Page 52
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
10
th
International Conference on
February 22-23, 2018 | Paris, France
Vascular Dementia
Volume 8
Journal of Alzheimers Disease & Parkinsonism
ISSN: 2161-0460
Vascular Dementia 2018
February 22-23, 2018
fMRI of healthy elderly during Stroop test and the serial count: Comparative analysis
Zuhra Gadzhieva, E Kremneva, S Morozova, A Sergeeva, M Zabitova, K Shamtieva, D Lagoda, M Krotenkova
and
L Dobrynina
Research Center of Neurology, Russia
Introduction&Aim:
The term executive function (EF) refers to a number of cognitive abilities that enable and control adaptive,
goal-oriented behavior. EF is vulnerable to white matter injury and to perturbations in neurotransmitter systems. As a result,
EF is impaired in plenty of neurologic and psychiatric conditions. The aim of the current study was to perform a comparative
analysis of the cerebral cortex activation in healthy subjects during task-fMRI with a color-word Stroop test modification and
a new suggested counting paradigm.
Materials & Methods:
12 healthy control subjects aged 45-63 (2 men) underwent blocked design fMRI on 3T scanner with
Stroop test and serial count task. Pre- and post-processing of fMRI data were performed using SPM8.
Results:
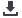
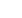
FMRI analysis showed presence of common activation areas across both tasks including bilateral dorsolateral
prefrontal cortex (BA 46, 9), premotor cortex (BA 6), supplementary motor area (BA 6), bilateral parietal cortex (BA 39, 40),
right anterior cingulate cortex (BA 32), anterior part of insular cortex (BA13), bilateral cerebellar hemisphere, integrated in
executive networks. However, serial count task showed no activation in the lenticular nuclei and occipital cortex, unlike the
Stroop test.
Conclusion:
According to our results, serial count could be used as alternative paradigm for EF mapping, especially in patients
with vision problems.
Biography
Zuhra Gadzhieva is a student in the Research Center of Neurology, Department of Angioneurology and Early Rehabilitation after Stroke in the Research Center of
Neurology, Moscow, Russian Federation. The main goal of her PhD work is to investigate the mechanisms of cognitive decline in patients with cerebral small vessel
disease (multimodal neuroimaging and neuropsychological study).
zuhradoc@mail.ruZuhra Gadzhieva et al., J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2161-0460-C1-037