Page 96
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 7, Issue 1 (Suppl)
J Biotechnol Biomater
ISSN: 2155-952X JBTBM, an open access journal
March 20-21, 2017 Rome, Italy
&
15
th
World Congress on
2
nd
International Conference on
Biotechnology And Biotech Industries Meet
Enzymology and Molecular Biology
Enzymology & Mol. Biology 2017
Biotechnology Congress 2017
March 20-21, 2017
Anew approach to obtain the catalytic sites region of human sACE with correct fold and activity
Regina Affonso
1
, Suelen de Barros Sampaio
1
, Fagner Sant’Ana Januario
1
, Larissa Miranda Pereira
2
, Danielle S Aragão
2
, Dulce E Casarini
2
and
Caroline Cristina
Elias
1
1
Institute of Energy and Nuclear Research - IPEN USP, Brazil
2
Federal University of Sao Paulo, Brazil
A
ngiotensin-converting enzyme I (ACE) is a membrane-bound that catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin I to the potent
vasopressor angiotensin II. ACE is a key part of the renin-angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure and is widely
distributed throughout the body. There are two isoforms of human ACE, including the somatic ACE (sACE) present in somatic tissue
and the testicular ACE (tACE) present in male germinal cells. The sACE possesses two domains, N- C- domains, with catalytic sites
which exhibit 60% sequence identity. These domains differ in terms of chloride-ion activation profiles, rates of peptide hydrolysis
of angiotensin I, bradykinin, Goralatide, Luliberin, substance P, angiotensina, beta-amyloid peptide and sensitivities to various
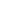
inhibitors. A more detailed analysis shows that these regions are composed of HEMGH and EAIGD sequences that bind zinc ions to
facilitate catalytic activity (Fig. 1). Our question is: If the synthesis of catalytic sites with corrects structure and activity could be a good
model
per si
to study new drugs. The objective was to obtain the Ala
361
a Gli
468
and Ala
959
to Ser
1066
catalytic regions sACE in a structural
conformation that resembles its native form. The catalytic regions were obtained from bacterial system; the expression of this protein
in soluble form enables completion of the solubilization/purification steps without the need for refolding. The characterization of
Ala
959
to Ser
1066
region shows that this has an α-helix and β-strand structure, Fig. 1b, which zinc ion (essential for its activity) binds
to, and with enzymatic activity. Our conclusion is that the strategy used to obtain the Ala
959
to Ser
1066
region in the correct structural
conformation and with activity was successful.
Biography
Regina Affonso has experience in the field of Biochemistry, with emphasis on protein in the area of molecular biology, working on the following topics: RNA extraction,
RT-PCR, PCR, cloning, expression and purification of recombinant human proteins in bacterial system and cell culture. In the structural area, she is interested in: circular
dichroism, fluorescence, crystallography, and bioinformatics.
reginaffonso@yahoo.com.brRegina Affonso et al., J Biotechnol Biomater 2017, 7:1(Suppl)
http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2155-952X.C1.071