Page 84
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 7, Issue 1 (Suppl)
J Biotechnol Biomater
ISSN: 2155-952X JBTBM, an open access journal
March 20-21, 2017 Rome, Italy
&
15
th
World Congress on
2
nd
International Conference on
Biotechnology And Biotech Industries Meet
Enzymology and Molecular Biology
Enzymology & Mol. Biology 2017
Biotechnology Congress 2017
March 20-21, 2017
Ayse Ezgi Unlu et al., J Biotechnol Biomater 2017, 7:1(Suppl)
http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2155-952X.C1.071Optimization of catalase activity by
Rhodotorula glutinis
using experimental design
Ayse Ezgi Unlu
and
Serpil Takac
Ankara University, Turkey
R
hodotorula glutinis
is a pigmented, salt tolerant yeast and also gains attention due to its oleogenic property. It has high capacity
to produce antioxidant molecules such as carotenoids. However, limited research has been conducted on the synthesis of other
antioxidant molecules such as catalase (CAT) enzyme. CAT is a heme protein that is present in animal cells, bacteria and plants and
it decomposes hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen (Eqn. (1)). It is widely used in various industrial areas such as textile, food
and cosmetics.
2H
2
O2→O
2
+2H
2
O (1)
The aim of this study is to investigate the parameters that provided the optimum conditions for high CAT activity by Rhodotorula
glutinis, and to search for the potential utilization of glycerol as a carbon source for high CAT activity, which is a by-product of
biodiesel plants. For this aim, central composite design (Design Expert 7.0.0) including 20 runs with 6 central points was performed
and temperature (TºC) (10.6-32.4ºC), initial medium pH (pH) (3.99-6.0) and glycerol concentration (Gly, gL
-1
) (9.77-60.23) were
selected as factors to be optimized for the response, CAT activity, according to the previous findings of the research group. The
following second order model (Eqn. (2)) was proposed:
CAT (U)=-4.36106+1.34381(pH)+ 0.051575(T)+ 0.028907(Gly)-0.13551(pH)
2
-3.78071x10
-4
(Gly)
2
(2)
The model was found to be statistically significant (R2=0.94, R2adj=0.92, model F value 40.95, lack of fit value 2.21). The most
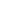
effective factor on CAT activity was found as temperature (p<0.0001). The response surface graphics are presented at Fig. 1. Fig. 1a
was obtained when Gly was 37.03 mg mL
-1
. According to the figure, the highest CAT activity was obtained at high T and low pH
values. Similarly, Fig. 1b showed that activity increased with increasing T however, medium values of Gly provided higher activity
values, maximum at 37.5 mg mL
-1
. According to Fig. 1c, the highest CAT activity values were obtained at the medium values of both
pH and Gly. As a result of the experiments, it was found that determination of the maximum predicted response required a shift of
the experimental region to higher temperature values.
Biography
Ayse Ezgi Unlu has expertise in enzymes, enzymatic reactions, fermentation, protein synthesis, proteomics, enzymatic biopolymers and green solvents. The
synthesis of Naproxen, a member of NSAIDs, was the subject of her Master’s thesis by using commercial lipase subjected to various pre-treatment strategies that
enhanced the activity. Investigation of different parameters on the production of lipase by
Candida rugosa
and also proteomic analysis of the isoenzymes was
another subject of her interest. She has done her Post-doctoral research on the synthesis of flavonoids using green solvents.
aeunlu@eng.ankara.edu.tr