Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
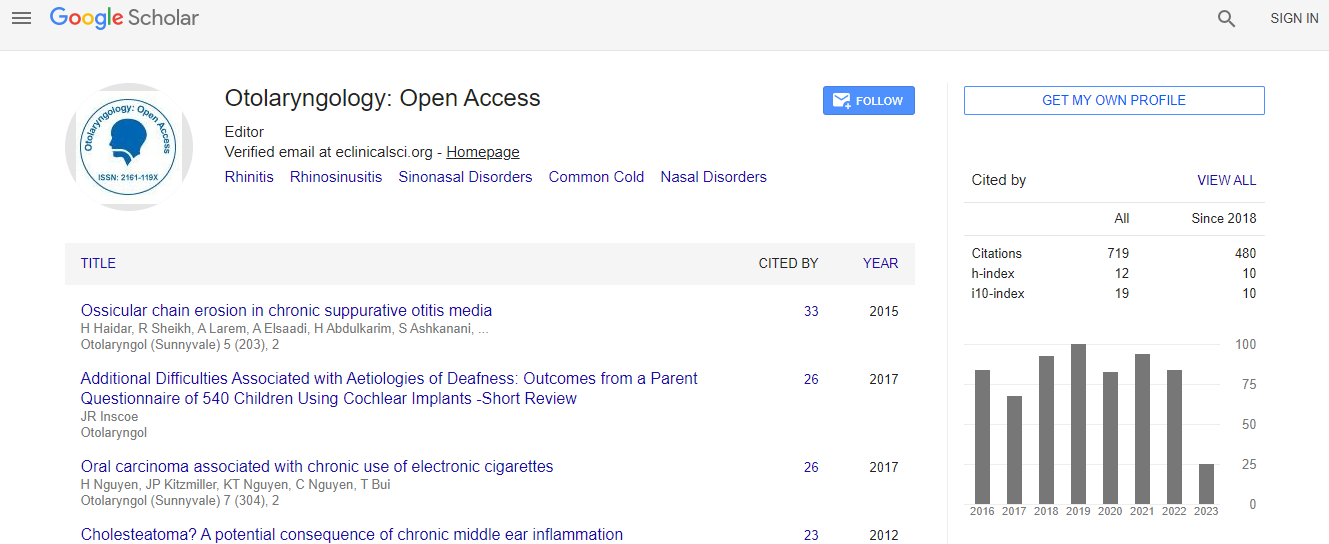
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 925
Otolaryngology: Open Access received 925 citations as per Google Scholar report
Otolaryngology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
The implication of peripheral hearing loss on temporal auditory processing in children
3rd International Conference and Exhibition on Rhinology & Otology
Amany Ahmed Shalaby, Shabana M, Dabbous A and Emara A
Ain- Shams University, Egypt Cairo University, Egypt Hearing and Speech Institute, Egypt
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Otolaryngology
Abstract
Objectives: To study temporal auditory processing abilities in SNHL children using behavioural [Auditory fusion test (AFT); Duration pattern test (DPT); Pitch pattern sequence test (PPST); time compressed sentence test (TCST)] and electrophysiological measure [Mismatch negativity (MMN)]. And to study whether there is a correlation, if any, between results of behavioural tests and MMN in assessment of temporal auditory processing. Methods: This study included 2 groups: A study group of 60 children with mild to moderate sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL); and a control group of 30 normal hearing children. The children's age ranged from 6-12 years. Results: The SNHL subgroups showed statistically significant lower scores in AFT, TCST, DPT and PPST as well as longer MMN latency than their controls. Age had significant effect on temporal auditory processing tests results and on MMN parameters but gender and aetiology of SNHL had no effect. There was no statistically significant correlation between results of behavioural tests and MMN in normal as well as SNHL children. Conclusion: Sensorineural hearing loss affects temporal auditory processing abilities reflected on both behavioural & electrophysiological test results. Age showed maturational effect on behavioural tests in all subjects, but this effect was not reflected on the MMN results of the controls, despite of the significant effect of SNHL on MMN parameters. There was no correlation between behavioural & electrophysiological test results.Biography
Amany Ahmed Shalaby, MD is the Professor of Audiology in Ain Shams University since 1994. She is the Member of International Auditory Physician Association (IAPA), Egyptian Otorhino-laryngology Society, Egyptian Audio-Vestibular Medical Society and Board Member in the Egyptian Audio-vestibular Medicine Association (EAVMA). She is a Certified Trainer of KAMPS method of Auditory Integration Training (AIT). She is a Reviewer in the ENT Committee for promotion of Professors and Assistant Professors and Reviewer of EJENTAS Journal and EJO Journal. She is specialized in diagnosis & management of hearing & balance disorders, main domain evaluation & management of children with learning disabilities, central auditory processing disorders (CAPD), Attention Deficit Hyperactive Disorder (ADHD), Autistic spectrum disorder.
Email: amani_shalaby@yahoo.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi