Page 87
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 2
Environment Pollution and Climate Change
ISSN: 2573-458X
Climate Change 2018 &
Global ENVITOX 2018
October 04-06, 2018
October 04-06, 2018
London, UK
16
th
Annual Meeting on
Environmental Toxicology and Biological Systems
&
5
th
World Conference on
Climate Change
JOINT EVENT
The energy-water-health nexus under climate change in the United Arab Emirates—impacts and
implications
William W Dougherty
Climate Change Research Group, USA
C
limate change poses serious energy, water and health challenges for the United Arab Emirates (UAE). While closely
interconnected, the development of sustainable energy, water and health policies has typically been viewed as independent,
sector-specific planning challenges. However, changing demographics, a rapidly growing economy, increasing reliance on
desalination, and worsening air quality—all taking place as climate change unfolds— suggest a need for a more integrated
approach to risk management. Accounting for the interactions between an “energy-water-health nexus” is one way to ensure
that development strategies are considered within a framework that addresses the range of potential tradeoffs, risks, and
synergies. To address the energy-water-health nexus under a changing climate, research activities were undertaken as part
of the Local, National, and Regional, Climate Change Programme (LNRCCP) of the Abu Dhabi Global Environmental Data
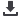
Initiative (AGEDI). Climate change modeling at the regional spatial scale (Arabian Peninsula; Arabian Gulf) was first carried
out to establish the atmospheric and marine physical conditions that will underlie energy, water, and health challenges in the
future. The results of this modeling were then used as inputs to an analysis of policies that aim to account for the linkages across
the energy-water nexus in one hand and the energy-health nexus on the other. The results show that climate change will render
an extreme hyper-arid climate even more so, while the waters of the Arabian Gulf will experience heightened salinity, changing
circulation patterns, and higher temperatures under intensifying desalination activities. The analysis of the energy-water nexus
shows that a range of water/energy efficiency and renewable energy measures can lead to significant reductions in energy
use and annual greenhouse gas emissions, while coming at negative societal cost. The analysis of the energy-health nexus
shows that the gradual introduction of energy efficiency and renewable energy measures can lead to substantial decreases in
premature mortality and health care facility visits in urban areas.
Recent Publications
1. Schile L, Kauffman J, Crooks S, Fourqurean J, Campbell J, et
al. (2018) Limits on carbon sequestration in arid blue carbon
ecosystems. Ecological Applications 27(3): 859–874.
2. Dougherty W, Yates D, and Kucera P (2017) Public health co-
benefits of the diffusion of innovative greenhouse gas mitigation
technologies in Abu Dhabi, Innovative Energy & Research S1:002.
3. Haidera M, Alhakimi S, Noaman A, Al Kebsi A, Noaman A, et
al. (2011) Adapting to climate change-water scarcity for Yemen's
vulnerable communities. Local Environment 16(5):473–488.
4. Dougherty W, Kartha S, Rajan C, Lazarus M, Bailie A, et al. (2009)
Greenhouse gas reduction benefits and costs of a large-scale transition to hydrogen in the USA. Energy Policy 37:56–67.
Biography
William W Dougherty has worked over the past 20 years on a wide variety of climate change related issues, with an emphasis on greenhouse gas mitigation
and adaptation to climate change. He has assisted governments in the development of national GHG mitigation and adaptation strategies, led vulnerability
assessments, formulated project documents, analyzed energy efficiency and renewable energy options for achieving emission reductions, and contributed to the
development of methodological approaches, training programs and software tools that are used throughout the world. He has been invited as a Speaker or Expert
Participant in meetings of the World Bank, United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, the United Nations Development Programme, the African
Development Bank, the World Future Energy Summit, and the United Nations Environment Programme. He has worked throughout North Africa, Sub-Saharan
Africa, and the Middle East in support of national government agencies, multi-lateral organizations, and development banks. He has authored or co-authored over
100 research reports.
billd@ccr-group.orgWilliam W Dougherty, Environ Pollut Climate Change 2018, Volume 2
DOI: 10.4172/2573-458X-C1-002