Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
Google Scholar citation report
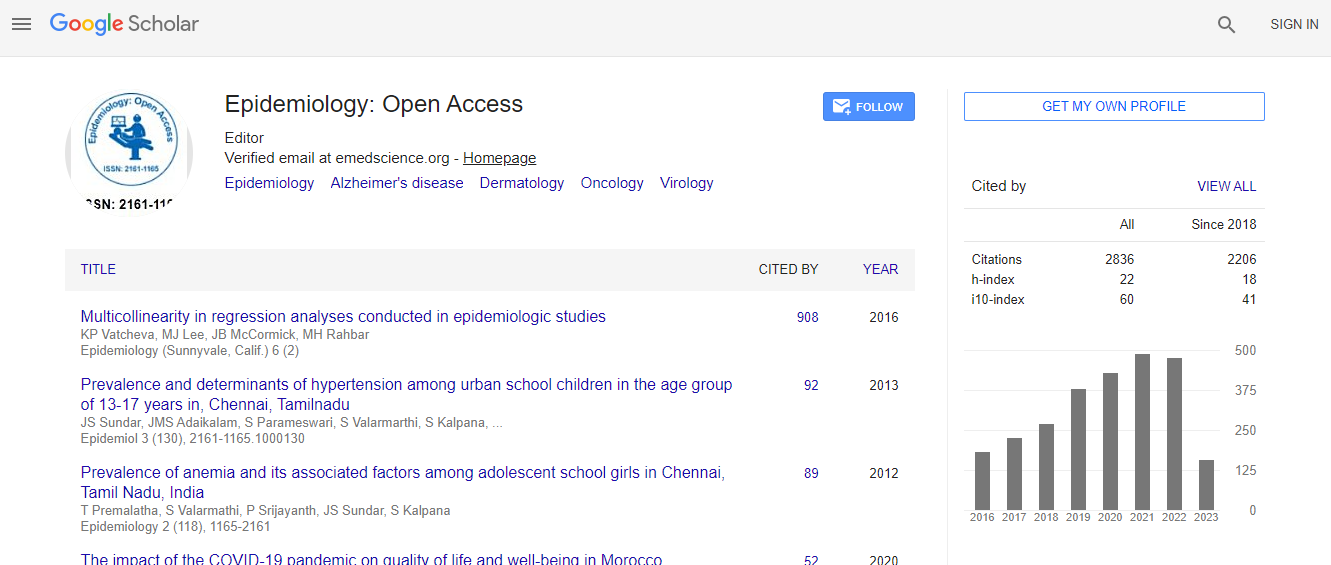
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Waterborne disease outbreak surveillance system in France: Perspectives for nationwide surveillance
8th International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Damien Mouly, Clement Vix and Jerome Pouey
French National Public Health Agency, France
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Outbreaks of infectious waterborne diseases are still a public health concern in developed countries [1-6]. France is also concerned by WBDO occurrence [7, 8], but to date, because of the absence of a nationwide specific surveillance system, the detection of these events is mainly based on the voluntary reporting of clusters of AGI by general practitioners to health authorities. The number of WBDO is thus most likely underestimated. In this context, an integrated approach to detect WBDO relying on the identification of medicalized AGI cases from the French health administrative database and drinking water networks (DWN) from French ministry of health database was developed [9] and tested in a pilot study. Each detected outbreak was investigated regarding environmental criteria during the days before the onset of the outbreak: results on bacterial water monitoring, weather (e.g. heavy rain), technical incidents in the drinking water system (e.g. chlorination breakdown, alarm malfunction). Sixty-seven potential WBDO were detected in 2014 and 2015 in the 7 french administrative districts of the pilot study. The combined population served by a DWN implicated in a WBO during the period was 914,599 inhabitants. Comparatively, only 2 WBDO had been detected and reported to the health authorities at the time of their occurrence. Four levels of strength of association have been defined based on epidemiological and environmental criteria: Strong, probable, possible and undetermined. The results of the pilot study highlight the public health utility of the implementation of a nationwide WBDO surveillance system in France based on data routinely collected by the Health Insurance. A web-application, named “EpiGEH”, was also developed to support the surveillance system. Such a specific surveillance system should help health authorities to formulate recommendations regarding the management of drinking water systems and propose appropriate preventive measures, in accordance with the water safety plans. Recent Publications 1. Craun, G.F., et al., Causes of outbreaks associated with drinking water in the United States from 1971 to 2006. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2010. 23(3): p. 507-28. 2. Hrudey, S.E. and E.J. Hrudey, Safe Drinking Water : Lessons from Recent Outbreaks in Affluent Nations. 2004, London: IWA publishing. 486. 3. Pons, W., et al., A Systematic Review of Waterborne Disease Outbreaks Associated with Small Non-Community Drinking Water Systems in Canada and the United States. PLoS One, 2015. 10(10): p. e0141646. 4. Nazareth, B., et al., Surveillance of waterborne disease in England and Wales. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev, 1994. 4(8): p. R93-5. 5. Murphy, H.M., et al., A systematic review of waterborne disease burden methodologies from developed countries. J Water Health, 2014. 12(4): p. 634-55. 6. Guzman-Herrador, B., et al., Waterborne outbreaks in the Nordic countries, 1998 to 2012. Euro Surveill, 2015. 20(24). 7. Beaudeau, P., et al., Lessons learned from ten investigations of waterborne gastroenteritis outbreaks, France, 1998-2006. J Water Health, 2008. 6(4): p. 491-503. 8. Mouly, D., et al., Description of two waterborne disease outbreaks in France: a comparative study with data from cohort studies and from health 9. Bounoure, F., et al., Syndromic surveillance of administrative databases. Epidemiology and acute gastroenteritis based on drug consumption.Infection, 2016. 144(3): p. 591-601.Epidemiol Infect, 2011. 139(9): p. 1388-95. 10. Coly, S., et al., Waterborne disease outbreaks detection: an integrated approach using health administrative databases. Journal of Water and Health, 2017. Available Online 25 March 2017.Biography
Damien Mouly has worked as epidemiologist at the French National Public Health Agency since 2004. He is qualified in pharmacy, drinking water treatment engineer and is university doctorate of ecology of human health. He is specialized in waterborne disease and in surveillance system. He has worked on chemical risk (disinfection by-products, arsenic) and microbiological risk associated with drinking water. He works at the head of the regional office Occitanie of the French Public Health Agency (Toulouse) and ensures the national coordination of the implementation of waterborne disease outbreak surveillance.
E-mail: Damien.mouly@santepubliquefrance.fr

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi