Volume 8
Journal of Biotechnology and Biomaterials
ISSN: 2155-952X
Biomaterials 2018
March 05-06, 2018
Page 78
conference
series
.com
March 05-06, 2018 | Berlin, Germany
3
rd
Annual Conference and Expo on
Biomaterials
Helen Reveron, J Biotechnol Biomater 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X-C1-087
Mechanical properties of new zirconia-based bioceramics with a metal-like behaviour
Y
ttria-stabilized (Y-TZP) zirconia ceramics are increasingly used for developing metal-free restorations and are now considered
as promising alternatives to titanium as dental implants. Zirconia indeed possesses high strength and good toughness for a
ceramic, together with excellent bio-integration, biocompatibility and translucency. However, Y-TZP ceramics are still considered
as brittle ceramics, since transformation induced toughening occurs after cracks start to propagate. Moreover, Y-TZP can undergo
low temperature degradation (LTD) or ageing, leading to a loss of strength and micro-cracking. Therefore, our current research
is focusing on strategies to develop alternative zirconia-based materials with better stability
in-vivo
and higher degree of ductility,
especially for dental implants applications in which the translucency is less important but for which a perfect stability, good
mechanical properties and long lifetime should be ensured. In this work the mechanical characterization of a new type of very-
stable zirconia-based composites is presented.These materials are composed of ceria-stabilized zirconia (Ce-TZP) and two second-
phases (alumina and strontium aluminate) and can exhibit very high strength, toughness and ductility. In other words, in these
ceramics, plastic deformation occurs before failure driven by the tetragonal (t) to monoclinic (m) zirconia phase transformation,
which leads to mechanical behavior laws similar to metals. During the oral presentation, the effect of the composition and/or
the microstructure on the strength-toughness relationship will be presented and the validity of various mechanical tests used to
measure the fracture strength on these materials discussed.
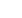
Figure 1: New developed Ce-TZP-based composite plastically deformed.
Recent publications
1. E Apel, C Ritzberger, N Courtois, H Reverón, J Chevalier et al. (2012) Introduction to a tough, strong and stable Ce-TZP/
MgAl2O4 composite for biomedical applications. J. Eur. Cer. Soc. 32(11)2697-2703.
2. P Palmero, R Traverso, C Esnouf, H Reveron, J Chevalier, L Montanaro (2015) Zirconia-based composites for biomedical
applications: role of second phases on composition, microstructure and zirconia transformability. J. Eur. Cer. Soc.
35(14):4039-4049.
3. P Palmero, M Fornabaio, L Montanaro, H Reveron, C Esnouf, J Chevalier (2015) Towards long lasting zirconia-based
nanocomposites for dental implants. Part I: innovative synthesis, microstructural characterization and
in vitro
stability.
Biomaterials. 50:38-46.
Helen Reveron
INSA de Lyon - Univ Lyon, France