Volume 08
Innovative Energy & Research
ISSN: 2576-1463
Advanced Energy Materials 2019
July 11-12, 2019
conference
series
.com
July 11-12, 2019 | Zurich, Switzerland
21
st
International Conference on
Advanced Energy Materials and Research
Page 22
Jikui Luo, Innov Ener Res 2019, Volume 08
Material synthesis and optimization for high performance triboelectric nano generators
E
nergy harvesting technology is an emerging technology, particularly important for the wireless sensor networks as it
is the core technology for internet of things (IoT), smart manufacturing and smart cities, etc. Since, wireless sensors
are typically installed on mobile objects, in remote areas or harsh environments, it is extremely challenging to maintain
their long-term sensing/monitoring function due to the requests for constant electrical power or periodical replacement
of batteries. Energy harvesting technologies have been explored to power wireless sensors by utilizing piezoelectric,
pyroelectric, electromagnetic and triboelectric effects. Triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) is regarded as the most
suitable one owing to its very high power outputs and conversion efficiency. Great efforts focus on the performance
enhancement through the innovations to increase surface charge density. Searching for better materials and optimal
combination and modifying materials properties are the two common methods for obtaining triboelectric materials
with high surface charge densities. We have been working on these for a while and achieved composite materials with
excellent triboelectric properties and various optimal material combinations for TENGs. The talk will highlight our work
on the best tribo-positive materials, synthesis of tribo-negative composites using polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) or
polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) incorporated with piezo/ferroelectric nanomaterials such as ZnO and Barium titanate
(BTO) etc, and specific design for the electrode and tribomaterial interfaces. Using the best material combination
and optimized device structures, we have fabricated flat-surface TENGs with peak voltage output over 1200 V and
instantaneous power density in the range of 40-120 W/m
2
with excellent stable function. Author will also present our
latest unique technologies of the TENG-based chipless wireless sensors with self-identification capability and TENG as a
wireless power source.
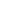
Figure 1:
Schematic and working mechanism of the TENG with an incorporated
interfacial ZnO nanosheets piezoelectric layer.
Figure 2:
Schematic drawing of the instantaneously self-powered chipless
wireless sensors with self-identification capability.
Jikui Luo
University of Bolton, UK