Page 34
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8, Issue 6 (Suppl)
J Bioremediat Biodegrad, an open access journal
ISSN:2155-6199
Biopolymers & Bioplastics 2017
October 19-20, 2017
October 19-20, 2017 San Francisco, USA
7
th
International Conference and Exhibition on
Biopolymers and Bioplastics
The use of recycled polymer in the decrease of moisture in concrete slabs used in cemeteries
Luciana N Magalhães
1
, Juliana S. M. Guedes
3
, Stéphanie S. R. D. Morais
2
, Ariádina S. Menezes
2
and
Maria Alzira P. Dinis
3
1
University Pontifícia Universidade Católica, Brazil
2
FUMEC University, Brazil
3
University Fernando Pessoa, Portugal
T
he conventional concrete together with masonry are the building processes used in Brazil at the traditional cemeteries, named
horizontal cemeteries. They are, composed of shallow graves and burial chambers. The physical and mechanical characteristics of
the structural materials influence pathologies that may occur affecting both the integrity of the tombs and the environment in which
they are settled. The alkali-aggregate reaction, RAA, consists of a chemical reaction that occurs in mortars or concretes, between the
hydroxyl ions (OH-), mineralogical constituents of the aggregates, related to the alkalis sodium oxide (NA
2
O) and potassium oxide (
K
2
O) from the Portland cement itself or from other sources. The product of this reaction is the formation of the expansive gel, arising
from the deterioration process of the hardened concrete that causes from the destruction of structures and cracks, to the reduction
of tensile and compressive strengths. These pathologies affect the durability and safety of concrete structures, which are enhanced by
the presence of moisture. The higher the humidity, the greater the expansion. The lubricity comes from several conditions such as,
whether the water/cement factor is higher than necessary or the relative humidity is greater than 85%, among other reasons. Burial
buildings in cemeteries must be more resistant, due to the fact that in its internal space the very process of body decomposition and
the release of necroslurry attacks and affects the structure, in addition to external factors (environment), such as temperature, that
may wear out different types of materials. By increasing the polymer chain, the coefficient of expansion also expands, thus making
burial buildings more resistant. Permeability and oxidation are two of the most important chemical properties among others. To stop
humidity from enhancing the occurring pathologies, it is convenient to reduce this internal moisture in concrete structures with the
use of waterproof agents. Keeping this in mind, this article intends to evaluate the use of recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
polymer in the structures of burial buildings at vertical cemeteries When evaluating the efficiency of these techniques, the state of
art of the vertical cemetery located in Recife, the capital of the state of Pernambuco, Brazil was assessed and taking into account the
lack of research approaching these subjects, the results of works developed in loco are presented. Advantages and drawbacks of the
application of polymers in the conventional concrete mix to reach the reduction of moisture. We have also pointed out proposals of
solutions concerning the conditions the structure is submitted to.
Biography
Luciana Nunes de Magalhães holds a degree in Civil Engineering from Universidade FUMEC, a master's degree and a PhD in Structural Engineering from
Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais. Currently, is a professor at Pontifícia Universidade Católica de Minas Gerais and provides updated courses for engineers
and architects in the construction / structural systems area at CREA MG. Has professional experience in the Structural Engineering field, besides publications in
magazines and congresses, with emphasis on those systems.
aldeialuciana@gmail.comLuciana N Magalhães et al., J Bioremediat Biodegrad 2017, 8:6 (Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2155-6199-C1-011
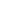
Figure 1 – Symbology used to identify polymer packages. Standard NBR 13.230 of ABNT (Brazilian Association of Technical Standards)