Page 65
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
ISSN: 2332-0877
Infection Prevention 2018
December 06-07, 2018
December 06-07, 2018 | Valencia, Spain
14
th
World Congress on
Infection Prevention and Control
Chicken immunological active proteins (ciap): The specific reaction against multiple resistance
bacterial strains in urinary tract infections
Liliana Viasu
1
, Ionel-Victor Pătraşcu
2
, Maria-Anca Petrini
2
, Mircea Nicolae Penescu
2
, Carmen Balotescu-Chifiriuc
3
, Maria Serdaru
1
, Rareş-Ilieş Preutu
1
,
Manea Ioana
1
1
Teaching Hospital of Nephrology dr.Carol Davila, Romania
2
Activeimmunity srl, Romania
3
University of Bucharest, Romania
Statement of the Problem:
The emergence of multidrug resistant bacteria in urinary tract infections (UTIs) is a challenge to
medical professionals. According to ECDC (2018), more than a third of K. pneumoniae and half of
E. coli
strains reported
were resistant to at least one of the antibiotics under surveillance. Moreover, the emergence of Colistin resistance among
Enterobacteriaceae leave few therapeutic options against these”superbugs”. Thus, immunological active proteins (IAP) have
emerged as a potential therapeutic agent.
Material and methods:
In this study, CIAP (egg proteins: IgY, holo-ovotransferrin, ovomucin, ovoalbumin and lysozyme)
were obtained from Rhode Island red chickens immunized with antigens from
E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus
spp, Pseudomonas sp, Proteus sp, Candida sp
, and MRSA strains. 90 patients were included in the study, 87 of them compliant
with the treatment; 20 were inpatients and 67 outpatients at Teaching Hospital of Nephrology dr.Carol Davila, Bucharest. 65%
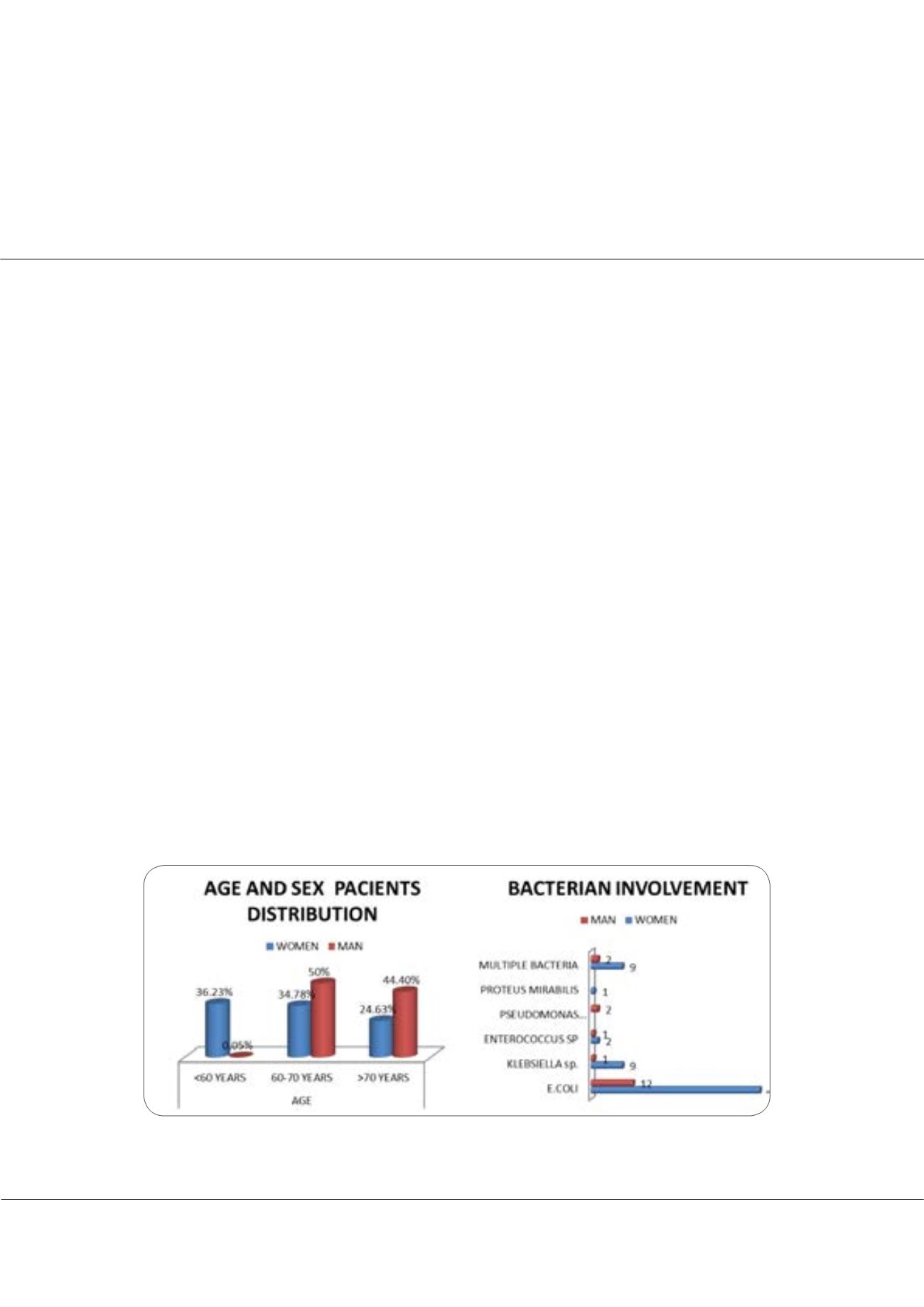
of them were known to have recurrent UTIs. The etiology of the UTIs: 68% E. coli, 12.6% multiple bacteria, 11.5% Klebsiella,
7.9% others. 35% of the isolates were MDR. CIAP efficiency was demonstrated in vitro by: quantitative assay for Chicken
IgY ELISA Kit - ABCAM, rapid and slow agglutination test and bacterial growth inhibition test - HB&L ALIFAX (IAP + live
bacterial cultures). CIAP were administered at diagnosis together with antibiotics, and as follow-up treatment for an average
of 2 months.
Results:
8 patients were non-responsive (7F+1M), 79 were responsive as follows: 90% of the patients were cured with no
recurrence, 10% had one recurrence during the study. For these patients, personalized treatment was made, using the strain
isolated by urine culture after recurrence; the new treatment was curative.
Conclusion:
Preliminary results reveal the possibility of using passive immunity to stimulate the active immunity in preventing
infection recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Liliana Viasu et al., J Infect Dis Ther 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2332-0877-C6-053