Page 25
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 7, Issue 2 (Suppl)
J Adv Chem Eng, an open access journal
ISSN: 2090-4568
Euro Chemical Engineering 2017
November 16-17, 2017
ADVANCES IN CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
November 16-17, 2017 | Paris, France
2
nd
International Conference on
Foaming in gas sweetening process: Comprehensive experimental efforts lead to better understanding
and predication of amine foaming
Emad Alhseinat
1
and
Fawzi Banat
2
1
Khalifa University, UAE
2
Petroleum Institute, UAE
C
omprehensiveexperimentalworkhasbeencarriedout to investigate the foamingbehaviorof aqueousMethyldiethanolamine
(MDEA) in presence of twenty different contaminates including degradation products i.e. N,N,N-tris-(hydroxyethyl)
ethylenediamine (THEED), hydroxyethyl ethylenediamine (HEED), N,N/-bis-(hydroxyethyl) piperazine (bHEP), N,N-
bis-(2-hydroxyethyl) glycine (bicine), organic acids, and liquid organics. This foaming study was combined with physical
characterization of the tested solution to enhance the understanding of the foaming behavior. The foaming tendency of aqueous
MDEA solution was reported in terms of foam volume. Foam stability was reported on the basis of the time required for the last
bubble to break. The results of this study showed that each contaminate has influenced the foaming behavior either by changing
the foam volume or breaking time or both. However, it has been noticed that whatever is the added contaminates to the amine
solution it drags the physical properties of the amine to a point where the foaming behavior will be changed. For example,
in case of THEED and HEED, the addition of these degradation products increased the foam tendency and stability of the
solution as a result of increasing solution viscosity; higher bulk viscosity retards the foam collapse caused by gravity drainage. It
is believed that the bottleneck of predicating the foam behavior of any solution would be the predication and monitoring of its
physical properties behavior and interaction. We are working now to develop the understating of the interaction between the
physical properties and their combined effect on the foaming behavior of the amine solution; this will lead to a breakthrough
in foaming monitoring and prediction. Mathematical models on tendency and stability of foaming are presented in this paper
to explain the effect of physical properties on foam volume and breaking time of aqueous MDEA solutions.
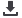
Figure1
.
Effect of time of foaming on foam volume for 0.1 wt. % BHCL with 50 wt. % MDEA solution at 100 ml/min.
Biography
Dr. Alhseinat is currently an Assistant Professor of Chemical Engineering at Khalifa University. Prior to join Khalifa University, Dr. Alhseinat completed his PhD from
the University of Edinburgh. Then he worked in Abu Dhabi Petroleum Institute as Research and Teaching Associate; where he was heavily involved in research
activity, writing and preparing scientific proposals and presentations, and publishing scientific articles. His current research activities address the development of
novel separation processes compatible with renewable energy i.e. Magnetic nanoparticles, Electrical and Magnetic separation technologies, Foaming predication
and monitoring, thermodynamics modelling and thermophysical properties characterization, Desalination and Water treatment, and Fouling science.
emad.alhseinat@kustar.ac.aeEmad Alhseinat et al., J Adv Chem Eng 2017, 7:2(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2090-4568-C1-002