Volume 7
Innovative Energy & Research
ISSN: 2576-1463
Advanced Energy Materials 2018
August 13-14, 2018
Page 63
conference
series
.com
August 13-14, 2018 | Dublin, Ireland
20
th
International Conference on
Advanced Energy Materials and Research
Olivier Joubert, Innov Ener Res 2018, Volume 7
DOI: 10.4172/2576-1463-C1-001
Promising oxy borates for solid-oxide fuel cell applications
T
he research on solid oxide fuel cell (H
+
or O
2-
SOFC) is based on both the synthesis of new materials and the design process
of the cell. The main advantage of SOFC is that they can work under hydrocarbon fuel at temperature higher than ≈700°C. In
the current SOFC systems, the most widely used electrolyte is yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) which is inexpensive and shows an
acceptable conductivity level. But YSZ is very refractory and its major drawback is its reactivity during the sintering process with
lanthanum- and strontium-based cathodematerials, which leads to the formation of an insulating layer such as SrZrO
3
or La
2
Zr
2
O
7
.
There is also a great interest to find ceramic based fuel cells, for mobile application, working at low temperature (≈400°C). This
can be achieved in H
+
-SOFC with a ceramic membrane showing a good proton conductivity level. The state of the art perovskite
type yttrium-doped BaCeO
3
(called BCY) shows a proton conductivity level above 1 mS/cm at 400°C. But due to its high basicity,
BCY tends to decompose, in this temperature domain, in air containing CO
2
. Finding new electrolyte material is one of the issues.
In this presentation, after a briefly state-of-the art concerning SOFC electrolyte, we will report on high-temperature proton and
oxide ion conductivities in two new class of oxyborates, La
26
O
27
(BO
3
)
8
and doped Ba
3
Ti
3
O
6
(BO
3
)
2
compounds. Both samples were
prepared by solid-state reaction and characterized using x-ray diffraction and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Quite
high conductivity level, about 6.8×10
–4
and 1.5×10
–4
S/cm at 700°C in air were observed respectively. The transport properties can
be understood in terms of the presence in high concentrations of oxygen and barium vacancies as well as oxygen interstitials as
observed in hybrid density-functional defect calculations.
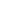
Figure 1:
Conductivity vs. temperature of the oxyborate La
26
O
27
(BO
3
)
8
under different atmospheres
Recent Publications
1. Lebreton M, Delanoue B Baron E, Ricoul F, Kerihuel A, Subrenat A, Joubert O and Le Gal La Salle A (2015) Effects
of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane on nickel/yttria - stabilized zirconia-based solid oxide fuel cells
performance for direct coupling with a gasifier. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 40(32):10231-10241.
2. Jarry A, Joubert O, Suard E, Zanotti J M and Quarez E (2016) Location of deuterium sites at operating temperature from
neutron diffraction of BaIn
0.6
Ti
0.2
Yb
0.2
O
2.6-n
(OH)
2n
, an electrolyte for proton-solid oxide fuel cells. Physical Chemistry
Chemical Physics 18:15751.
3. Quarez E, Noirault S, Caldes M T and Joubert O (2010) Water incorporation and proton conductivity in titanium
substituted barium in date. Journal of Power Sources 195(4):1136-1141. Noirault S, Célérier S, Joubert O, Caldes M T
and Piffard Y (2007).
Olivier Joubert
Jean Rouxel Institute of Materials in Nantes – CNRS, France