Page 107
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 9
Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation
ISSN: 2155-6199
Biofuel Congress 2018 &
Biomass 2018
September 04-06, 2018
JOINT EVENT
September 04-06, 2018 | Zurich, Switzerland
13
th
Global Summit and Expo on
Biomass and Bioenergy
&
12
th
World Congress on
Biofuels and Bioenergy
Pyrolysis of aerobic sewage sludge in fluidized bed reactor between 700 and 830
o
C: Comparison with
woody wastes
Sid Ahmed Kessas
and
Mehrdji Hémati
Laboratoire de Génie Chimique - CNRS, France
I
n this study, the pyrolysis of dry aerobic sewage sludge was carried out under nitrogen inert atmosphere in a dense fluidized
bed reactor (2.5 m height, 0.214 m inner diameter). Firstly, the effects of pyrolysis temperature between 700 and 830°C on
product distributions in terms of syngas, liquid and char and the gas composition were investigated. Results indicate that the
increase of temperature leads to an increase in syngas yield and a decrease in tar yield. However, the char amount is not affected
by temperature beyond 700°C. The gas composition is strongly changed by temperature. H
2
/CO ratio increases from 1.15 at
700°C to 1.53 at 830°C. In addition, these runs were compared to experiments performed during pyrolysis of lignocellulosic
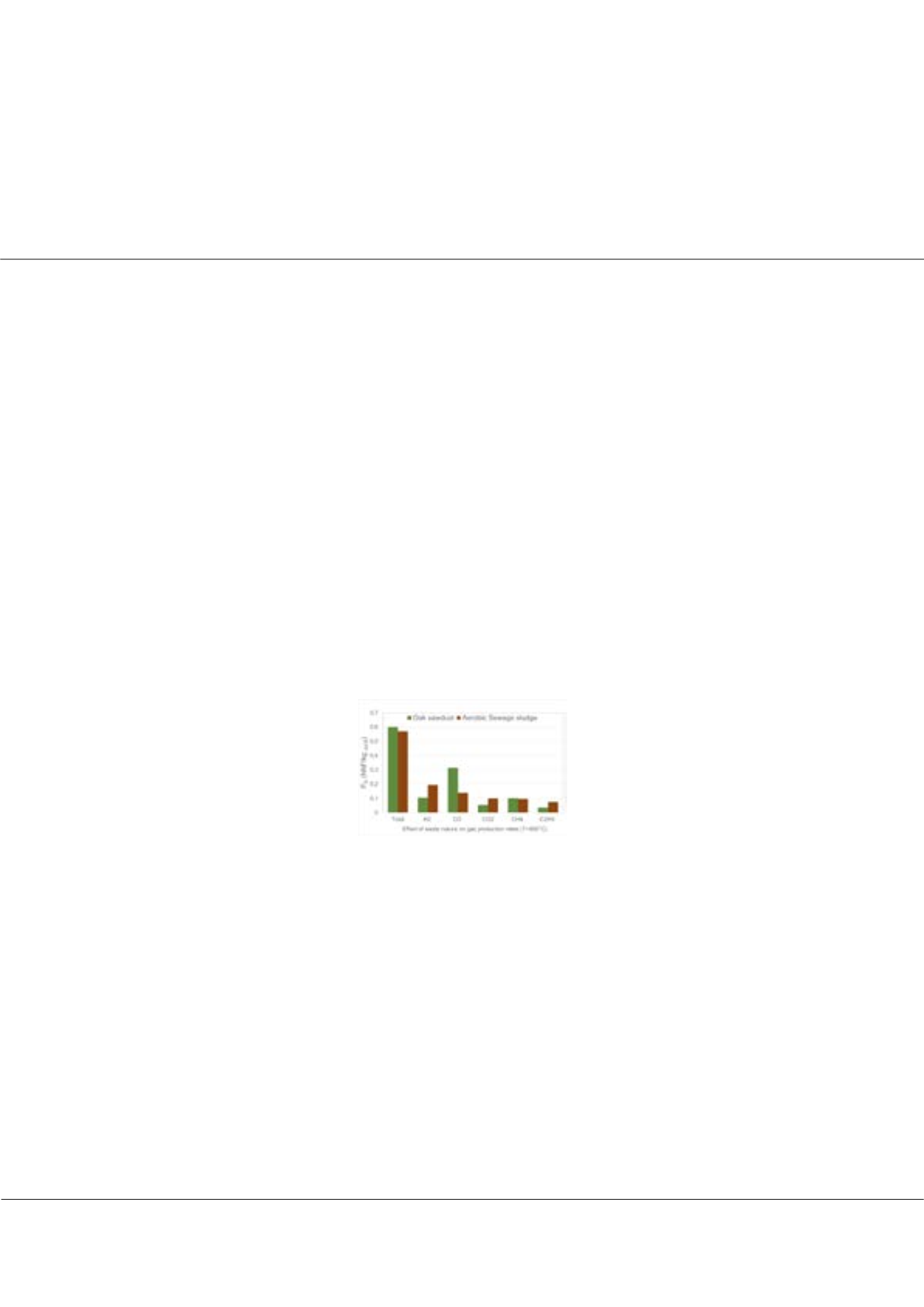
biomasses (oak, pine and beach sawdust). Results show that the syngas yield produced with sewage sludge is comparable to
that obtained with woody biomasses (0.57 Nm
3
/kg daf, B at 800°C). The syngas composition is strongly affected by the nature
and the composition of waste. The low oxygen content in the sewage sludge leads to the formation of a syngas rich in H
2
, CH
4
,
and C
2
Hx with a H
2
/CO ratio higher than that obtained with woody wastes. The tar yield produced using sewage sludge (294
g/kg daf, B) is much more important than that obtained with woody wastes (60 g/kg daf, B for beech sawdust). According to
these results, we proposed a pyrolysis reaction scheme by estimating stoichiometric coefficients related to different pyrolysis
products. Finally, pyrolysis run carried out at 830°C was compared with another test performed under steam atmosphere.
Results show that the presence of steam in reactor increases syngas yield & H
2
/CO ratio from 0.65 to 0.88 Nm
3
/kg daf and 1.53
to 2.02 respectively which reduces four times the tar yield. These results can be explained by concentration or steam partial
pressure effect on tar reforming and water-gas shift reactions.
Recent Publications
1. Nipattummakul N, Ahmed II, Kerdsuwan S and Gupta A K (2010) Hydrogen and syngas production from sewage
sludge via steam gasification. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 35(21):11738–45.
2. Gomez-Barea A, Nilsson S, Vidal Barrero F and Campoy M (2010) Devolatilization of wood and wastes in
fluidized bed. Fuel Processing Technology 91(11):1624–33.
3. Liu H, Hu H, Luo G, Li A, Xu M, Yao H (2013) Enhancement of hydrogen production in steam gasification of
sewage sludge by reusing the calcium in lime-conditioned sludge. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy
38(3):1332–41.
4. Jaramillo-Arango A, Fonts I, Chejne F and Arauzo J (2016) Product compositions from sewage sludge pyrolysis
in a fluidized bed and correlations with temperature. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis 121:287–96.
5. Fonts I, Azuara M, Gea G and Murillo M B (2009) Study of the pyrolysis liquids obtained from different sewage
sludge. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis 85(1–2):184–91.
Biography
Sid Ahmed Kessas is a second year PhD student working on thermal & chemical conversion of wastes in fluidized bed reactors.
sidahmed.kessas@ensiacet.comSid Ahmed Kessas et al., J Bioremediat Biodegrad 2018, Volume 9
DOI: 10.4172/2155-6199-C1-015