Volume 6
Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
ISSN: 2332-0877
Infection Prevention 2018
December 06-07, 2018
Page 67
conference
series
.com
December 06-07, 2018 | Valencia, Spain
14
th
World Congress on
Infection Prevention and Control
Chicken immunologically active proteins for the development of anti-idiotypic vaccines
Ioana Manea
Activeimmunity srl, Romania
Introduction:
According to Jerne’s network theory, antibodies contain in their variable region a representation of the ‘universe’
of antigenic structures, the idiotype. It is possible to induce antibodies against the antigen-binding site of other antibodies
(2-6); these new antibodies, called anti-idiotypic (Ab2B), can be used to manipulate the immune system (1,5,6). They have
been successfully used in the induction of humoral immune responses against several antigens including bacteria and
viruses (2,3,5,6). Chicken Immunologically Active Proteins [CIAP] including Immunoglobulin (Ig)-Y, that are produced by
immunizing chickens, have further advantages compared with mammalian IgG (1,2,5,6). This study investigates the use of the
chicken and egg system for the development of an immune response against antimicrobial resistance (AMR) bacteria.
Methodology:
Stage I: Brown leghorn chickens were immunized with I-spga immunogen which contained antigens from
more than 20 inactivated AMR bacteria. Indirect ELISA was used to measure anti-bacterial antibody titers in the watery
soluble fraction of eggs up to 14 weeks after the third immunization. Stage II: chicken groups have been formed that have
individually consumed yolk or white egg from either hiperimune eggs or from eggs produced by unimmunized chicken. At the
end of the experiment, presence of antibodies against original AMR bacteria was checked by ELISA in blood samples and eggs
of birds used in the Stage II of the experiment.
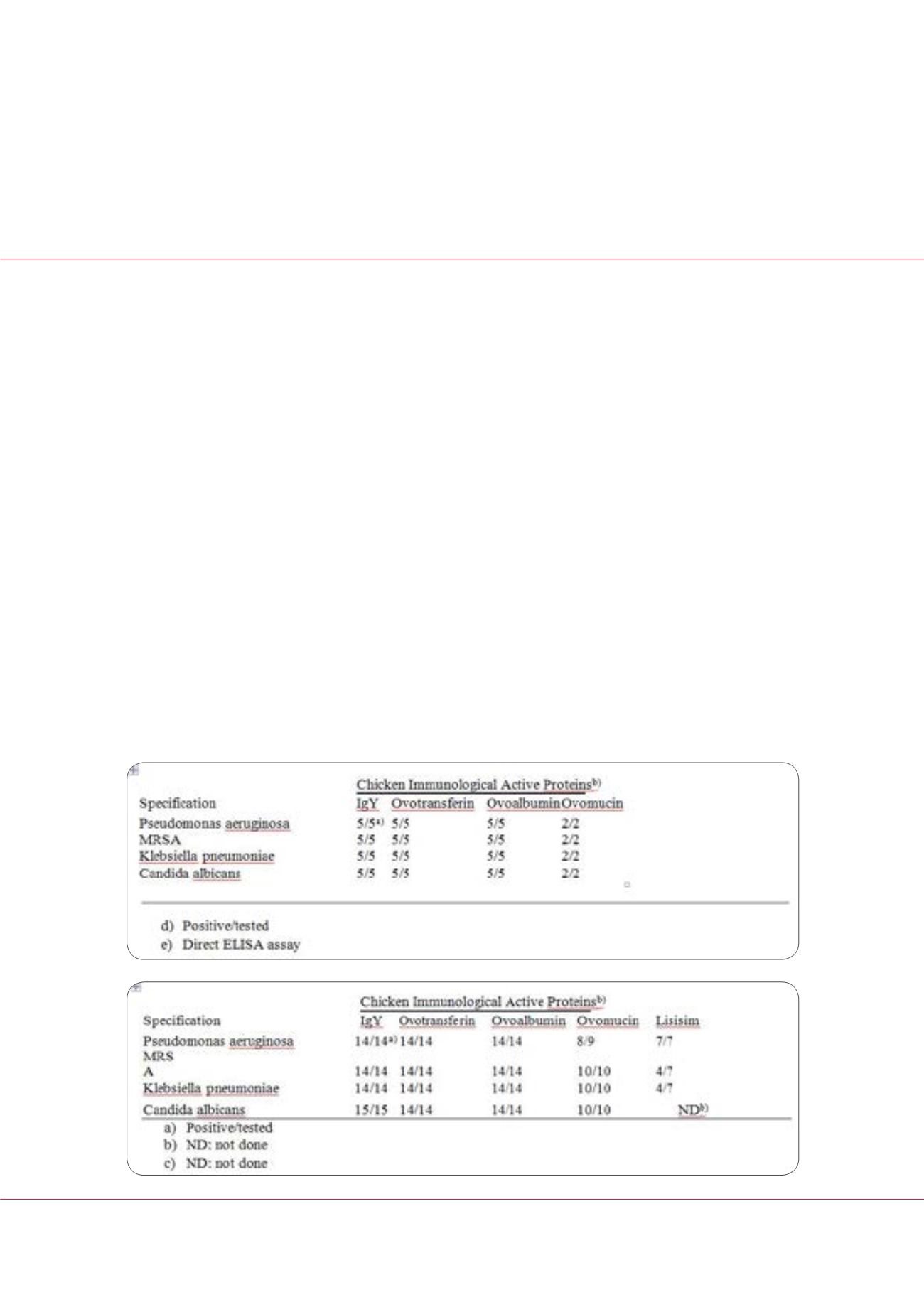
Results:
Antibodies against AMR bacteria were detected only in the blood and eggs of chicken that consumed hiperimmune
eggs; these antibodies inhibited the growth of AMR bacteria in vitro.
Conclusion:
The results of this study suggest that eggs from immunized hens could be considered as a CIAP source in the
management of AMR infections. The chicken and egg system is a potential and novel approach for the development of anti-
idiotypic vaccines that could prove useful in the treatment of microbial infections.
Ioana Manea, J Infect Dis Ther 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2332-0877-C6-053