Volume 4
Toxicology: Open Access
ISSN: 2476-2067
Toxicology Congress 2018
March 12-14, 2018
Page 23
conference
series
.com
March 12-14, 2018 Singapore
14
th
World Congress on
Toxicology and Pharmacology
Microbial bioactive compound for food preservation with antioxidant
F
ood safety is a global issue with significant implications for human
health. The World Health Organization reports that, annually, unsafe
food results in the illnesses of at least 2 billion people worldwide and
can be deadly. Some countries have made great progress in controlling
foodborne diseases, but the number of those affected by foodborne
diseases is growing globally. Foodborne disease is a global issue with
significant impact on human health. With the growing consumer demand
for natural preservatives to replace chemical compounds, plant and
microbial antimicrobial compounds must be thoroughly investigated
for their potential to serve as bio-preservatives. Our research focuses
the microbial-derived products as antimicrobial agents for use in food
preservation and to control foodborne pathogens in foods. Structure,
modes of action, stability and resistance to these plant compounds will
be discussed as well as their application in food industries and possible
technologies by which they can be delivered. Benefits as well as challenges,
such as the need for further research for implementation and governmental regulation, will be highlighted. Thermal processing
is a common method of destroying vegetative microorganisms to ensure food safety, but this technique may cause undesirable
nutritional and quality effects. Preservatives are commonly used to reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses. Increasing regulatory
restrictions and consumer negative response to chemical compounds and to the use of antibiotics in agriculture have contributed
to the pressure for the development of alternative compounds for use as antimicrobial agents. Antimicrobial agents have been
predominantly isolated from bacteria and fungi and either produced through fermentation. Worldwide, spending on anti-
infective agents has increased in recent years due to the limited effective lifespan of antibiotics as new resistant microbes emerge.
New sources, including microbial bioactive molecules, must be thoroughly investigated for identification of novel antimicrobial
compounds. Prodigiosin is a natural red colored bacterial secondary metabolite, widely used in pharmacological and biological
applications. This investigation focused on nutraceutical and food functionalization potential of natural colorant PG. The
antioxidant potential of PG was examined by DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging method. The bactericidal efficiency of PG
was analyzed against six foodborne pathogens. The food Shelf life extant ability of PG was analyzed using meat extract powder
as a model food material. The PG (70.19 g/kg) was biosynthesized from
Serratia marcescens
by solid state fermentation. The
scavenging activity of PG was calculated to be 99% and 99.9% were DPPH and ABTS, respectively. The bactericidal efficiency
of PG against the selected foodborne pathogens exhibited significant inhibition on growth than the synthetic colorant and the
shelf life of the food was extended in the presence of PG containing food model. Hence, the PG may be used as food colorant
and thus significantly reduce the addition of synthetic colorant in food processing industry. This study will bring an innovative
approach on food additive for safe and sustainable food process. Because of variation in stability and efficacy to various food
processing parameters and food systems, it is critical that natural prodigiosin be selected and delivered so that they are active
against potential pathogens in particular food and are stable throughout the food’s shelf life. Effects of natural prodigiosin in
Regina Mary R
Auxilium College, India
Regina Mary R, Toxicol Open Access 2018, Volume 4
DOI: 10.4172/2476-2067-C1-004
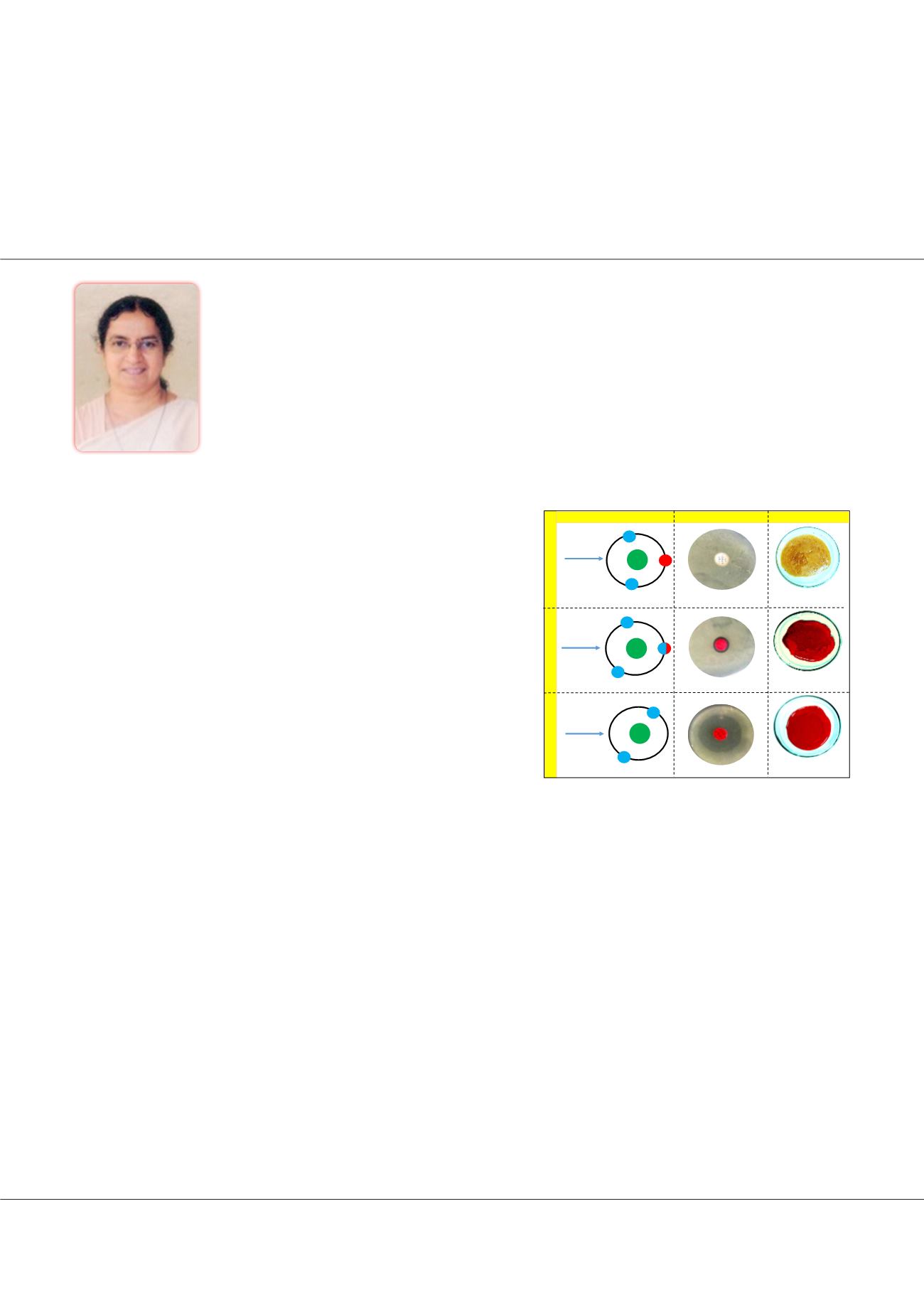
DPPH˙
+
ABTS˙
+
No Radical scavenging
Partial radical scavenging
Complete Radical scavenging Zone of inhibition (0.7cm)
Zone of inhibition (0.1cm)
No zone of inhibition
ERYTHROSINE
PRODIGIOSIN
Bacterial
contamination
Bacterial
contamination
No bacterial
contamination
radical
No colorant (control)
Synthetic colorant
Natural colorant
Bacterial growth inhibition
Free radical scavenging
Food preservative
DPPH˙
+
ABTS˙
+
DPPH˙
+
ABTS˙
+