Page 40
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 7 (Suppl)
J Infect Dis Ther, an open access journal
ISSN: 2332-0877
Infection Prevention 2017
December 14-15, 2017
December 14-15, 2017 | Rome, Italy
13
th
World Congress on
INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL
Is the passive immunization in horses the way to prevent a WNV outbreak in Brazil?
Tatiana Ometto
University of São Paulo, Brazil
W
est Nile virus (WNV) has emerged in the last three decades as a significant burden to public health and a major veterinary
concern in Europe and the Americas. The emergence of WNV, particularly the invasion into North America in 1999 and
its subsequent spread throughout the Western Hemisphere, corroborates the view that the virus is moving southward, placing
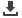
millions of individuals at risk for infection. The first report of WNV activity in South America surfaced in April 2006, when
three horses died in Argentina. WNV seropositivity in horses in Brazil was reported in 2009, molecular positivity in two birds
was found in 2010/2012 and the first clinical report of a human case occurs in 2014. Although, the established transmission foci
in South America unknown. However, Brazil is a large tropical country with major ecological reserves and different biomes
that provide ideal conditions for many arboviruses, including WNV. Brazil has the largest herd of horses in Latin America
and the third largest in the world. The total population is approximately 8 million head, equaling US$3.2 billion including
herd management costs. Following the introduction of WNV vaccinations for horses in the United States, the incidence of
neuroinvasive disease in horses decreased, suggesting that the WNV vaccination had a substantial impact on equine health.
Our discussion proposes that Brazil has a low prevalence of WNV antibodies in equids, therefore, the vaccination of horses
should be discussed from an economic standpoint with a model of free demand by the owners, as the cost-benefit of the
vaccination may be greater than that of treating the animals. Many questions regarding the potential for WNV spread in Brazil
remain. The objective of this discussion was to address these questions by evaluating the importance of passive immunization
in horses is to prevent a possible WNV outbreak in Brazil.
Biography
Tatiana Ometto has her expertise in emergent viruses in wild animals. Her experience involves work on field with wild animals, sampling, serological and molecular
analyses in a BSL3+ laboratory. She has built this expertise after years working in different projects involving different emergent virus in Brazil.
tatiometto@usp.brTatiana Ometto, J Infect Dis Ther 2017, 5:7(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2332-0877-C1-036