Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
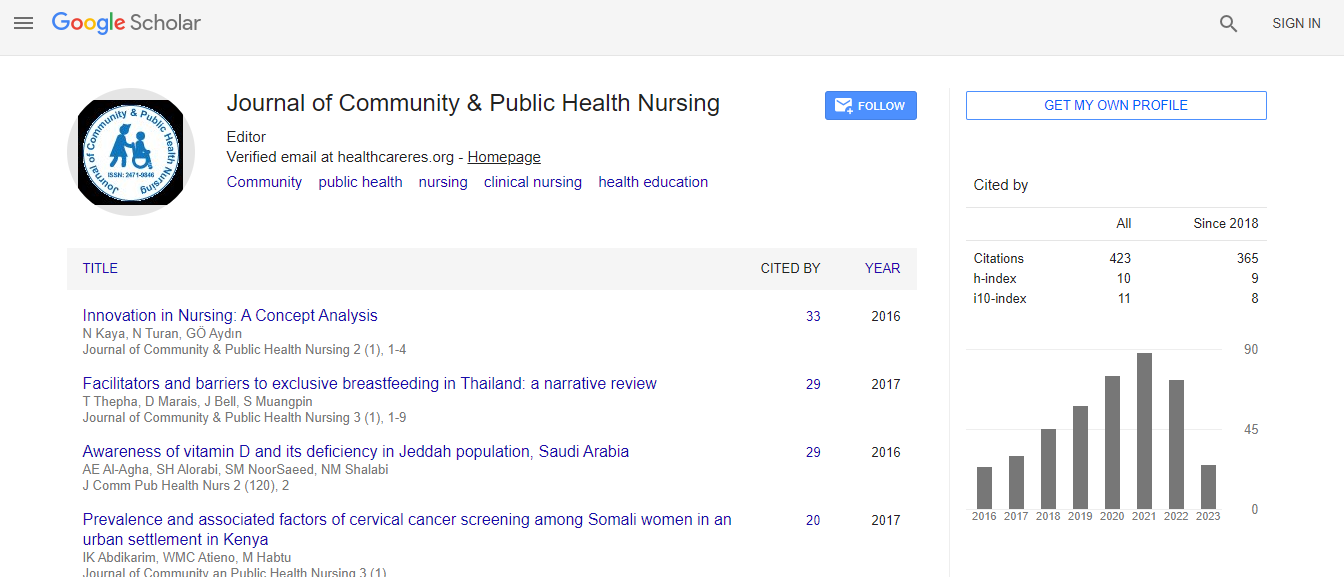
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 421
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing received 421 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
The effects of progressive muscle relaxation training as a complementary nursing therapy on fatigue and sleep quality in patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy
Joint Event on 21st World Congress on Registered Nurse and Nurse Practitioner Meeting & Nursing Education and Management
Ahmad Yousef Alafafsheh
Jordan
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Comm Pub Health Nursing
Abstract
Background: Fatigue and sleep disturbances are reported as two of the most common and distressing symptoms for patients with cancer as a result of the disease and as a side effect of chemotherapy treatment. Progressive muscle relaxation is one of the complementary interventions that are used in combination with pharmacological drugs to reduce the effects of fatigue and improve quality of sleep among patients with breast cancer. Purpose: The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of progressive muscle relaxation training on fatigue and quality of sleep in patients with breast cancer and receiving chemotherapy in Jordan. Methods: This study used a Quasi-experimental design with experimental and control groups. A purposive sample of 60 participants with breast cancer was divided into the two groups. The participants in the experimental group received training on PMRT and were given an audio CD to practice PMRT daily for four weeks. Participants in the control group received usual care. Both groups were asked to self-report fatigue severity and quality of sleep every week for the total of four weeks by using Piper Fatigue Scale-12 and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Results: The participants in the experimental group didn’t show a significant difference in fatigue severity but within the group, the comparison showed a significant reduction in fatigue severity over time. The participants in the experimental group showed a significant improvement in sleep quality compared to the control group. Also, within-group comparison showed a significant improvement in sleep quality over time. The control group didn’t show a significant improvement. Conclusion: The results of this study revealed that progressive muscle relaxation can be used as a complementary nursing intervention to reduce fatigue and improve quality of sleep among patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy.Biography
E-mail: aalafafsheh@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi