Page 85
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 7
Biosensors Journal
ISSN: 2090-4967
Electrochemistry 2018
June 11-12, 2018
June 11-12, 2018 | Rome, Italy
4
th
International Conference on
Electrochemistry
Nanocrystalline scaffold of AMT-Ag for electro-sensing of ciprofloxacin drug in biological fluid and
pharmaceutical formulation
Vinita, Madhu Tiwari, Ashish Kumar
and
Rajiv Prakash
Banaras Hindu University, India
T
he advancement in the chemistry of the coordination polymers having designable architectures fabricated from
functionalized building blocks is an emerging area from last two decades. The further challenges are the construction of
coordination network assembly having electro-active nano-pores. We are first time exploring a nanocrystalline coordination
polymer (NCCP) framework resulting from 2–amino–5–mercapto–1,3,4–thiadiazole (AMT) and silver nitrate. In the infinite
polymer arrangement of AMT–Ag, silver (I) centers are bridged by tecton AMT through the amino linkage and exocyclic thiol.
The grasped nano–sized granules of AMT–Ag are investigated by FE-SEM. The crystalline nature along with the oxidation
state of silver is studied through XRD, TEM and XPS respectively. Additionally, the thermal stability and activation energy
for thermal decomposition of NCCP are scrutinized by thermo–gravimetric analysis. Furthermore, the efficient electron
transfer kinetics is probed by using Fe (II)/Fe (III) redox couple in phosphate buffer pH 7 via cyclic voltammetry. The excellent
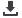
electroactivity is employed in the electro-detection of a biologically active drug molecule ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (CFX).
The anodic peak current revealed a linear dependence with CFX concentration with sensitivity and limit of detection as 0.001
μA/μM and 5.0 nM, respectively. The effective assay of the drug is caused by the excellent electron channeling through the
pores of polymeric nano–crystallites. Further, the concept is extended and established in the voltammetric detection of CFX
in biological fluid and pharmaceutical formulation by a considerably high sensitivity (0.002 mA/mM and 0.007 mA/mM) and
the detection limit (22 nM and 60 nM) respectively. Our established system has potential for fabrication of high performance
electro-chemical sensors for assay of biologically significant drug molecule.
Recent Publications:
1.
Tiwari M, Gupta S and Prakash R (2014) One-pot synthesis of coordination polymer- 2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-
gold and its application in voltammetric sensing of resorcinol. RSC Advances 4:25675-25682
2.
Li Y and Chen S M (2012)The electrochemical properties of acetaminophen on bare glassy carbon electrode. International
Journal of Electrochemical Science 7(3):2175-2187.
3.
Li B, Wen HM, Cui Y, ZhouW, Oian G and Chen B (2016) Emerging multifunctional metal–organic framework materials.
Advanced Materials 28:8819–8860.
4.
Tiwari M, Kumar A and Prakash R (2016)The nanocrystalline coordination polymer of AMT–Ag for an effective detection
of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulation and biological fluid. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 85:529–
535.
5.
Cai W and Chu C C (2015) Metal–organic framework-based nanomedicine platforms for drug delivery and molecular
imaging. Small 11(37):4806-22.
Vinita et al., Biosens J 2018, Volume 7
DOI: 10.4172/2090-4967-C1-002