Volume 7, Issue 3(Suppl)
J Biotechnol Biomater, an open access journal
ISSN: 2155-952X
Euro Biotechnology 2017
September 25-27, 2017
Page 10
conference
series
.com
17
th
EURO BIOTECHNOLOGY CONGRESS
September 25-27, 2017 Berlin, Germany
Denis Spitzer, J Biotechnol Biomater 2017, 7:3(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X-C1-075
Spray flash evaporation for the continuous production of high performance nano-drugs: New
challenges for a new disruptive process
N
S3E laboratory developed the Spray Flash Evaporation (SFE) for preparing drug nanoparticles at industrial scale. The
process was several times patented up to now. The solution is kept in a pressurized tank separated from a vacuum chamber
by a hollow cone nozzle, used both to heat and spray the liquid. The instantaneous evaporation of the solvent originates from
the combination of the abrupt pressure drop and the high energy stored by the overheated solvent prior to nebulisation.
The flash evaporation leads to small crystallites with narrow size distribution. The nanoparticles may be composed of single
compounds, mixtures of several substances or co-crystals. In the domain of medicaments, co-crystals are of critical importance
as they enhance bioavailability and up-take by the human body of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API). Up to now, most
used techniques are of batch nature and are not able to give access in big amounts to nano-sized crystals or co-crystals of
therapeutic interest. The SFE permits the continuous manufacturing of nano-sized co-crystals, in large amounts with a kinetic
complying with the pharmaceutical industry’s requirements. The efficiency of SFE is shown by the manufacturing of pure
nano-medicaments but also of nano-co-crystals such as resveratrol/4-aminobenzamide (1/1), caffeine/oxalic acid (2/1) and
caffeine/glutaric acid (1/1), with a mean particle size of between 30 and 100 nm. After showing the possibility to continuously
nano-crystallize medicaments, the presentation will focus on different main challenges to further enhance the production
capacity and also to understand the SFE process itself. Among different techniques and metrologies used or specially developed
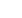
such as phase Doppler interferometry (Figure) and AFM-TERS spectroscopies, the presentation will also focus on different
crystallization configurations used.
Figure: Phase Doppler interferometry for the on-line metrology
Biography
Denis Spitzer received his PhD in Physical Chemistry in 1993 at University Louis Pasteur of Strasbourg. He is the founding and current Director of the NS3E Research
Laboratory UMR 3208 ISL/CNRS/UNISTRA. He conducts research in continuous nano-crystallization processes of organic nanomaterials such as model medicaments
and energetic materials. He is the inventor of the SFE process. He is the author of more than 150 publications and scientific reports.
denis.spitzer@isl.euDenis Spitzer
French-German Research Institute of Saint-Louis, France