Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
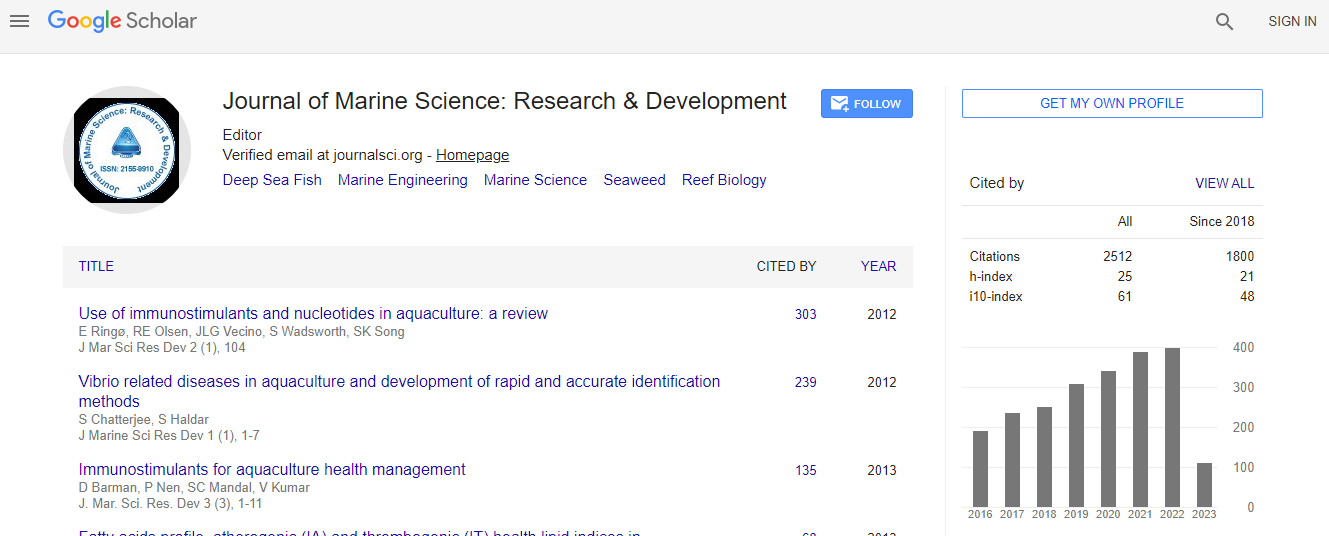
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3189
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- ResearchBible
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Study on Deep Water Warming Trend and Ocean Contaminated State Restoration in the Bay of Bengal : The Implementation of Site Remediating Environmental Modeling
4th International Conference on Oceanography & Marine Biology
Nomana Intekhab Hadi
University of California at Berkeley, USA
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Marine Sci Res Dev
Abstract
The article is written based on the introspection of taking required measures of the worldâ�?�?s one of the biggest oceans garbage problem which is one of the largest environmental challenges mankind faces today. This paper is not only will represent the remediating aspects of coastal zones by discussing how the cleanup array can contribute to cleaner waters and coastal zones, but it will also disclose how simultaneously will it be an essential step towards our goal of establishing the argument on consideration table highlighting how the deployment will enable to study the systemâ�?�?s efficiency and durability over time. The Environmental Modeling will disclose the present haphazardness and dificulties and its adverse consequences on coastal areas and associated lives. Moreover, this paper will propose the deep-water warming trend in the Bay of Bengal showing exponential deterioration over the past six decades and how the temperature of the deep water below 300 m has increased by ~0.9�?°C. The warming trend is due mainly to the reduction of cold-water deep convection over this period, which is associated with milder winters in the region. Despite deep-water warming, density stratification is maintained at depths below 100 m. The observed warming trend is interrupted at least twice by abyssal cooling events that are associated with the wettest years on record. This paper will propose that rainfall and cool river inflow are critical factors that control thermal structure and the rate of deep-water recharge in this deep, tropical zone. This paper will focus on recorded case studies and will address the recommended measures with the association of government and non govenment ogranizations that can be effective.Biography
Nomana Intekhab Hadi is a PhD student from University of California at Berkeley.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi