Page 43
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
Journal of Biotechnology & Biomaterials
ISSN: 2155-952X
Pharma Biotech 2018
December 10-11, 2018
December 10-11, 2018 | Rome, Italy
23
rd
International Conference on
Pharmaceutical Biotechnology
Effect of biosurfactants obtained from different sources on pathogenic microorganisms
Rodríguez-López L, Rincón-Fontán M, López-Prieto A, Vecino X, Cruz J M
and
Moldes A B
University of Vigo, Spain
Statement of the Problem:
Biosurfactants are amphiphilic compounds with surface properties produced by microorganisms
or obtained from biological cells. They have not only the same applications than their synthetic counterparts but also better
characteristics in terms of biocompatibility and biodegradation. Although they have been proved in different areas such as
bioremediation, their uses are increasing in food and cosmetic formulations. In these areas, microbiology properties are one of
the most important parameter to control, so it is necessary to evaluate biosurfactants behavior in presence of microorganisms.
Methodology:
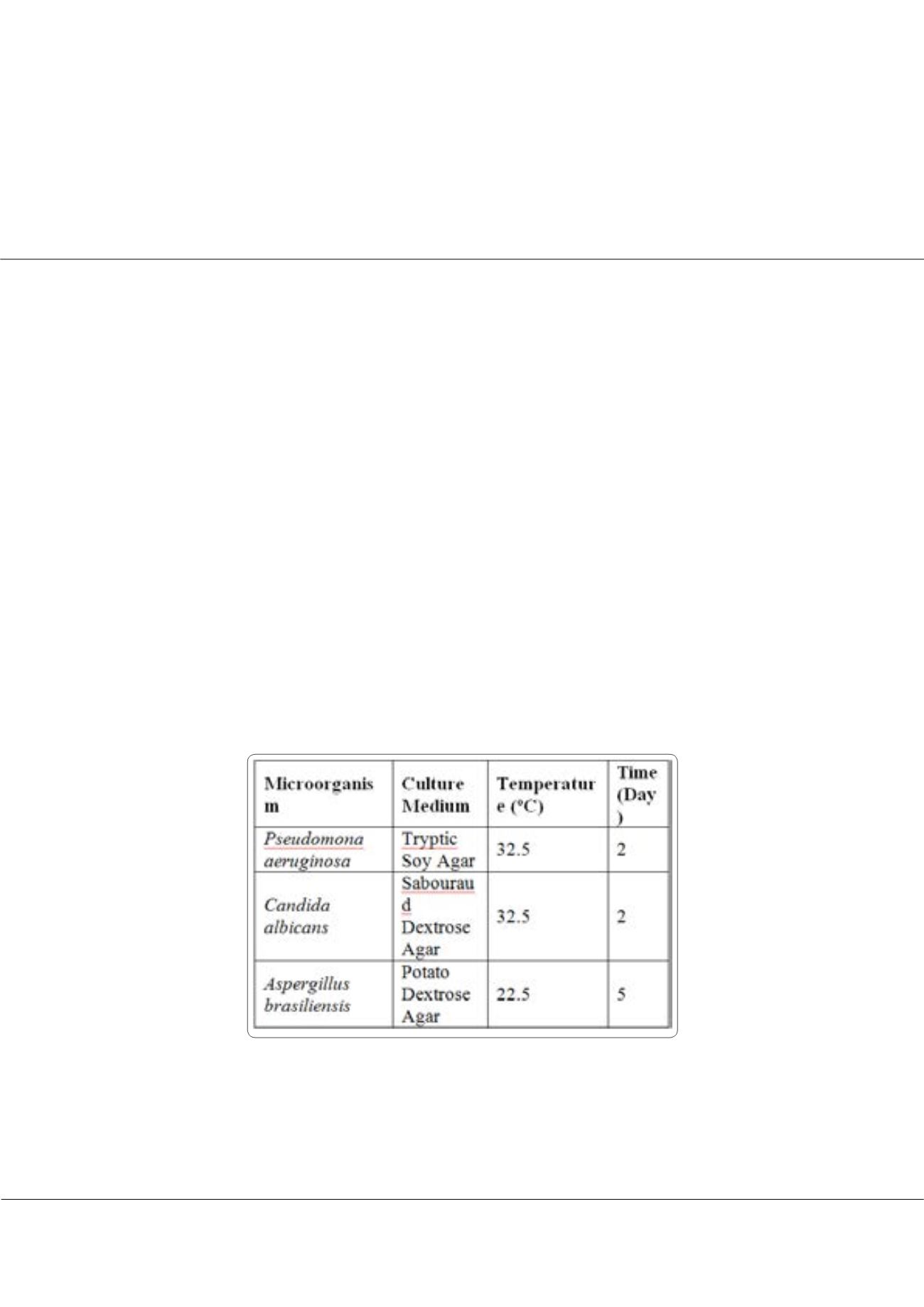
Two biosurfactant extracts were produced following the methodologies established by Vecino et al. one obtained
from corn steep liquor (CSL) and the other from
Lactobacillus pentosus
. Both biosurfactants were diluted up to 1 g/L of and put
in contact with a known concentration of pathogenic microorganisms including
Candida albicans, Aspergillus brasiliensis
and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
, at 22.5ºC. The effect of these biosurfactants on the microorganism growth was evaluated each 7 days
during a month. The culture conditions for obtaining the inoculum of each microorganism were reflected.
Findings:
The experiment carried out with biosurfactant from CSL, showed antimicrobial activity against
P. aeruginosa and
A. brasiliensis
, thus the concentration of microorganisms was reduced from 2*10
6
and 2*10
4
UFC/mL, to 1 and 4*10
3
UFC/
mL, respectively. In the case of
C. albicans
, the amount of colonies slightly increased from 2*10
4
to 8*10
4
UFC/mL. For the
biosurfactant from
L. pentosus
, the behavior observed was completely different, thus the number of colonies did not change
significantly in any of the pathogens tested.
Conclusion & Significance:
These results have demonstrated interesting effects of biosurfactant extract from CSL against
pathogenic microorganisms, what is in concordance to its antioxidant properties. Furthermore, the biosurfactant from
L.
pentosus
showed lower antimicrobial activity.
Recent Publications
1. Irorere V U, Tripathi L, Marchant R, McClean S and Banat I M (2017) Microbial rhamnolipid production: A critical
re-evaluation of published data and suggested future publication criteria. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology
101(10):3941-3951.
Rodríguez-López L et al., J Biotechnol Biomater 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X-C8-109