Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
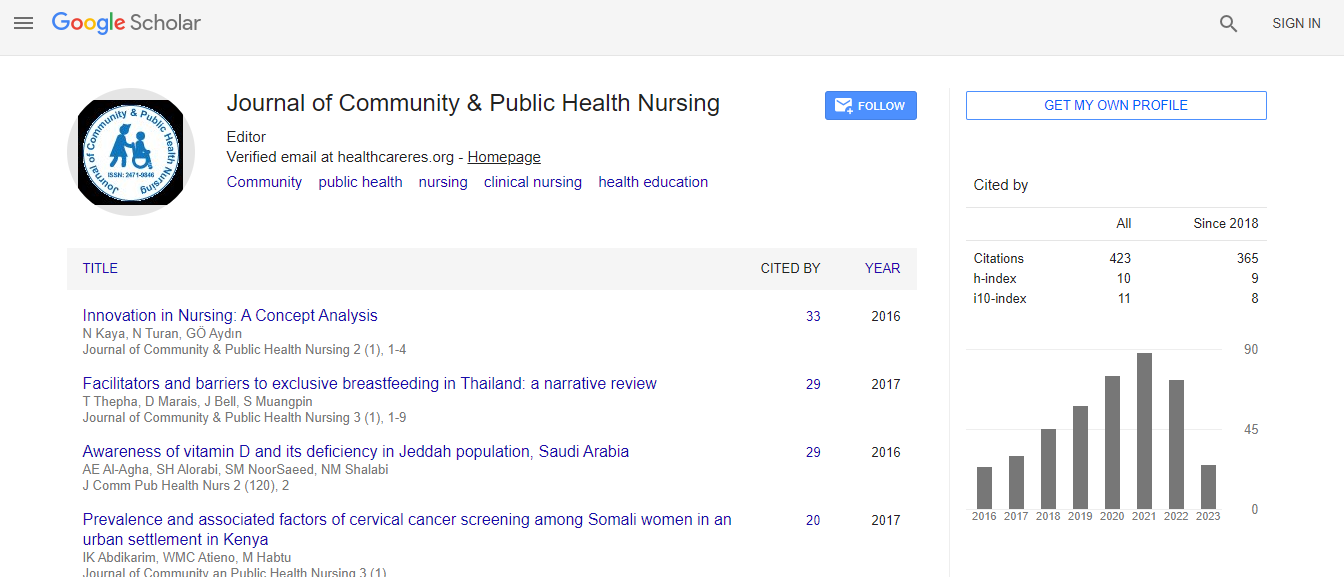
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 421
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing received 421 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
The use of traditional medicine by women during pregnancy in Sub-Saharan Africa: A scoping review
Joint Event on 21st World Congress on Registered Nurse and Nurse Practitioner Meeting & Nursing Education and Management
Nokuthula G Mafutha
University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Comm Pub Health Nursing
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to describe the traditional medicines utilized in sub-Saharan Africa, during pregnancy and their possible adverse effects. Method: A scoping review was used; five databases (PubMed, Cinahl, Cinahl plus, Wiley Online, Scopus and SAGE) were the search for the collection of data, with specific search terms such as sub-Saharan Africa, adverse effects, traditional medicine, and complementary alternative medicine, pregnancy, labor and postpartum. The literature had to be in English, have a full abstract. Data included literature from sub-Saharan Africa of both quantitative, qualitative articles and grey literature in peer-reviewed journals published between January 2007 and August 2018. A data extraction sheet was developed to record the authors, year study was published, the country study was conducted, research aim and question, participants and methods and the key themes. Results: Results revealed three themes such as factors that precipitate the use of traditional medicine by women, and that women had their own reasons for using traditional medicines and the prevalence of traditional medicine use in sub-Saharan Africa. Conclusion: There is significant use of traditional medicine amongst women in sub-Saharan Africa to treat various conditions related to pregnancy. However, little is known of the adverse effects that these traditional medicines may have on the women or the unborn baby. This lack of knowledge poses a risk to both mother and the unborn baby; therefore, further investigation is required on the use and safety of traditional medicines.Biography
E-mail: Nokuthula.mafutha@wits.ac.za

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi