Page 70
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
Epidemiology: Open Access
ISSN: 2161-1165
Epidemiology 2018
September 17-19, 2018
September 17-19, 2018 | Rome, Italy
8
th
International Conference on
Epidemiology & Public Health
Evaluation of gastroesophageal reflux disease and related factors in seasonal agricultural workers
Yasemin Saglan
1
, Ugur Bilge
2
, Dilek Oztas
3
, Ramazan Saglan
2
, Yunus Emre Sari
2
, Hüseyin Balcioglu
2
and
Ilhami Unlüoglu
2
1
Eskisehir Odunpazari District Health Directorate, Turkey
2
Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Turkey
3
Ankara Yıldırım Beyazıt University, Turkey
Statement of the Problem:
Seasonal agricultural workers are agricultural workers migrating to places where agricultural
demand is high, migrating to their own countries at the end of the season. This group is a vulnerable group because of the
inadequacy of living conditions and the inability to reach basic human rights services (health, education). Our aim is to
determine the frequency of gastroesophageal reflux disease in seasonal agricultural workers that is exposed to the worst
conditions of working life.
Methodology:
The study is a cross-sectional study was carried out on seasonal agricultural workers working in the countryside
of Eskişehir (Turkey) in 2017. A total of 536 seasonal agricultural workers agreed to participate in the study constituted the study
group. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS®)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Scale was used to assess the frequency of gastroesophageal reflux disease in the
study. Logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the independent variables associated with gastroesophageal
reflux disease.
Findings:
In the study group, 201 (37.5%) were male and 335 (62.5%) were female. The age of the seasonal agricultural workers
ranged from 18 to 92 years, with a mean age of 39.05 ± 13.59 years. The prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in
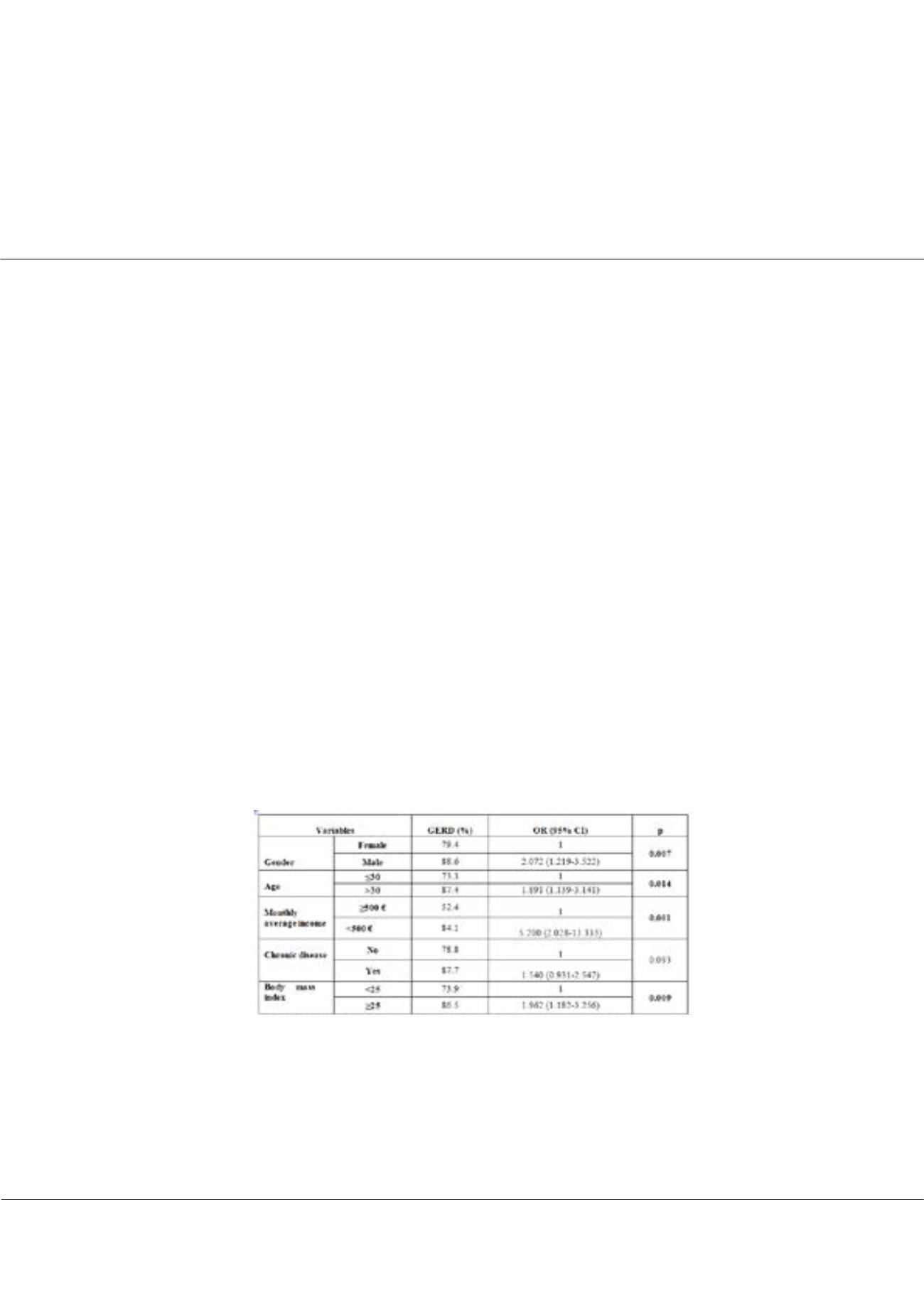
seasonal agricultural workers was found 82.8 (n = 444) in the study. In multivariate analysis, gastroesophageal reflux disease
was found to be higher in male (OR: 2.072), those age >30 (OR: 1.891), with monthly average income <500€ (OR: 5.200) and
body mass index of ≥25 (OR: 1.962) (p ≤ 0.05 for each).
Conclusion & Significance:
In order to reduce the frequency of gastroesophageal reflux disease in seasonal agricultural
workers, the average family income situation should be corrected and combated with obesity
Recent Publications:
1. Villarejo, Don. The health of US hired farm workers. Annual review of public health 24.1 (2003): 175-193.
2. Katz, P.O., Gerson, L.B., Vela, M. F. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
The American journal of gastroenterology, 2013. 108(3), 308.
Yasemin Saglan et al., Epidemiology (Sunnyvale) 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2161-1165-C1-020
Table 1. Multiple logistic regression results of gastroesophageal reflux disease related factors in the study group