Page 72
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 9
International Journal of Advancements in Technology
ISSN: 0976-4860
3D Printing 2018
March 19-20, 2018
March 19-20, 2018 | London, UK
2
nd
International Conference on
3D Printing Technology and Innovations
Investigation on the effect of processing parameters on 3D printed structures
Chao Zhu, Chamil Akeykoon
and
Anura Fernando
University of Manchester, UK
T
he Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), which is one of the main additive manufacturing technologies, is widely used
in many fields with multiple materials. Additive manufacturing shows a rapid development over the last decade and
hence FDM printing machines have been improved remarkably. In this work, the effects of several set parameters on 3D
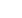
printed samples’ mechanical properties and their printing quality were explored. It seems that the fill density affects samples’
mechanical properties significantly and the variation of maximum load stress and the Young’s modulus changed linearly
with increased density. Moreover, the fill pattern affects fiber’s structure and determines the products’ structural properties.
The mechanical properties of samples and the printing time were also affected significantly with different layer thicknesses.
Samples with different fill patterns showed highly varying properties; e.g. samples with linear fill pattern showed the best
tensile properties where samples with “diamond” fill pattern can have a large deformation during tests. Furthermore, the effects
of different materials (e.g. PLA (Poly Lactic Acid), ABS (Acylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), carbon fibre reinforced PLA/ABS) on
the properties 3D printed structures were also observed and the results showed that the samples with both carbon reinforced
PLA and ABS are better in tensile properties than pure PLA and ABS. However, they were found to be more brittle in nature.
Moreover, the samples printed from carbon fibre reinforced materials showed a 45-55% increase in tensile properties and a
40-55% increase in Young’s modulus compared to pure PLA and ABS.
Biography
Chao Zhu graduated with a Bachelor’s Degree from Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xian, People’s Republic of China. He will get a M Eng Degree from The
University of Manchester next year. His interest lies in manufacturing especially in 3D Printing Future Technology.
chao.zhu-3@student.manchester.ac.ukChao Zhu et al., Int J Adv Technol 2018, Volume 9
DOI: 10.4172/0976-4860-C1-002
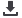
Figure 1:
Fracture surface of samples: fill density
(a).35%, (b).50%, (c).65%, (d).80%, (e).95%.
Figure 3:
The variation of maximum load stress
and the Young’s modulus with fill density.
Figure 4:
Maximum load stress and Young’s modulus of
carbon reinforced polymer and pure PLA and ABS.
Figure 2:
Changes to the fracture plane with fill density.