Page 80
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 07
Advances in Crop Science and Technology
ISSN: 2329-8863
Agri 2019
August 15-16, 2019
August 15-16, 2019 | Rome, Italy
14
th
International Conference on
Agriculture & Horticulture
Cadmium stress in rice plants: The effect of cadmium on seed germination and seedling growth of rice
plant (
Oriza sativa
L.)
Elham Abedi
1
and
Ramazan Ali Khavari-Nejad
2
1
Islamic Azad University, Iran
1,2
Kharazmi University, Iran
C
admium (Cd) non-essential, but toxic, element for animals and plants is frequently present in paddy fields.
Oryza
sativa
L., a staple food for at least the half of world population, also aquatic plants are known to accumulate heavy
metals, easily absorbs Cd by the root, and in this organ the pollutants evoke consistent damages and reducing the root
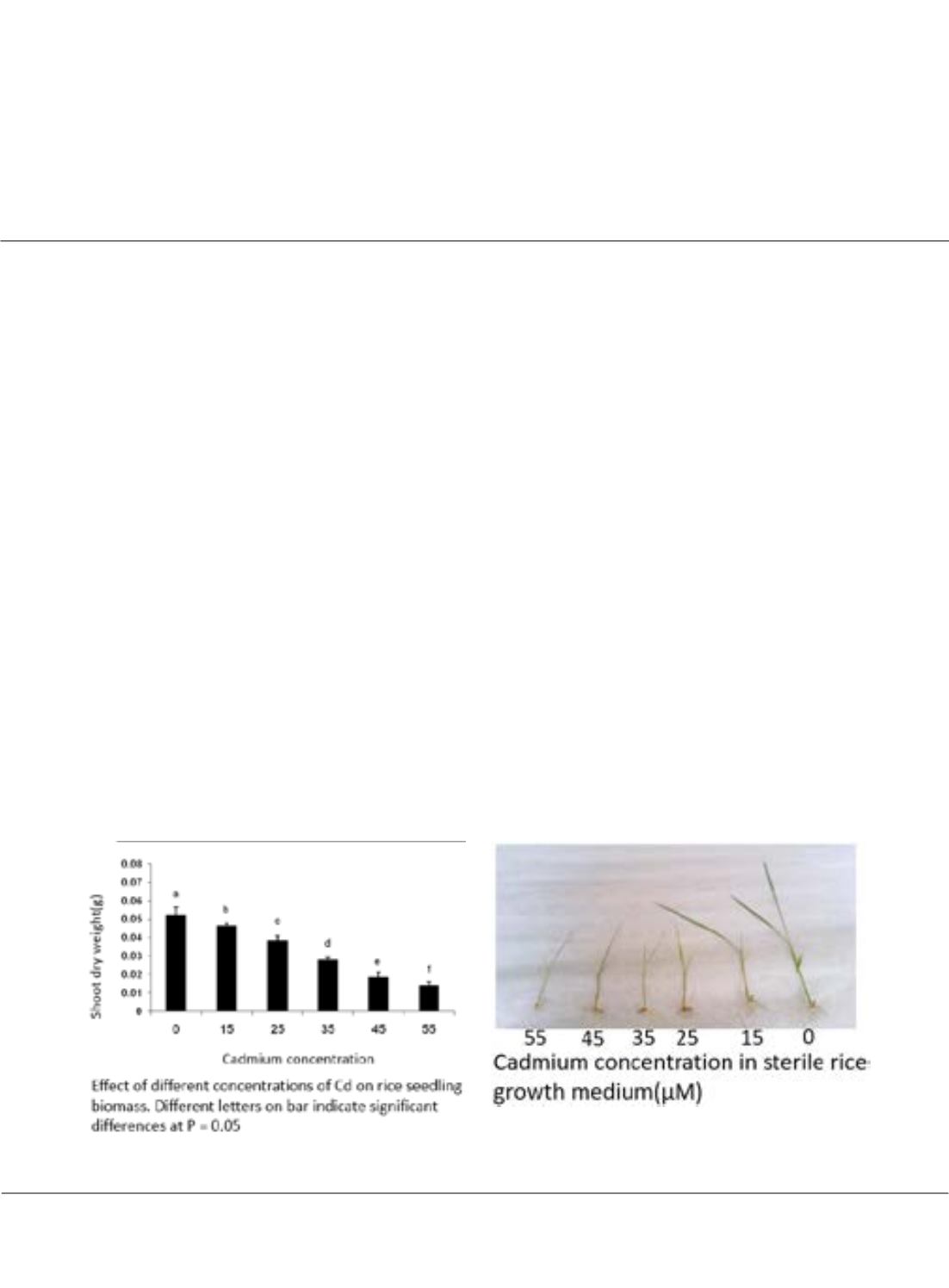
system. In this study the effects of different cadmium chloride concentrations (0 ,15, 25, 35, 45 and 55 µM) on some
physiological and biochemical processes including seed germination, root and shoot fresh and dry weight in rice
were investigated. The results showed that after treated, seed germination rate was less affected, but root growth was
restrained evidently. It affected the subsequent growth rate in these plants. Higher cadmium concentrations specially
at 45 and 55 µM reduced plant growth significantly. Leaf chlorosis, wilting and leaf abscission were observed in
plants treated with cadmium. Also Cd treatment reduced the germination percentage 6.9%, root and shoots length
68.9% and 85.6%, respectively. The decrease of 42.3% in fresh weight was noticed following the treatment with 45,
and 55 µM cadmium doses compared with control treatment, respectively.
Based on the results we concluded that, these traits of rice plant are seriously affected by Cd treatment and also
these are symptoms of toxicity of Cd element. Our results demonstrate that Cd affect rice root system, by interfering
with the formation of the roots and their development. This results into an important change in the root system
architecture, which may negatively affect plant survival in highly polluted paddy soils. Therefore, less amount of
reduction in a special genotype is referred to the index of tolerance to Cd. Finally, in the metal contaminated areas,
further research is needed to determine different levels of metals in the environment and various parts of the plants.
Having in mind the value of this crop as a food all over the world, the consequences of the reactivity of its root system
to these pollutants is very important for evaluating possible economic losses, and for executing repair strategies.
Elham Abedi et al., Adv Crop Sci Tech 2019, Volume 07