Page 44
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 7 (Suppl)
J Infect Dis Ther, an open access journal
ISSN: 2332-0877
Infection Prevention 2017
December 14-15, 2017
December 14-15, 2017 | Rome, Italy
13
th
World Congress on
INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL
The role of surfaces in transmission of nosocomial infections at the regional hospital of Korce,Albania
Zhinzela Qyli
Fan S Noli University, Albania
Statement of the problem:
Hospital surfaces are potential sources of health care–associated infection. Contamination of
hospital surfaces by bacteria is increasingly recognized . In recent years, a variety of interventions have been shown to be
effective in improving cleaning and disinfection of surfaces. The purpose of this study was to identify the microbial pollution of
the hospital surfaces and to demonstrate the importance of hospital surfaces contamination in the transmission of nosocomial
infections.
Methodology &Theoretical Orientation:
A total of 640 samples were taken from the surfaces of the hospital. A swab soaked
in nutrient broth was used to collect samples. Swabs were streaked in Blood agar. These culture plates were incubated at 37°C
for 24 hrs. After incubation identification of isolates was performed.
Findings:
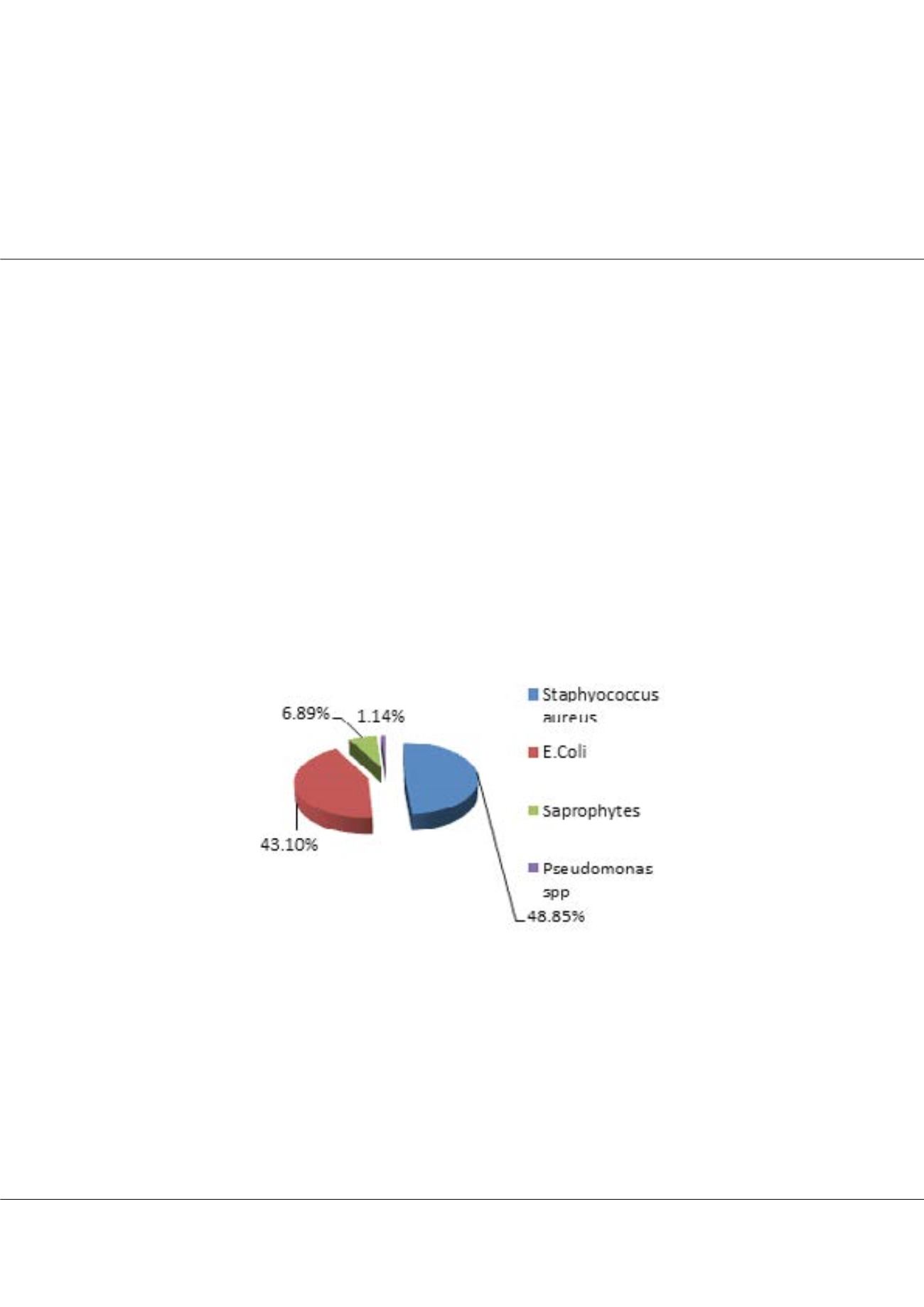
The study revealed that the prevalence of bacterial isolates was 27.18%. Prevalence of samples contaminated with
Staphylococcus.aureus was 48.85% , E.Coli 43.10%, Pseudomonas 1.14% and Saprophytes 6.89%.
Conclusion & Significance:
The microbial contamination of surfaces in the hospital is high. High prevalence of microbial
isolates with Staphylococcus aureus and E.Coli are considered as a indicator of poor hygiene in the hospital.
Key words:
Sample, hospital, contamination.
Figure 1. Prevalence of microbial isolates
Biography
Zhinzela Qyli has completed the Faculty of Medicine and specialization in Microbiology in the University of Tirana, Albania. She is lecture in the Nursing Department
of Fan S Noli University, Korca and is following the doctoral school in the Faculty of Technical Medical Sciences, University of Medicine, Tirana, Albania.
zhinzelaqyli@gmail.comZhinzela Qyli, J Infect Dis Ther 2017, 5:7(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2332-0877-C1-036