Page 32
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 07
Advances in Crop Science and Technology
ISSN: 2329-8863
Agri 2019
August 15-16, 2019
August 15-16, 2019 | Rome, Italy
14
th
International Conference on
Agriculture & Horticulture
Qi Wei, Adv Crop Sci Tech 2019, Volume 07
Short-term response of soil N
2
O and CO
2
emissions and their global warming potentials to irrigation
salinity
Qi Wei
Hohai University, China
I
rrigation of brackish water (2-5 g L
-1
) instead of fresh water, modify soil microbial activities such as carbon and
nitrogen cycle, and thus affect soil emissions of nitrous oxide (N
2
O) and carbon dioxide (CO
2
). However, the effects
of irrigation salinity on global warming potentials (GWPs) caused by N
2
O and CO
2
emissions are rarely investigated.
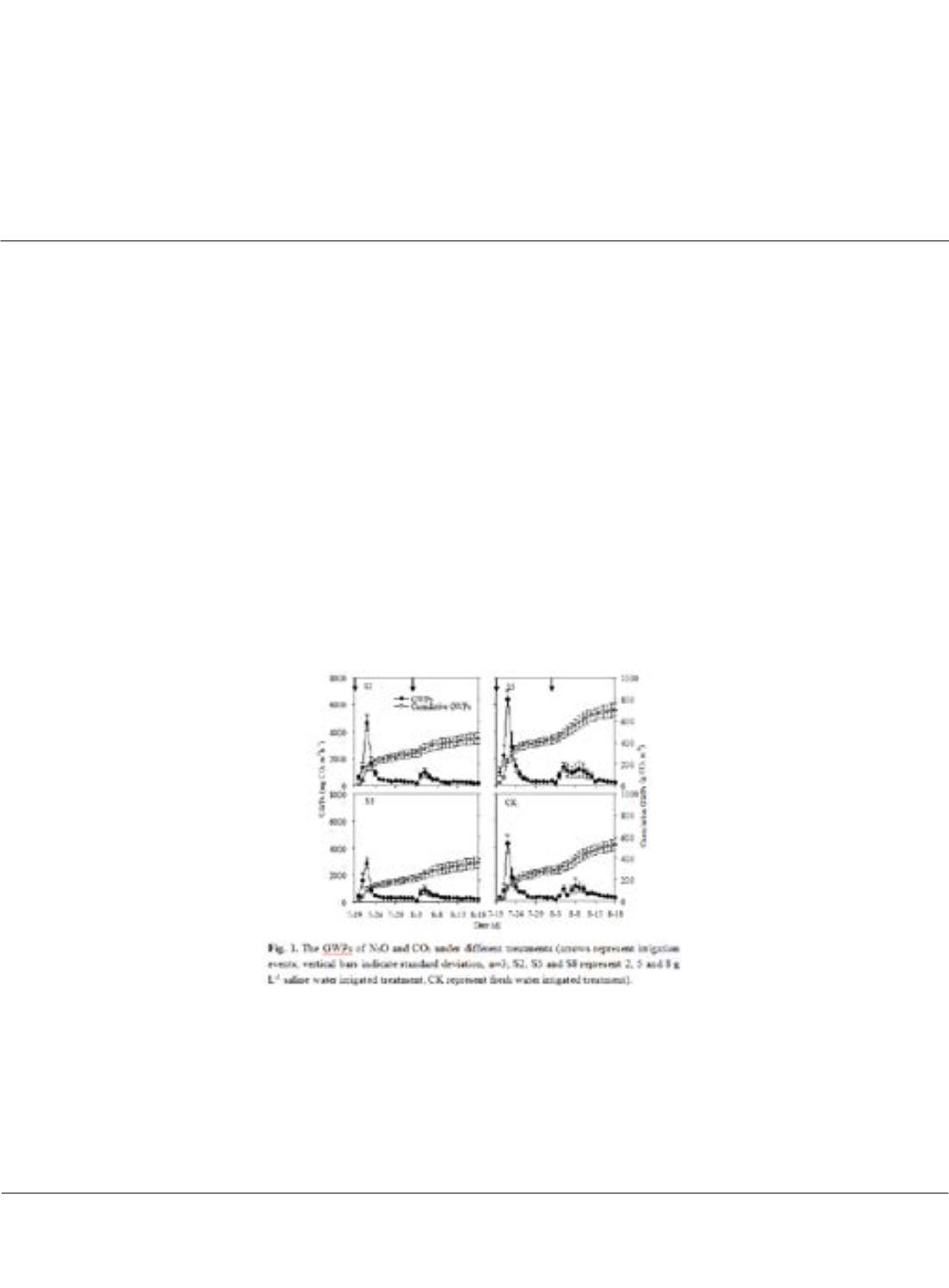
Pot experiments with three irrigation salinity levels (2, 5 and 8 g L
-1
) were designed to study the responses of GWPs
and the contribution of N
2
O and CO
2
to various salinity levels. Results indicated that soil CO
2
flux reduced with the
increase of irrigation salinity and was obviously lower than that from fresh water irrigated soil (CK). By comparison,
for N
2
O, 2 and 8 g L
-1
saline water decreased the cumulative fluxes by 22.6% and 39.6% compare to CK
(p<0.05),
respectively, whereas 5 g L
-1
saline water enhanced it by 87.7%. Overall, the cumulative GWPs of N
2
O and CO
2
from
irrigated soils using saline water (2-8 g L
-1
) were 3.2%-51.1% lower than that from CK, with the relative change to CK
at 2 g L
-1
salinity level significantly higher than those at 5 g L
-1
salinity level. These results suggested that the degree
to which soil Ec affected soil microbial processes might vary significantly among irrigation salinity ranges. Reducing
the salinity of irrigated brackish water can mitigate soil GHGs and provides a potential strategy for solving water
resources scarcity and reducing soil salt accumulation.
Recent Publications
1. Wei Qi, Xu Junzeng*, Yang Shihong, Qi Zhiming, Wang Yanhua, Liao Linxian (2017). Partial wetting irrigation
resulted in non-uniformly low nitrous oxide emissions from soil. Atmospheric Environment.161:2 00-209.
2. Wei Qi, Xu Junzeng*, Yang Shihong, Liao Linxian , Jin Guangqiu, Li Yawei, Fazli Hameed (2018). Subsurface
watering resulted in reduced soil N
2
O and CO
2
emissions and their global warming potentials than surface
watering. Atmospheric Environment. 173: 248-255.