Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
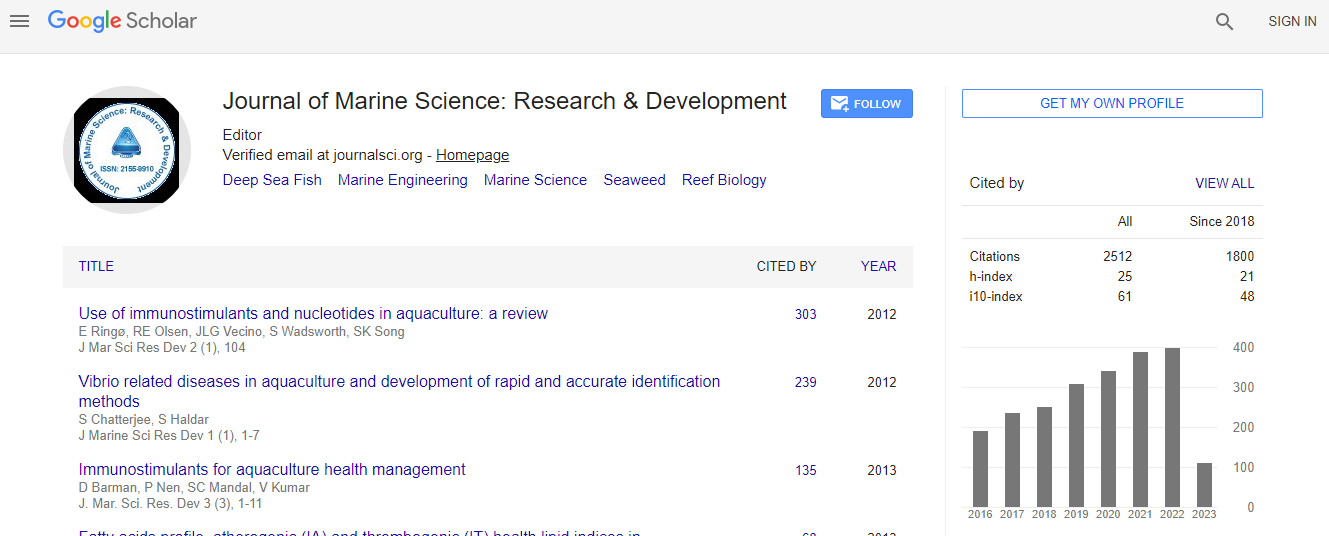
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3189
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- ResearchBible
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
The influence of environmental factors on growth and condition of larval Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus) in the Saint-Lawrence middle estuary in Quebec, Canada
4th International Conference on Oceanography & Marine Biology
Laurence Levesque
Universit√?¬© du Qu√?¬©bec √?¬† Rimouski-Institute of Marine Sciences, Canada
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Marine Sci Res Dev
Abstract
The Atlantic herring population has experienced a strong decline in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, possibly due to overfishing. A subset of this metapopulation migrates in spring and fall upstream into the St. Lawrence middle estuary to spawn. However, their recruitment has not been studied in this region for two decades. To better understand recruitment pattern of this part of the herring population, our first objective was to verify if herring spawning grounds remained in the same area as twenty years ago and to evaluate the number of larval cohorts produced. Moreover, our second objective was to explore the link between environmental factors and larval herring growth and condition. Sampling was conducted on 3 small vessels during the summer 2014, using bongo-nets and a CTD. Environmental factors recorded were temperature, depth, salinity, turbidity and tides. Our results revealed that spawning grounds were similar to those known 20 years ago. However, reproductive patterns changed, as more larval cohorts appeared over the summer period. Growth rates of the cohorts varied according to hatching dates, growing faster when hatched in the warmest months. Nevertheless, comparing the degree days of each cohort revealed that temperature was not the only environmental factor responsible, suggesting that potentially food availability might be important. Linking the environmental factors of each sampling site identified different habitats using cluster analysis. We will discuss pattern of larval growth and condition in relation to habitat characteristics in the view of the overall recruitment of larval herring in the St. Lawrence middle estuary.Biography
Laurence Lévesque is in third year of her Master’s degree in Oceanography at Université du Québec à Rimouki (UQAR-ISMER). She completed a Bachelor’s degree in Biology at McGill University in 2013. She has been for Parks Canada at the Sagenay-Saint-Lawrence Marine Park every summer as a Biology Technician since 2012.
Email: laurence.levesque@uqar.ca

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi