Page 86
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 9
Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation
ISSN: 2155-6199
Biofuel Congress 2018 &
Biomass 2018
September 04-06, 2018
JOINT EVENT
September 04-06, 2018 | Zurich, Switzerland
13
th
Global Summit and Expo on
Biomass and Bioenergy
&
12
th
World Congress on
Biofuels and Bioenergy
Scalable concepts for microwave pyrolysis
John Robinson
University of Nottingham, UK
M
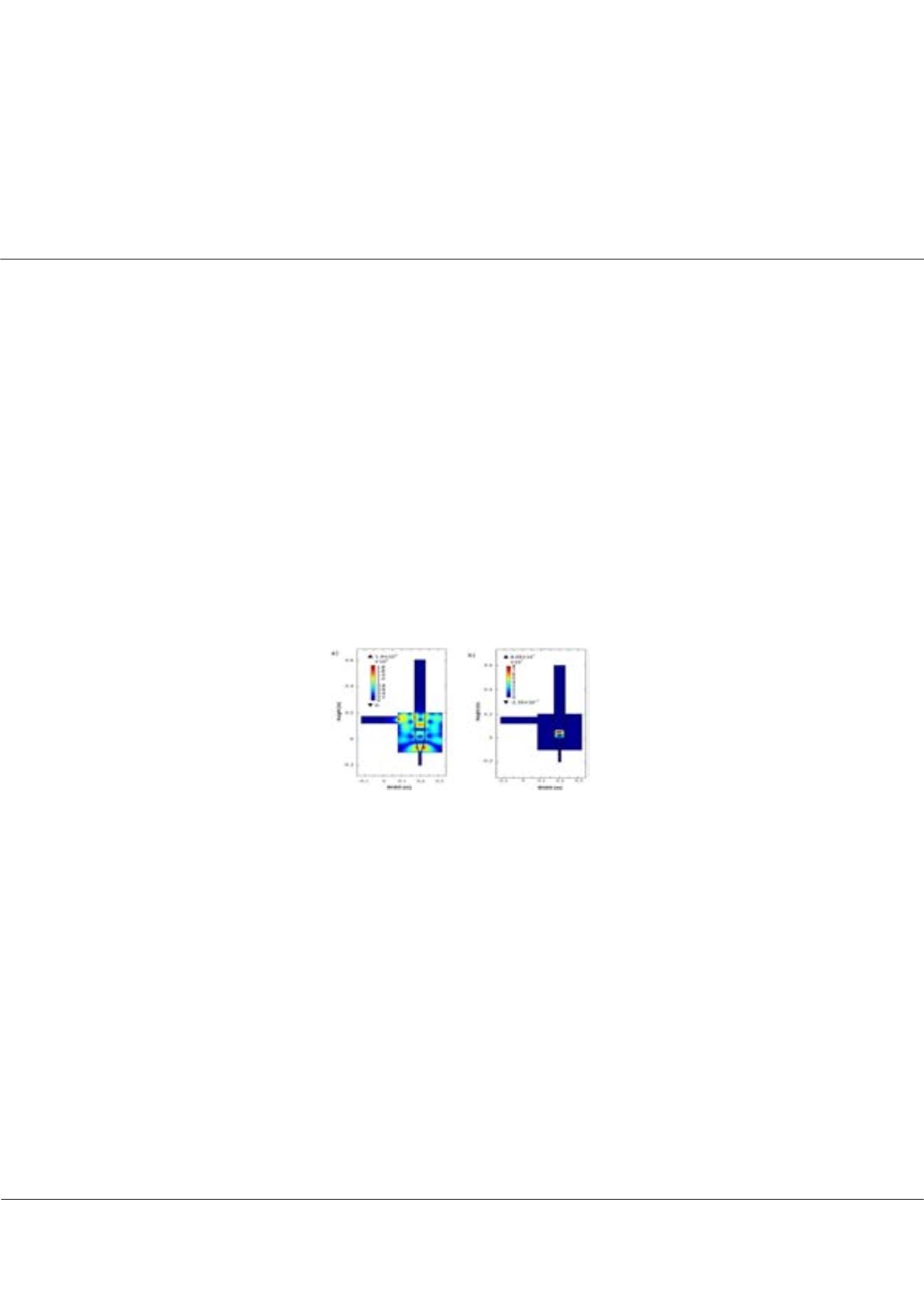
icrowave pyrolysis of biomass has long been recognized to provide potential opportunities for producing a range of
bio-based products. Unlike conventional heating, microwave heating occurs through the interaction of biomass with
electromagnetic energy, with the biomass heated volumetrically by energy conversion instead of conventional heat transfer
mechanisms. With microwave heating pyrolysis can be achieved within a cold surrounding environment, a feat that is not
possible with conventional heating processes. This unique phenomenon presents a number of opportunities for processing of
biomass feed stocks, which include enhanced product quality and a significantly simplified process flow sheet, both of which
improve the economic viability of industrial biomass processing. Examples of the benefits of microwave heating include the
elimination of size-reduction and particulate removal steps and simplification of inert-gas preparation and recycling systems.
These are discussed within the paper, along with the enhanced product quality that can be produced as a result. Previous studies
in this field have typically made use of fixed bed reactors, in which heating heterogeneity issues and undesired thermal run
away of the biomass are inherent. This paper presents five alternative and scalable microwave processing concepts which have
already proven to successfully operate at scale, within an industrial environment. The potential application of these concepts
for biomass processing and their ability to deliver a step-change in product quality and flow sheet simplification is discussed
within the paper.
Recent Publications
1. C S Lee et al., (2018) Techno-economic assessment of scale-up of bio-flocculant extraction and production by using okra as
biomass feedstock. Chemical Engineering Research and Design 132:358-369.
2. B Shepherd et al., (2018) Microwave pyrolysis of biomass within a liquid medium. Journal of Analytical and Applied
Pyrolysis. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2018.07.004.
3. Y Zhang et al., (2018) Impact of oil composition on microwave heating behavior of heavy oils. Energy and Fuels 32(2):1592-
1599.
4. E T Kostas et al., (2017) The application of microwave heating in bioenergy: A review on the microwave pre-treatment and
upgrading technologies for biomass. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 77:12-27.
5. D Beneroso et al., (2017) Microwave pyrolysis of biomass for bio-oil production: Scalable processing concepts. Chemical
Engineering Journal 316(1):481-498.
Biography
John Robinson is an Associate Professor in Chemical & Environmental Engineering at the University of Nottingham. His expertise is in the development and scale-
up of microwave heating processes and has taken several processes from a laboratory scale curiosity to a commercial operation. His current research interests
are based on understanding the opportunities and advantages for microwave heating within the bioenergy and biorefinery field and developing scalable processes
for the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass.
john.robinson@nottingham.ac.ukJohn Robinson, J Bioremediat Biodegrad 2018, Volume 9
DOI: 10.4172/2155-6199-C1-014