Page 63
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 07
Advances in Crop Science and Technology
ISSN: 2329-8863
Agri 2019
August 15-16, 2019
August 15-16, 2019 | Rome, Italy
14
th
International Conference on
Agriculture & Horticulture
Soil salinity: a significant factor affecting soil nitrous oxide emissions
Yawei Li
Hohai University, China
N
itrous oxide (N
2
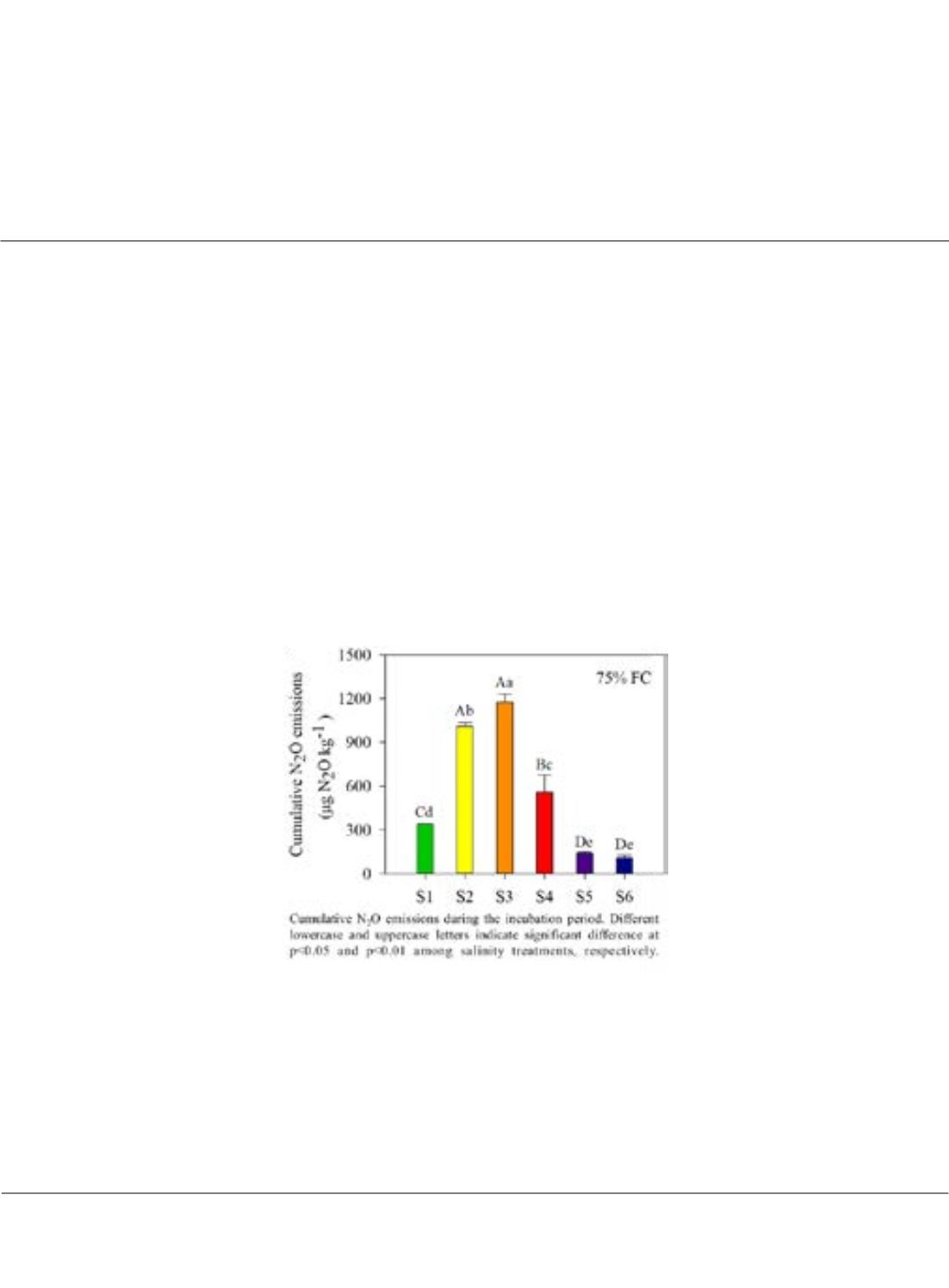
O) as a by-product of various soil nitrogen (N) transformation pathways, its production may
be affected by soil salinity which has been proved to have significant negative effect on microbial-driven soil
N cycling processes. However, it is little known that the response of N
2
O production to different soil salinities from
non-saline to heavily saline. We conducted a laboratory incubation experiment using the soils with six different
salinity levels from 0.25 to 6.17 dS m
-1
. With powdered organic fertilizer, rich of ammonium (NH
4
+
-N), as N
source, the soils were incubated at three soil moisture levels (50%, 75% and 100% of field capacity) for six weeks.
N2O fluxes and inorganic N (NH
4
+
, NO
2
-
and NO
3
-
) concentrations were measured throughout the incubation
period. Results showed that N
2
O fluxes increased first then decreased with the increase of soil salinity at all three
soil moisture levels, and N
2
O emissions were significantly promoted in soils with EC of 1.01 and 2.02 dS m-1. The
rates of NH
4
+
consumption and NO
3
-
production decreased with increasing soil salinity, while the accumulation of
NO
2
-
increased first then decreased. It suggests that soil salinity inhibits both the two steps of nitrification, but the
inhibition of salinity on nitrite oxidation was stronger than that on ammonia oxidation. Enhanced N
2
O emissions
by soil salinity may be mainly derived from nitrifier denitrification promoted by cumulative NO
2
-
.
Recent Publications
1. Y.W., Li., Q., Wei., J.Z., Xu., Y.H., Wang., H.Y., Wang., F., Hameed. (2018). Soil water-air replacement during
water infiltration process and its non-neglectable contribution to water-induced CO2 pulse emission. Pakistan
journal of agricultural sciences. 56(1):275-281
2. Y.W., Li., J.Z., Xu., Q., Wei., W.H., Bai., K.L., Li., X.Y., Liu. (2018). Soil nitrification process under different soil
moisture and salinity conditions. Journal of drainage and irrigation machinery engineering. 36(9):909-913 (in
Chinese)
Yawei Li, Adv Crop Sci Tech 2019, Volume 07