Page 66
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 9
International Journal of Advancements in Technology
ISSN: 0976-4860
3D Printing 2018
March 19-20, 2018
March 19-20, 2018 | London, UK
2
nd
International Conference on
3D Printing Technology and Innovations
Selective laser melting of a new medium manganese steel alloy for automotive industry
Bernd Schob
1
, Frank Schubert
1
, Lothar Kroll
1
, L Heemann
2
and
V Uhlenwinkel
2
1
Chemnitz University of Technology, Germany
2
IWT, Germany
I
n the last few years Additive Manufacturing has established itself in many branches of business. Especially in the automotive
industry, the technology of powder-based laser additive melting (LAM) is eminently suitable for the production of
customized, high-performance lightweight parts and geometrically complex components. Currently the range of usable
materials is limited to a few titanium, nickel, aluminium, cobalt-chromium alloys, as well as some stainless steels and tool
steels. Therefore, development of new powder alloys for the LAM - process is required. Medium manganese steel alloys
are distinguished materials due to adjustable mechanical properties, such as high strength and significant ductility, which
are beneficial for automotive applications. However, the comparatively difficult processing of a medium manganese steel is
bounded by the resulting densities, among other limitations. The aim of the work was to develop suitable and robust LAM
process parameters for medium manganese steel combined with heat treatment to create microstructures that possess
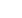
advanced mechanical properties. During the development, material densities of approximately 99.98 % could be achieved. The
mechanical investigations are determined by static load in the second step. Due to the processing of the new manganese steel
alloy and the resulting mechanical properties, new application potentials can be realised e.g. in automotive future body-in-
whites structures.
Biography
Bernd Schob graduated in Mechanical Engineering studies at Westsächsische Hochschule - University of Applied Sciences Zwickau, Zwickau, Germany in 2007
and graduated in Economics studies at Freiberg University of Mining and Technology, Germany in 2015. Since 2016, he is a Research Assistant in the Department
of Mechanical Engineering at Chemnitz University of Technology, Germany. His research focuses on additive manufacturing, specializing in processing of new
materials and development of material parameters in laser additive manufacturing.
bernd.schob@mb.tu-chemnitz.deBernd Schob et al., Int J Adv Technol 2018, Volume 9
DOI: 10.4172/0976-4860-C1-002
Figure 1
:
high density of medium manganese steel.