Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
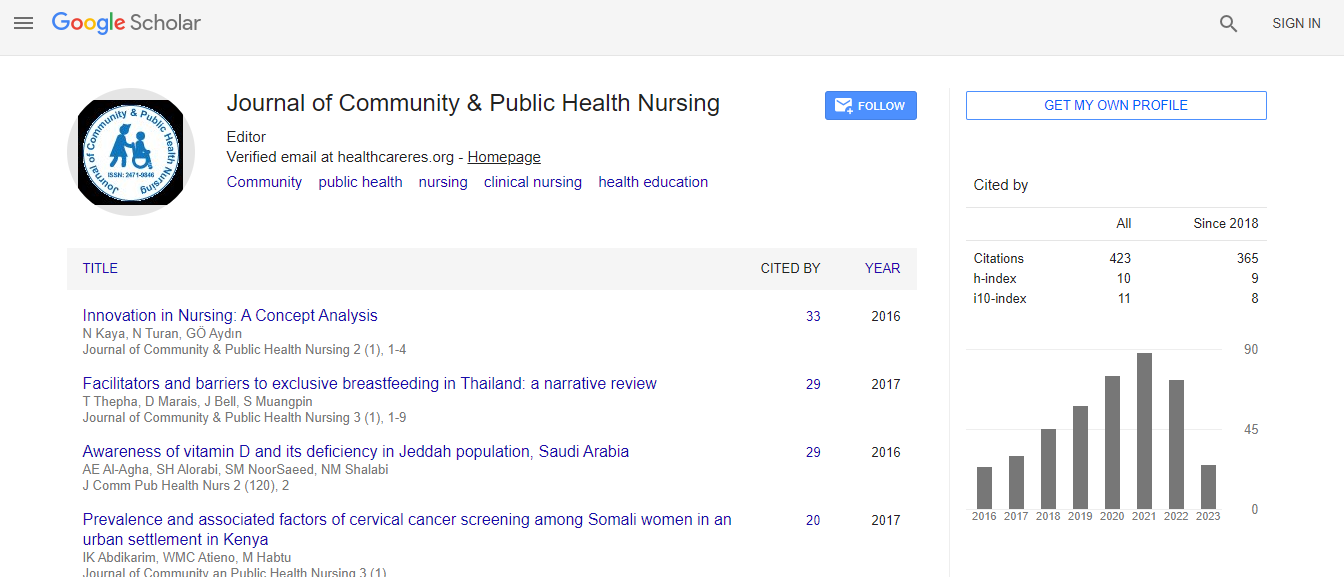
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 739
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing received 739 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
The effect of Indwelling urinary catheter clamping method on catheter-associated Complicatioons in Intensive care patients: a randomized controlled study
7th World Nursing Education & Nursing Practice
Hulya KOCYIGIT Serife KARAGOZOGLU
Sivas Cumhuriyet University, Turkey
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Comm Pub Health Nurs
Abstract
This study was carried out to investigate the effects of bladder training performed by catheter clamping for the termination of indwelling urinary catheterization on infectious complications, non-infectious complications, first urination, first urine volume, urinary retention development status and need for recatheterization, and length of hospital stay due to catheterization. Method This randomized controlled experimental type study was conducted with intensive care patients undergoing gastroenterology surgery. Three forms were used to collect the data: ├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬ó├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?Individual Identification Form├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬ó├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬Ł, ├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬ó├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?Catheter-Related Infectious Complications Follow-up Form├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬ó├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬Ł, and ├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬ó├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?Catheter-Related Non-Infectious Complications Follow-up Form├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬ó├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬?├?┬Ł. Results When the descriptive characteristics of the free drainage group and the clamped drainage group randomized by gender were compared, it was concluded that there was no statistically significant difference between the groups. Bladder training through indwelling urinary catheter clamping and free drainage application had a statistically significant effect on non-infectious complications, first urination time, first urine volume, urinary retention development status, need for recatheterization and hospital stay after catheter removal. Conclusion A statistically significant difference was found between the clamped drainage group and the free drainage group in terms of at least one infectious complication in terminating indwelling urinary catheterization, infectious complications were found to be higher in the clamped drainage group. Apart from this important finding, no advantage or disadvantage of the catheter clamping method has been determined. Keywords: Urinary Catheter Clamping, Catheter-Related ComplicationsBiography
Hulya Kocyigit is currently working as Research Assistant at the Sivas Cumhuriyet University. She graduated a doctoral program in the Department of Nursing at the same university in 2022.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi