Page 108
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
Journal of Biotechnology and Biomaterials
ISSN: 2155-952X
Biomaterials 2018
March 05-06, 2018
March 05-06, 2018 | Berlin, Germany
3
rd
Annual Conference and Expo on
Biomaterials
Pegylated and amphiphilic Chitosan coatedmanganese ferrite nanoparticles for pH-sensitive delivery
of methotrexate: synthesis and characterization
Leila Karimi
Islamic Azad University, Iran
M
agnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are the major class of nanoparticles (NPs) with specific functional properties that make
them good candidates for biomedical applications. Due to their response to the magnetic field, they can be used in
targeted drug delivery systems. In current research, the MNPs were synthesized with the general formula of Fe1-xMnxFe2O4
by the co-percipitation technique. First, the effect of the Fe2+ ions in the system was investigated. Succinid anhydride was
used as the first stabilizer to prepare surface for binding two types of polymer, including Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and
palmitoylated polyethylene glycol-grafted (Cs-PEG-PA) were introduced as a polymeric shell. The composition, size, structure
and magnetic properties of NPs were determined by the particle size analysis (PSA), X-ray diffractometry (XRD), Fourier
transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). Determining the well-defined properties
of MNPs, methotrexate (MTX), as a common anticancer drug, was encapsulated into the coatedMNPs. The drug encapsulation
efficiency was as high as 92.8 % with the magnetization value of 19.7 emu/g. The in-vitro release pattern was studied, showing
only 6% of the drug release in pH= 7.4 (as a model of the physiological environment) and 25% in pH= 5.4 (as a model of the
tumor tissue environment) after 72 h. Based on these results, we may be able to introduce this specific system as a novel pH
sensitive MNP system for MTX targeting to tumor tissues in cancer chemotherapy.
Recent Publications
1. Z. Karimi, H. Shokrollahi, L. Karimi, (2013) Nano-magnetic particles used in biomedicine: core and coating materials,
Materials science and Engineering: C 33:2465–2475.
2. L. Karimi, H. Shokrollahi, (2011) Structural, micro structural and magnetic properties of amorphous/nanocrystalline
Ni63Fe13Mo4Nb20 powders prepared by mechanical alloying, Journal of Alloys and Compound 509:6571–6577.
3. L. Karimi, H. Shokrollahi, Z. Karimi, M. Mohammadi, (2013) Improvement of magnetic properties of nanostructured
Ni79Fe16Mo5 alloyed powders by a suitable heat treatment, Advanced Powder Technology 24:653–658.
4. Y. Mohammadifar, H. Shokrollahi, Z. Karimi, L. Karimi, (2014) The synthesis of Co1−xDyxFe2O4 nanoparticles and
thin films as well as investigating their magnetic and magneto-optical properties, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic
Materials 366:44–49.
5. Z. Karimi, Y. Mohammadifar, H. Shokrollahi, Sh. Khameneh asl, L. Karimi, Magnetic and structural properties of
nano sized Dy-doped cobalt ferrite synthesized by co-precipitation, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 361
(2014) 150–156
Biography
Leila Karimi holds a BA in ceramic Materials. She received MA in Materials Science and Engineering by the Islamic Azad University with a focus in Magnetic
Materials and Drug Delivery. Where she furthers her research on the magnetic materials physical concepts of ferrofluids, drug delivery, magnetic properties and
synthesis methods of Nano sized ferrites to provide a suitable selection of magnetic core, surfactant layer and liquid type for influential cancer treatment
leeila.karimi@gmail.comLeila Karimi, J Biotechnol Biomater 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2155-952X-C1-089
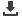
Figure1:
Schematic illustration of coating
and drug loading of manganese ferrite
nanoparticles for pH-sensitive delivery of
methotrexate