfield, USA
L
ysyl oxidase is an extracellular matrix, copper-dependent, amine oxidase that catalyzes a key crosslinking step in collagen and
elastin. The enzyme is synthesized as a proenzyme that, upon excretion to the extracellular matrix, is cleaved at the Gly168-
Asp169 bond by procollagen C-proteinase in the mammalian form of the enzyme. Lysyl oxidase is highly regulated and changes in its
regulation have been shown to play a role in fibrosis and several other diseases. More recently, the enzyme has been shown to play a
paradoxical role in cancer. In the early stages of cancer, the cleaved pro-peptide has been shown to inhibit the RAS oncogene, whereas
in late stages of cancer lysyl oxidase has been shown to promote metastasis. Lysyl oxidase is highly insoluble and this has hampered
its full characterization. Recent work in the by our study group has addressed some of the issues associated with the insolubility and
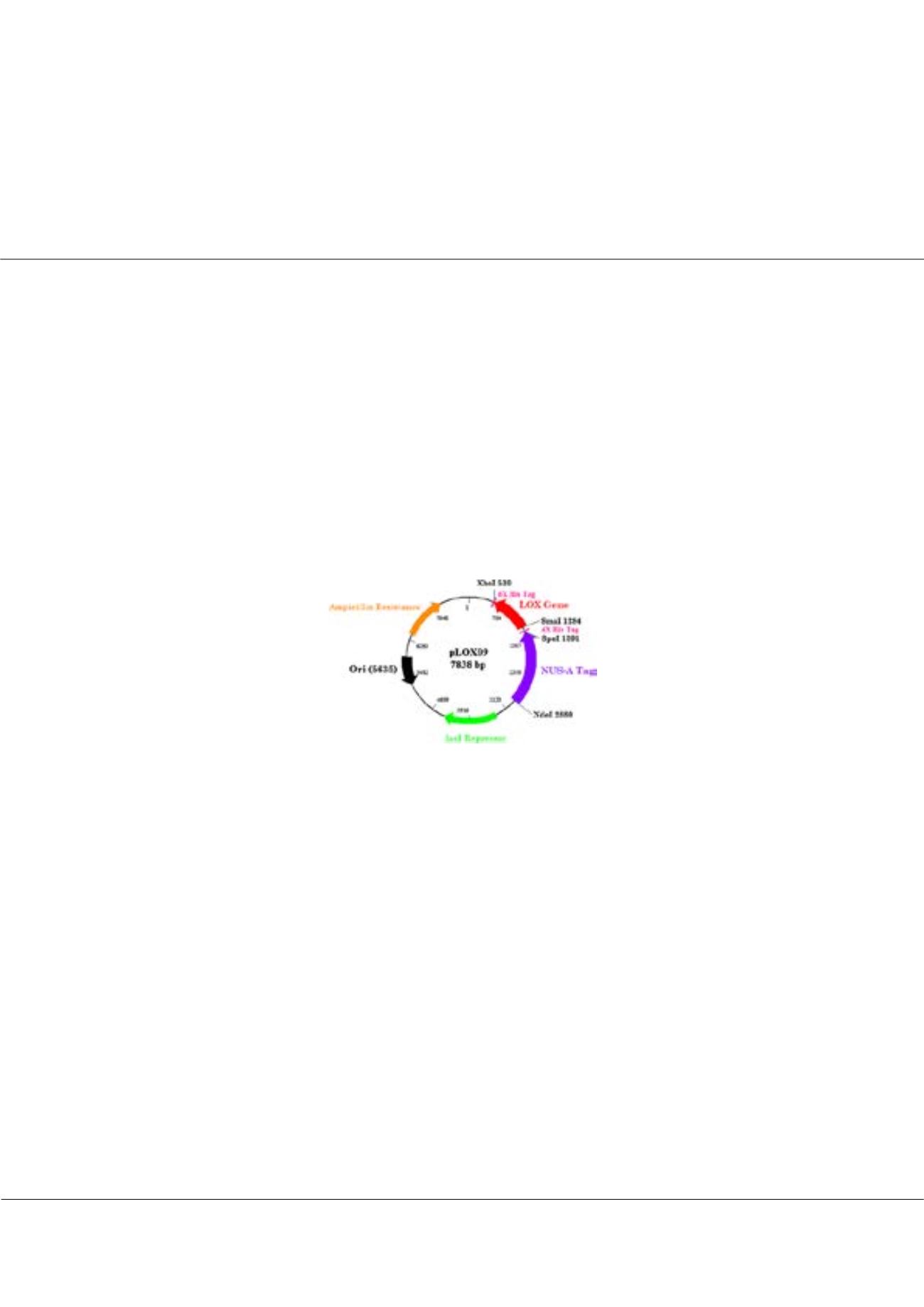
characterization of the enzyme. In particular, this talk will address how plasmids were used to increase enzyme yields over those
obtained directly from bovine aortic tissue, the role solubility tags play on enzyme activity and suitability for characterization studies,
and will end with an innovative new approach to drug delivery that targets lysyl oxidase in cancer cells but remains inactive in normal
cells.
Recent Publications
1.
Oldfield R, Johnston K, Limones J, Ghilarducci C and Lopez K (2017) Identification of histidine 303 as the catalytic base of
lysyl oxidase via site – directed mutagenesis. The Protein Journal, doi: 10.1007/s10930-017-9749-3.
2.
Smith M A, Gonzalez J, Hussain A, Oldfield R N, Johnston K A, et al. (2016) Overexpression of soluble recombinant human
lysyl oxidase by using solubility tags: effects on activity and solubility. Enzyme Research 2016:1-7.
3.
Lopez K and Greenaway F T (2011) Identification of the copper-binding ligands of lysyl oxidase. Journal of Neural
Transmission 118:1101-1109.
4.
Herwald S, Greenaway F and Lopez K (2010) Purification of high yields of catalytically active lysyl oxidase directly from
Escherichia coli cell culture. Protein Expression and Purification 74:116-121.
Biography
Karlo M Lopez is currently an Associate Professor of Biochemistry at California State University, Bakersfield. He received a PhD from Clark University and was a
Howard Medical Institute Fellow at Pomona College. His research focuses primarily on the structural characterization of lysyl oxidase and understanding the role
this enzyme plays in cancer metastasis. He is a member of the Committee on Ethics of the American Chemical Society and was part of the Task Force for Safety
Education Guidelines.
klopez@csub.eduKarlo M Lopez, J Biotechnol Biomater 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X-C2-091