Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
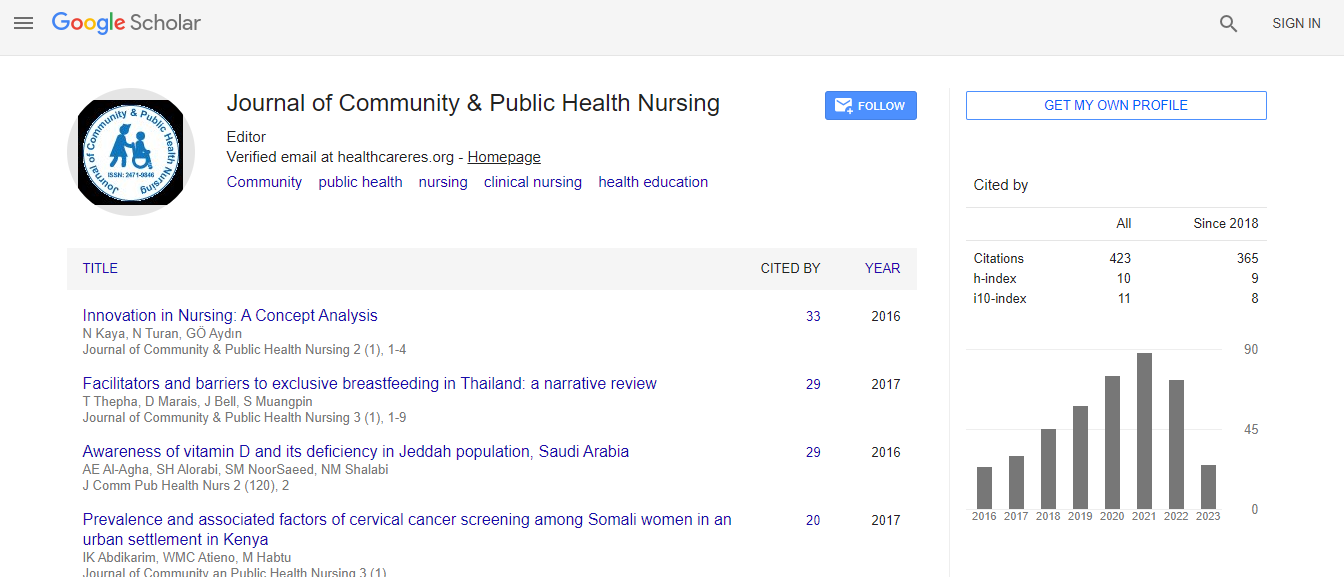
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 739
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing received 739 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Title: Sentiment and emotion trends of nurses tweets about the COVID-19 pandemic
24th World Nursing Education Conference
Teenu Xavier
University of Cincinnati, USA
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Comm Pub Health Nurs
Abstract
Purpose: Twitter is being increasingly used by nursing professionals to share ideas, information, and opinions about the global pandemic yet there continues to be a lack of research on how nurse sentiment is associated with major events happening on the frontline. The purpose of the study was to quantitatively identify sentiments, emotions, and trends in nurses├ó┬?┬? tweets and to explore the variations in sentiments and emotions over a period in 2020 with respect to the number of cases and deaths of COVID-19 worldwide. Design: A cross-sectional data mining study was held from March 3, 2020, through December 3, 2020. The tweets related to COVID-19 were downloaded using the tweet ids available from a public website. Data were processed and filtered by searching for keywords related to nursing in the profile description field using the R software and JMP Pro Version 16 and the sentiment analysis of each tweet was done using AFINN, Bing, and NRC lexicon. Findings: A total of 13,868 tweets from the Twitter accounts of self-identified nurses were included in the final analysis. The sentiment scores of nurses├ó┬?┬? tweets fluctuated over time and some clear patterns emerged related to the number of COVID-19 cases and deaths. Joy decreased and sadness increased over time as the pandemic impacts increased. Conclusions: Our study shows that Twitter data can be leveraged to study the emotions and sentiments of nurses and the findings suggest that the emotional realm of nurses was affect- ed during the COVID-19 pandemic according to the emotional trends observed in tweets.Biography
Teenu Xavier is a PhD nursing student at the University of Cincinnati. Her dissertation work focuses on understanding the unique needs, experiences and strategies used by ICU nurses to be resilient during the COVID-19 pandemic. Her long-term career goal focuses on promoting resilience among nurses and to develop novel, targeted interventions to preserve and/or enhance resiliency. She has presented various papers at international conferences and has various publications to her credit.. This study was done as sub-study of the investigator’s dissertation project. The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the nurses tremendously as they were in the frontlines providing care to the patients and these nurses used social media platforms to express their frustrations, emotions, and needs. So, we decided to look at the data available through Twitter to take a deep dive into the sentiments of nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi