Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
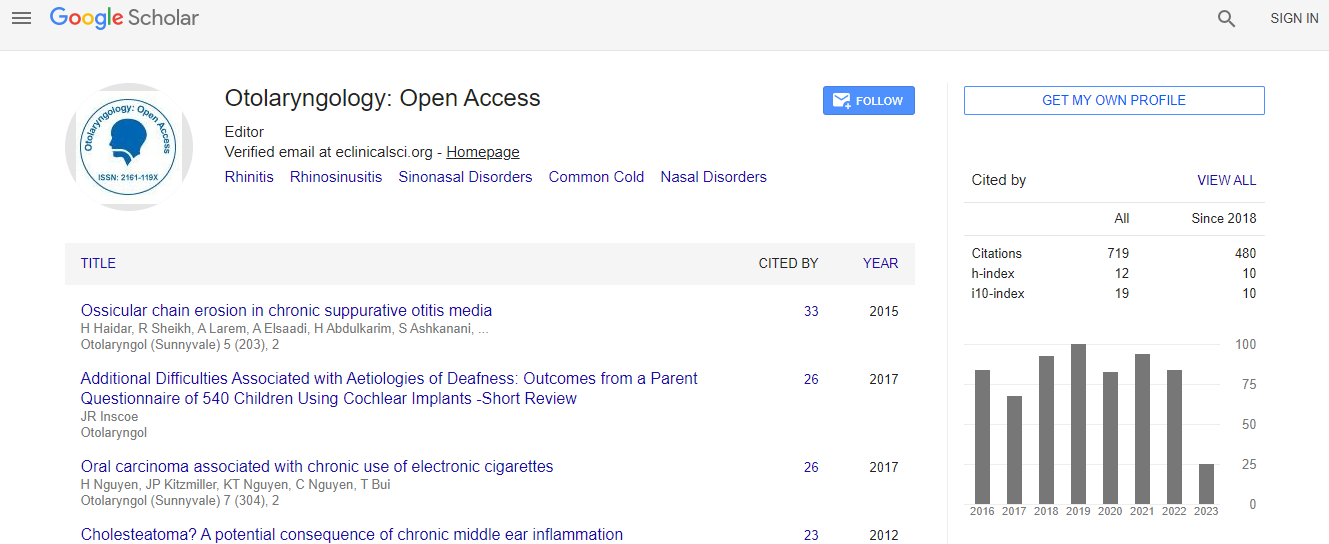
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 925
Otolaryngology: Open Access received 925 citations as per Google Scholar report
Otolaryngology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Topical hyaluronic acid in rhinitis medicamentosa: Could our perspective be changed?
4th International Conference on Rhinology and Otology
Manuele Casale
Campus Bio-Medico University, Italy
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Otolaryngol
Abstract
Background & Aim: Th is study was designed to prospectively evaluate the role of nebulized hyaluronic acid (HA) as a treatment for patients with rhinitis medicamentosa (RM). RM is a pathological condition of the nasal mucosa induced by prolonged, excessive or improper use of topical decongestants. Methods: Twenty-fi ve (25) patients were treated with HA nebulized via Spray-sol twice a day (morning and evening) for 10days (T1). Subsequently, aft er three days of washout, patients were treated with physiological saline nebulized via Spray-sol twice a day (morning and evening) for 10 days (T2). Results: Th e HA Spray-sol treatment group signifi cantly improved visual analogue scale (VAS) scores, whereas there was no statistically signifi cant diff erence in the saline Spray-sol treatment group, results confi rmed by the anterior active rhinomanometry (AAR) data. An improvement in the Global Rhinitis Score (GRS) was recorded in both groups, but plus in HA Spray-sol treatment group. Both groups showed a signifi cant reduction in mucosal edema and nasal secretions. Patients treated with HA Spray-sol reduced or even eliminated (11/25 patients) the use of topical decongestant within 10 days of treatment with HA. Conclusion: Th e results of this study suggest nebulized topical 9-mg sodium hyaluronate plays a pivotal role in the management of RM.Biography
Manuele Casale has worked in Thomas Starzl Transplantation Institute in Pittsburgh, Humber River Hospital and the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, University Hospital in Soï¬ a and House Ear Institute in Los Angeles. He has attended the 20th Advanced Course of Surgical Anatomy and Dissection in Otology, the Course of Surgical Anatomy, Microsurgery Intranasal Endoscopic Anterior Skull Base at the University of Zurich and Masters in Head and Neck Surgery at the National Cancer Institute Regina Elena in Rome. He carries out research on several topics which include molecular biology, clinical research and innovative design tools in otolaryngology.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi