Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
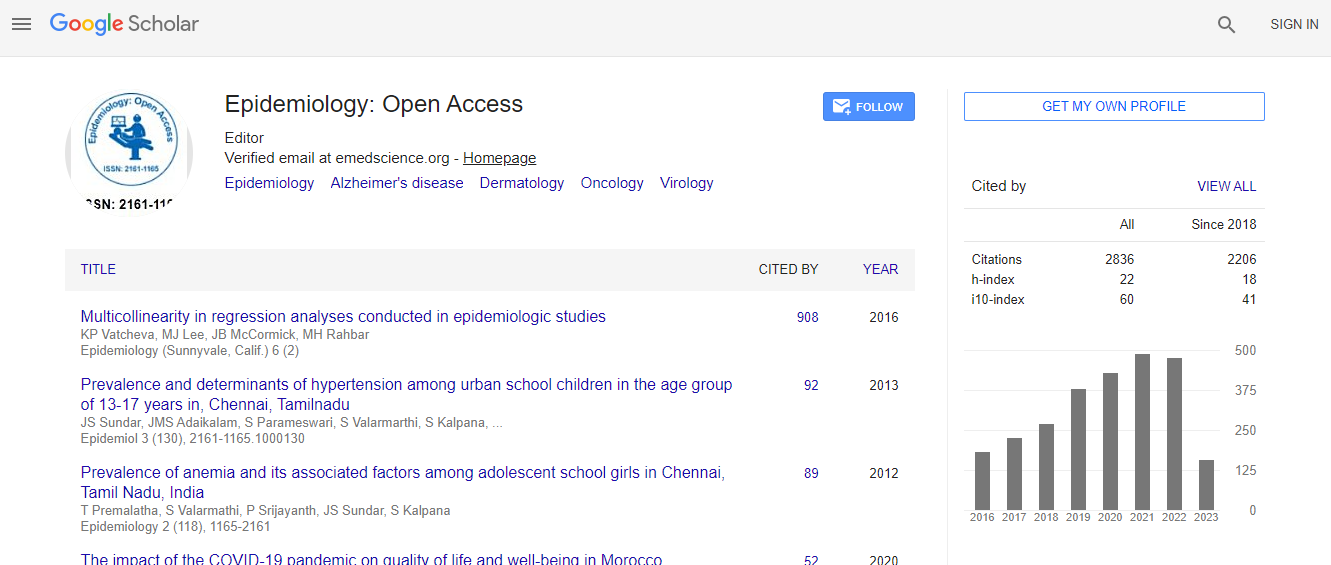
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
The economic burden of gestational diabetes mellitus in China: 2001-2012
3rd International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Wai-kit Ming
Posters-Accepted Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
The prevalence of gestational diabetes (GDM) is growing in China, and it is associated with a boosted risk of complications
for the mother and neonate, such as pre-eclampsia, intrauterine death, stillbirth, post-partum type 2 diabetes, and
macrosomia. GDM is also related with birth trauma, hypoglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia, respiratory distress, long-term
obesity and childhood diabetes. Early determination and treatment of GDM can significantly diminish the incidence of these
complications. The purpose of this study was to estimate the cases of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) diagnosed with
seven major GDM clinical guidelines between 2001 and 2012, and to estimate the economic burden of GDM. This study
used seven major clinical guidelines (WHO, ADA2010, ADA2011, NICE, NDDG, Japan 2002, national guideline - China
2007) to estimate the cost of GDM across China. We synthesized the best available national census and statistics published
data to estimate the cases and the economic burden of GDM diagnosed with seven major Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
(GDM) guidelines. The prevalence of GDM varies from 1.01% to 23.12%, according to the different clinical guidelines. The
economic burden was associated with the criteria factors of clinical guidelines. In the years 2001-2012, the economic burden
approximated US$9.94 billion with the current clinical guidelines (ADA2011), and the range of different guidelines varies from
US$1.43 billion to US$32.88 billion. The economic burden of GDM is substantial. The diagnostic criteria for GDM, however,
remain questionable regarding whether or not it is cost-effective. The next step is to conduct a cost-effectiveness study on GDM
screening.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi