Page 25
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6, Issue 4(Suppl)
OMICS J Radiol, an open access journal
ISSN: 2167-7964
Medical Imaging and Clinical Research 2017
September 11-12, 2017
September 11-12, 2017 | Paris, France
2
nd
World Congress on
Medical Imaging and Clinical Research
Study of Common Requested Radiographs and Relative Exposure Dose in Qassim Province
Abdulrahman A S Alsayyari
Qassim University, Saudi Arabia
T
he objective of the article was to study the common requested radiographs and relative exposure dose in Qassim province in
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The method was retrospective and analytical study for collected variables as radiographs, relative
entrance surface dose (ESD) and the effective dose, patient age, gender and causative factors. The doses have been derived from the
product of system output, mAs, back scatter factor BSF, focal detector distance FDD and focus – skin- distance FSD based on the
equation stated by ICRU, (2005) and Davies et al, (1997):
Dose (mGy) = (Output(mGy⁄mAs)×(mAs)×(BSF)×(FDD)
2
)/(FSD)
2
Then the effective dose in mSv has been derived from the equation stated by ICRP, 2007 report 103.
EffD=∑(W
T
[H
T
(female)+ H
T
(male)])/2
Where WT refers to weighting factor for organ or tissue and HT refers to equivalent dose to organ or tissue. The analysis with excel
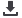
software revealed that: the common requested radiographs were skull, abdomen and chest with male incidence as 75%, 72.2% and
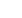
64% respectively relative to whole sample. Traffic accident (71%) and fall-down (45%) were the most causative factors among male,
female respectively, with injuries as skull fissure fracture (77%), and intracranial hemorrhage (23%). The skull radiographs noted
among the age group of 11-21 years and peaking at 36% among the age group of 22-32 years. The requested abdominal radiographs
appeared among the age group of 13-21 years; with frequency of (19%) and peaking at 30% among the age group of 22-30 years; with
injuries as spleen ruptures (42%) and liver (27%). The chest radiographs observed among age group of 3-13 years; with frequency
of 4% and peaking among age groups of 14-24 & 25-35 years old with frequencies of 19% and 21% respectively, and injuries as ribs
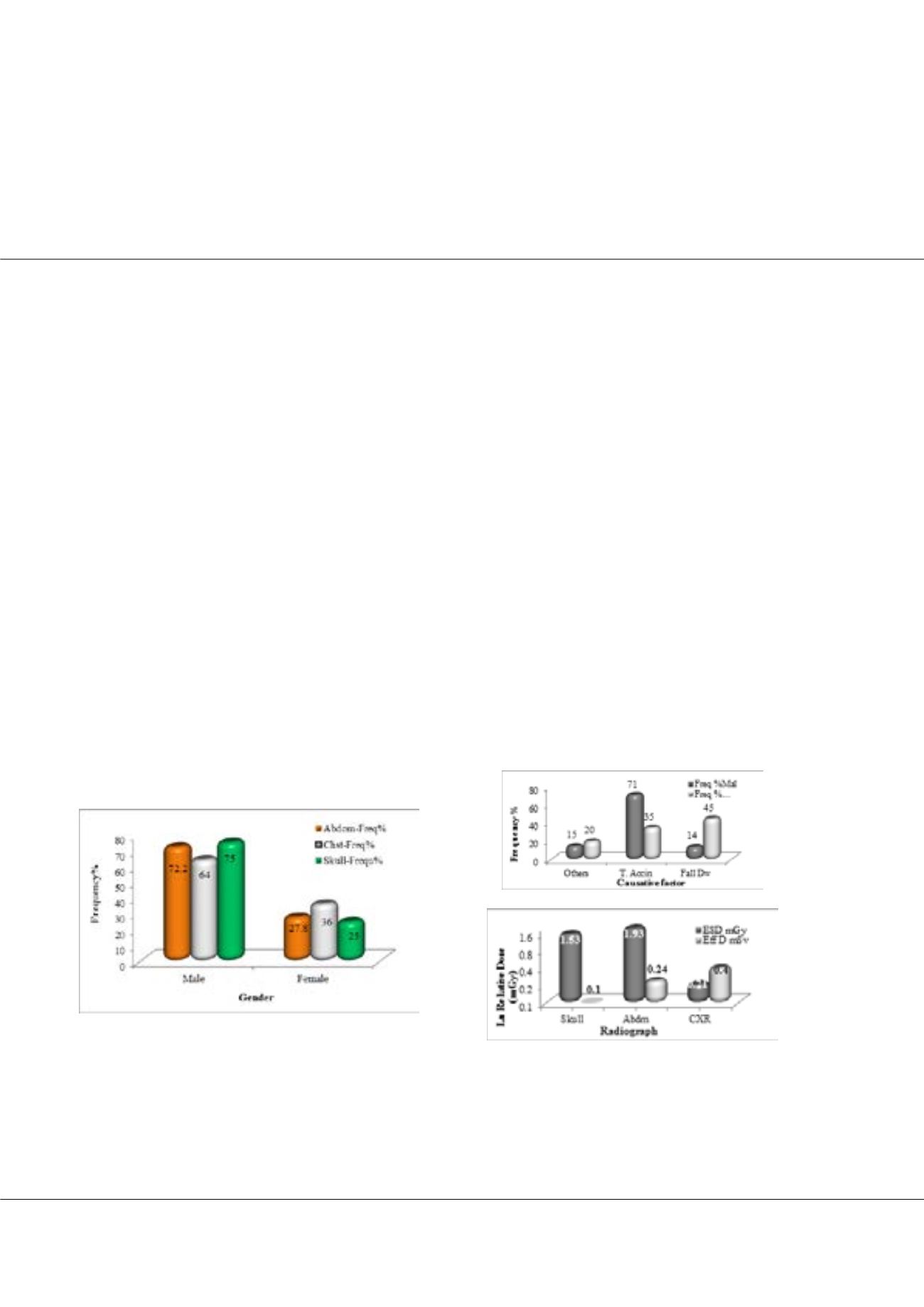
fracture (55%), ribs dislocation (15%), pierced lung (20%) hemorrhage (10%). The average ESD for abdomen, skull and the chest
radiographs were 1.93±0.8, 1.53±0.6 and 0.21±0.2 mGy, which were increase linearly following the aging, and the average effective
doses were 0.24±0.1, 0.1±0.1 and 0.4±0.2 mSv respectively.
Biography
Abdulrahman Alsayyari, is a vice dean of the college of applied medical sciences at Qassim university. He obtained his PhD degree from university of Queensland
at Australia. He worked in both sector clinical and educational where he developed his experience and knowledge to improve the healthcare services for the Saudi
population.
a.alsayyari@qu.edu.saAbdulrahman A S Alsayyari, OMICS J Radiol 2017, 6:4(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964-C1-012
Figure 1: shows distribution of requested radiographic based on gender
Figure 3: shows the average ESD in mGy & EffD in mSv received by
common anatomical site radiography
Figure 2: shows the distribution of requested radiographic cases based on causes