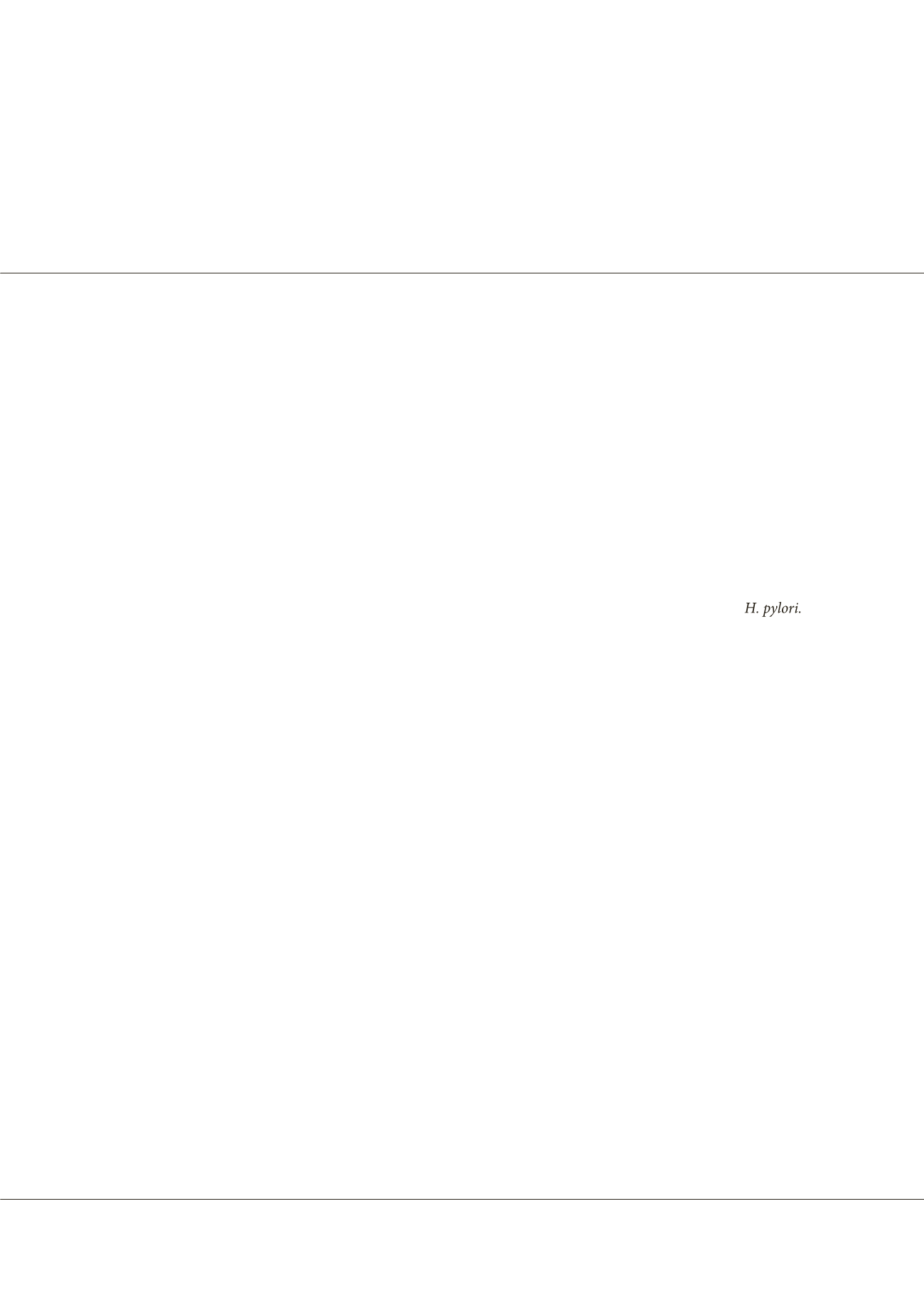
Notes:
Page 45
Clinical Gastroenterology 2016
October 03-05, 2016
Volume 6, Issue 6(Suppl)
J Gastrointest Dig Syst
ISSN:2161-069X JGDS, an open access journal
conferenceseries
.com
October 03-05, 2016 Toronto, Canada
8
th
International Conference on
Clinical Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Fernando Kawaguchi, J Gastrointest Dig Syst 2016, 6:6(Suppl)
http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2161-069X.C1.041Increased in-vitro and in-vivo biological activity of lipopolysaccharide extracted from clinical low
virulence vac A genotype
Helicobacter pylori
strains
Fernando Kawaguchi
Faculty of Medicine, Concepcion University, Chile
H
elicobacter pylori
infection in man is associated with chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. The virulence factors of
the species are still under investigation. Among these, the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a potential pathogenic factor of
the micro-organism, whose biological activity can be estimated by immunological parameters. The aim of this study was to
determine the ability of pure LPS extracted fromclinical isolates of
H. pylori
to inducemitogenicity, secretion of tumour necrosis
factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and spleen growth in a murine model. Rough and smooth LPS from
Salmonella typhimurium
were
used as controls. The results showed that, like the control LPS, all extracts of LPS induced mitogenic activity, stimulated
synthesis of TNF-alpha and induced spleen growth, although the effects produced by the majority of the
H. pylori
LPS samples
analysed were less intensive than those produced by the
S. typhimurium
LPS. The immunological parameters analysed allowed
the detection of two types of
H. pylori
LPS: one of low biological activity and one of high biological activity. The most active
LPS were extracted from strains isolated from patients with increased mucous damage associated with epithelial regeneration.
Surprisingly, these strains were cagA negative and belonged to a low virulence genotype according to vacA gene (slbm2 and
s2m2). The results suggest the need to re-evaluate the role of the LPSas a virulence factor for some strains of
Biography
Fernando Kawaguchi has completed his Medical Studies at the age of 26 years from Faculty of Medicine – Concepcion University- Chile (1987) and postgraduated
studies from Gifu University School of Medicine-Japan (1988-1993). Pancreas and Biliar Studies from Aichi Cancer Center-Japan, includying Echoendoscopy
Training (1991-1993). He obtained Clinical Digestive Oncology PhD from Gifu University (March 1993). He returned to Chile at Concepcion University Faculty
of Medicine, Internal Medicine Department, Gastroenterology Unit (1993-2012). He obtained Academical degree of Associated Prof level, obtaining H Pylori
National Project to identify its pathogenicity and virulence through Biomolecular and Microbiology Research (1996). Became Director of Gastroenterology Unit
from Trabajador Hospital (1998-2008) introducing an Multidisciplinary group in immunopathology cancer research through Flow Cytometry analysis in fresh solid
tumours. And also Echo endoscopy in diagnosis and Minimal Invasive Cancer Theraphy from Stomach, Colon and Biliopancreatic areas supporting many papers
and scientific meetings in reputed nationals and Internationals journals.
itarokawaguchi@vtr.net