Page 36
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 07
Advances in Crop Science and Technology
ISSN: 2329-8863
Agri 2019
August 15-16, 2019
August 15-16, 2019 | Rome, Italy
14
th
International Conference on
Agriculture & Horticulture
Shihong Yang et al., Adv Crop Sci Tech 2019, Volume 07
Evaluation of ecosystem services by paddy fields under different irrigation management in Taihu Lake
region of China
Shihong Yang, Junzeng Xu, Xiaoyin Liu
and
Qi Wei
Hohai University, China
S
tatement of the Problem: Irrigation mode is an important factor in regulating ecosystem services from croplands.
However, there are no studies on the effects of rice irrigation mode practiced on the ecosystem service value
(ESV) of paddy fields. Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: Thus, we present the results of a field experiment
study of ecosystem services and their economic values provided by paddy fields under different irrigation modes in
Taihu Lake region of China. Conclusion & Significance: The results showed that nine kinds of rice paddy ecosystem
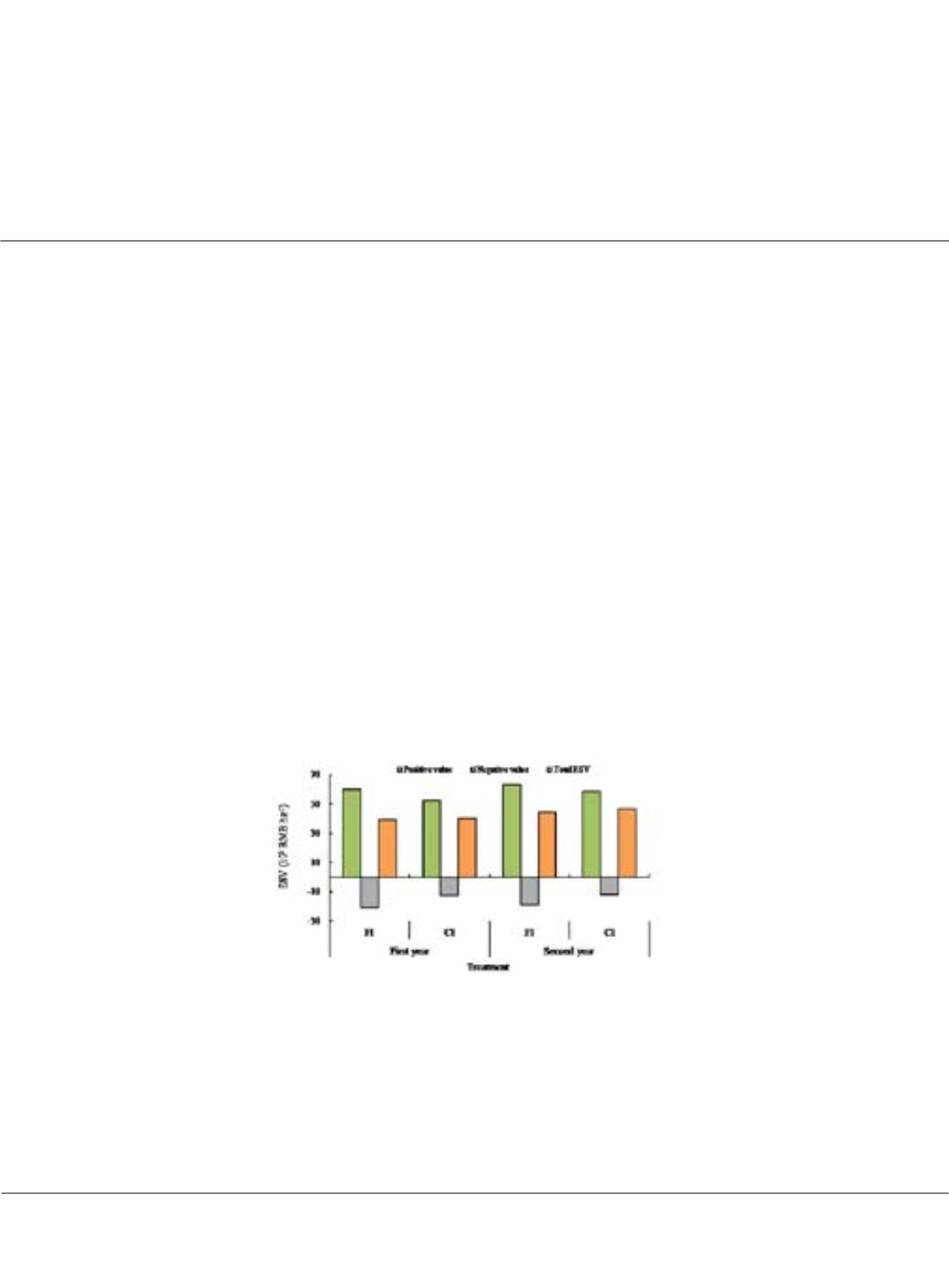
services were clearly affected by irrigation mode of rice. Compared to traditional flooding irrigation (FI), controlled
irrigation (CI) led to more than half reduction of irrigation water input while maintaining high rice yield. The
positive ESV of CI paddy fields were reduced by 10.00% due to the reduction of air temperature, groundwater
conservation and soil organic matter accumulation values. Meanwhile, application of water-saving irrigation also
reduced negative ESV of paddy fields by 38.20% compared to FI treatment. CI management significant reduced the
negative ESV of agricultural non-point source pollution and water resource depletion by 61.27% and 25.47%. In
summary, total ESV of CI paddies were 43.41 ×10
3
CNY ha
-1
, reduced on average by 3.43% compared to FI fields.
According to the results of this study, 4.85 billion m3 of irrigation water will be saved and 1.83 billion CNY of
ecosystem service value provided by gas exchange in paddy field will be increased in the event of a comprehensive
promotion of rice water-saving irrigation in the Taihu Lake region of China. Our results suggest that CI can increase
the ESV of paddy fields while drastically reducing irrigation water input and ensuring the crop yields.
Recent Publications
1. Zhang ZH, Zhong YM, Yang JP (2019) Effect of nitrogen fertilizer rates on carbon footprint and ecosystem
service of carbon sequestration in rice production. Science of the total environment. 670:210-217.
2. Carrijo DR, Lundy ME, Linquist BA (2017) Rice yields and water use under alternate wetting and drying
irrigation: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Research. 203, 173-180.
3. Fang FP, Feng JF, Li FB, Peng SB (2017) Impacts of the northmigration of China’s rice production on its ecosystem
Figure1: ESV of paddy fields under different water managements