Notes:
conferenceseries LLC Ltd
Page 48
December 03-04, 2018 | Lisbon, Portugal
Public Health, Women's Health, Nursing and Hospital Management
Joint Event
Journal of Community Medicine & Health Education | ISSN : 2161-0711 | Volume 08
Year-long Rhinovirus detection in nostrills of young healthy volunteers
R
hinovirus are picornavirus with over 150 serotypes and 3 species. Although usually
causing common colds, in Asthma, COPD and elders it may cause life-threatening
disease. In the present study we evaluated the year-long presence of rhinovirus in the
nostrils of healthy individuals in Porto, Portugal.
Monthly nasal swabs were collected from 89 volunteers. RNA was purified with Qiagen
column-based kits. Viral RNA was quantified by RTqPCR on Lightcycler 1.1 (Roche).
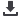
Frequency of positive nasal samples showed a single peak in autumn with a maximum
frequency of 40% in November (fig.1). A similar distribution was found for viral titers with
a maximum in November, but with a second 100x weaker peak in spring (fig.1). Rhinovirus
positivity was found to be more frequent (17%) in individuals reporting relevant symptoms
(frequent sneezing, dripping nose, stuffy nose or nose symptoms plus lacrimation/eyes-
pruritus) than in individuals with no such symptoms (6%), indicating that in most of these
cases productive infection was taking place.
Conclusions:
Rhinovirus circulation among healthy volunteers in Porto shows a strong
peak in autumn, and a minor one in spring. The spring peak was only observed when nostril
rhinovirus quantification is taken into account, as no increased frequency of rhinovirus
was observed, but rather an increase in maximum viral titters among positive samples.
The present results are in accordance with the literature reporting peaks of rhinovirus
circulation in autumn and spring, but suggest the need to use sensitive and quantitative
methods for the characterization of viral circulation in healthy populations.
30816@ufp.edu.ptAna Maria Pereira da
Silva Costa Ferreira
Fernando Pessoa University, Portugal
Ana Maria Pereira da Silva Costa Ferreira et al., J Community Med Health Educ 2018, Volume:8
DOI: 10.4172/2161-0711-C7-051
Co-Authors
AF. Rodrigues, AM. Santos
and
JM. Cabeda
Fernando Pessoa University, Portugal