Page 55
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
Journal of Biotechnology and Biomaterials
ISSN: 2155-952X
Biomaterials 2018
March 05-06, 2018
March 05-06, 2018 | Berlin, Germany
3
rd
Annual Conference and Expo on
Biomaterials
Development of HA-modified hydrogel for adipose derived stem cells based articular cartilage
regeneration
Mei-Ling Ho, Shun-Cheng Wu, Chung-Hwan Chen
and
Je-Ken Chang
Kaohsiung Medical University, Taiwan
R
egenerating the damaged articular cartilage to be a functional hyaline cartilage has been a clinically unmet need. Although
several current treatment methods, micro-fracture, osteo-chondral grafting and autologous chondrocytes implantation, have
been used to repair the damaged cartilage, the most concerned issue is the formation of unwanted fibrous cartilage rather than
hyaline cartilage in the repaired tissue. The most difficult challenge in cartilage regeneration is that the tissue mainly possesses
differentiated chondrocytes to maintain extra-cellular matrix homeostasis, which lacks of
in situ
and circulatory stem cells. One
of the current approaches to solve this clinically unmet need is the stem cell-based tissue engineering. Adipose-derived stem cells
(ADSCs) have been thought to be beneficial for use because of easy harvest, higher yield numbers and multi-potent differentiation.
To make it possible for ADSCs-based articular cartilage regeneration, the most important thing to be solved is the
in situ
chondral-
induction for ADSCs. We have conducted a series of studies to develop biomaterials that can provide the extra-cellular micro-
environment, including chemical and physical cues, to optimize the ADSC chondrogenesis in the repair site of articular cartilage.
We found that hyaluronan (HA) enrichedmicro-environment can initiate and enhance ADSC chondrogenesis via CD44mediation.
On the other hand, matrix stiffness has been indicated to direct stem cell differentiation into different tissues. We further developed
the chondral-induction biomaterials by ways of adjusting chemical and physical cues. We found that the modified cross-linked HA
products can be optimized by tuning the HA molecular weight and matrix stiffness. Most importantly, the cartilage regeneration
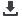
effect of the newly developed HA-modified hydrogel product has been confirmed in an osteo-chondral defect rabbit model (Fig.1).
The findings and biomaterial development from these studies provide the important information to persuade the possibility for the
future clinical use of ADSCs-based articular cartilage regeneration.
Recent publications
1. Wu S C, Chen C H, Wang J Y, Lin Y S, Chang J K, et al. (2018) Hyaluronan size alters chondrogenesis of adipose-derived
stem cells via the CD44/ERK/SOX-9 pathway. Acta Biomater 15(66):224-237.
2. Teong B, Wu S C, Chang C M, Chen J W, Chen H T, et al. (2018) The stiffness of a cross-linked hyaluronan hydrogel
affects its chondro-induction activity on hADSCs. J Biomed Mater Res. B 106(2):808-816.
3. Wang Y H, Rajalakshmanan E, Wang C K, Chen C H, Fu Y C, et al. (2016) PLGA-linked alendronate enhances bone
repair in diaphysis defect model. J Tissue Eng Regen M. 11(9):2603-2612.
4. Fu Y C, Wang Y H, Chen C H, Wang C K, Wang G J, et al. (2015) Combination of calcium sulfate and a simvastatin-
controlled release microsphere enhances bone repair in critical-sized calvarial bone defects. Int J Nanomed 10:7231-
7240.
5. Wu S C, Chen C H, Chang J K, Fu Y C, Wang C K, et al. (2013) Hyaluronan initiates chondrogenesis mainly via CD44 in
human adipose derived stem cells. J Appl Physiol 114(11):1610-8.
Biography
Mei-Ling Ho has focused her study on Regenerative Medicine, especially Tissue Engineering of articular cartilage and bone, as well as degenerative diseases like osteoarthritis and
osteoporosis, in the recent 20 years. In the field of research, she has published her study results in high ranking journals including
Biomaterials, Acta Biomaterialia, Journal of Tissue
Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
and as well as
Journal of Applied Physiology
. Besides, she has also studied the stem cell biology for searching effect mechanism of drugs, nature
products and physical agents, magnetic field and laser therapy. She also studied the novel gene effects on bone and cartilage by gene knock animals for searching the new drugs in future.
homelin@kmu.edu.twMei-Ling Ho et al., J Biotechnol Biomater 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X-C1-088