Page 66
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
Epidemiology: Open Access
ISSN: 2161-1165
Epidemiology 2018
September 17-19, 2018
September 17-19, 2018 | Rome, Italy
8
th
International Conference on
Epidemiology & Public Health
Evaluation of the relationship between social phobia and internet addiction in adolescents
Ramazan Saglan
1
, Saniye Tulin Fidan
1
, Neriman Kilit
2
, Aziz Soysal
1
and
Selma Metintas
1
1
Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Turkey
2
Cevdet Aykan Mental Health and Diseases Hospital, Turkey
Statement of the Problem:
Adolescents with social phobia are trying to socialize via the internet in order to avoid the stress
of face-to-face communication with others. However, if they cannot cope with the social challenges in the real world, the
increased use of the internet to provide social support increases the risk of the individual being addicted to the internet. The
aim of the study was to determine the frequency of social phobia and to evaluate the relationship between internet addiction
among high school students.
Methodology:
This cross-sectional study was performed on high school students in semi-rural area of Eskisehir (Turkey) in
2017. The study group included 793 (91%) students educated in school during the study and agreed to participate in the study.
Social phobia was assessed by the Social Phobia Scale for Çapa Children and Adolescents, and internet addiction was assessed
by the Young Internet Addiction Scale. Logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the independent variables
associated with social phobia.
Findings:
Of the study group, 402 (50.7%) were male and 391 (49.3%) were female. The age of the students ranged from 14 to
18 years, with a mean age of 15.94±0.99 years. The frequency of social phobia was found 11.0% (n = 87) and internet addiction
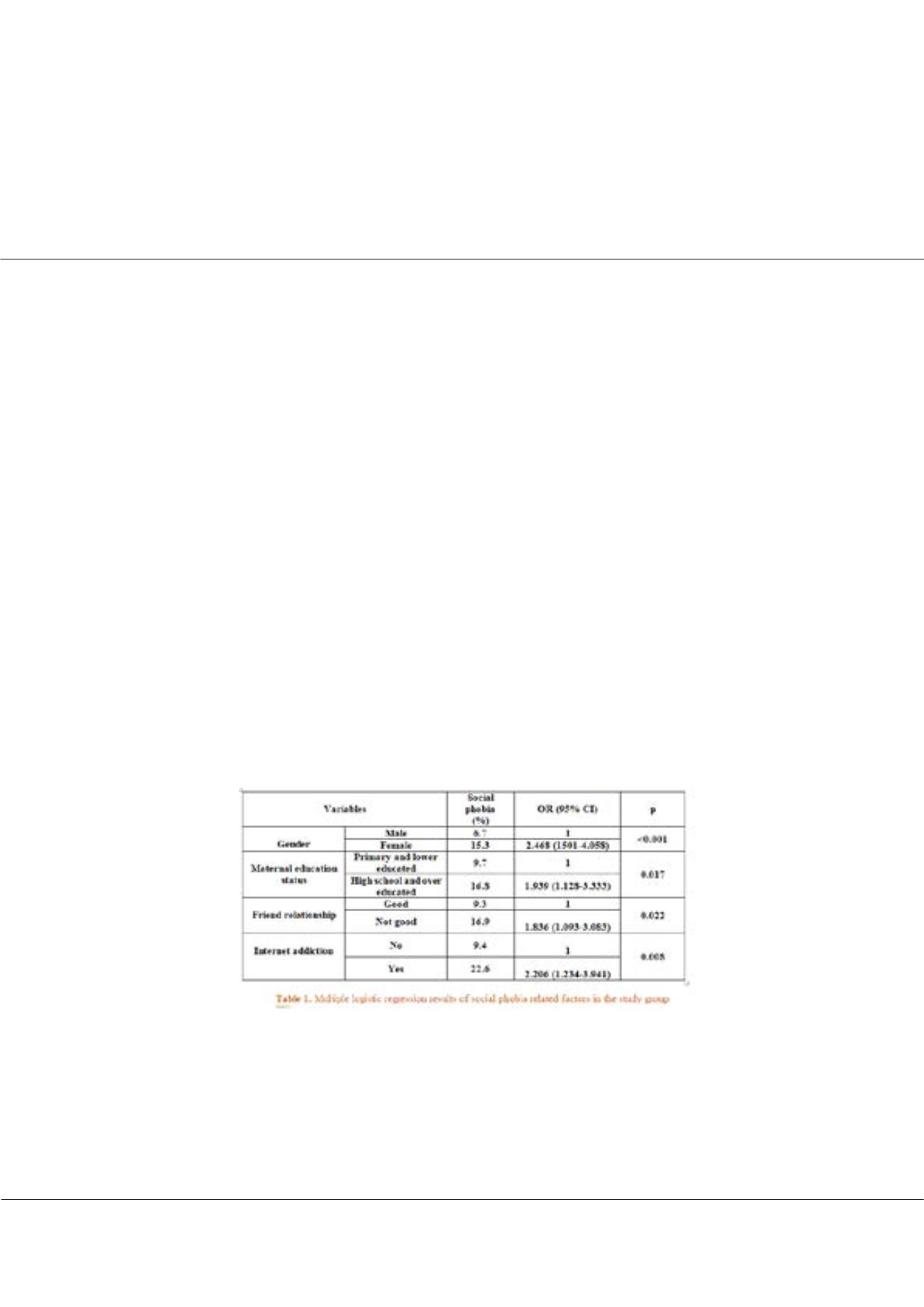
was found 11.7% (n = 93) in the study. In multivariate analysis, the prevalence of social phobia was higher in females (OR:
2.468), high school and over educated maternal education status (1.939), not good friend relationship (1.836) and have internet
addiction groups (2.206) (for each; p≤0.05).
Conclusion & Significance:
Social phobia and internet addiction are important health problems related to each other in
adolescents. Social phobia can be prevented by controlled use of the internet. Screening programs on social phobia and internet
addiction should be done in adolescents.
Recent Publications:
1. Bayraktar, F. 2001. 'İnternet kullanımının ergen gelişimindeki rolü (Yüksek lisans tezi, Ege Üniversitesi, Sosyal Bilimler
Enstitüsü, İzmir)’, UlusalTezMerkezi/tezSorguSonucYeni. jsp adresinden edinilmiştir.
2. Demir, Türkay, Demet Eralp-Demir, Erdoğan Özmen, and Ömer Uysal. 1999. 'Çapa Çocuk ve Ergenler için Sosyal
Fobi Ölçeğinin geçerlilik ve güvenilirliği', Düşünen Adam, 12: 23-30.
3. Ko, C-H, J-Y Yen, C-F Yen, C-S Chen, and C-CChen. 2012. 'The association between Internet addiction and psychiatric
disorder: a review of the literature', European Psychiatry, 27: 1-8.
Ramazan Saglan et al., Epidemiology (Sunnyvale) 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2161-1165-C1-020