Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
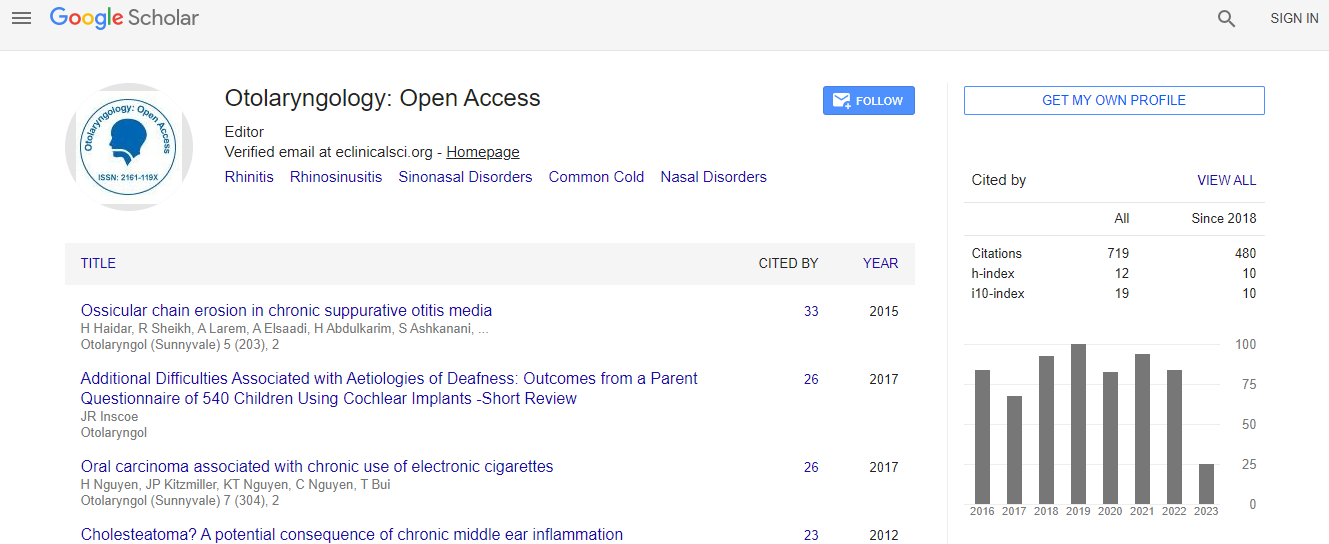
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 925
Otolaryngology: Open Access received 925 citations as per Google Scholar report
Otolaryngology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Retropharyngeal abscess: Our experiences
5th Global Summit and Expo on Head, Neck and Plastic Surgery
Sumit Sharma
Mayo Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Otolaryngol (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
The retropharyngeal space has a very complex anatomy and is located posterior to the pharynx (nasopharynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx), larynx and trachea. The space largely contains retropharyngeal group of lymph nodes. Retropharyngeal abscesses are deep neck space infections that occur in this space and can pose an immediate life-threatening emergency with potential for catastrophic complications. The high mortality rate of retropharyngeal abscess is due to its association with respiratory distress and airway obstruction, mediastinitis, aspiration pneumonitis, jugular venous thrombosis, sepsis and sometimes erosion into the carotid artery. The incidence of the disease in gradually going down due to the widespread availability of good antibiotics; this is also reducing a clinician�s experience in managing such cases. This is a retrospective study of cases with the discharge diagnosis of retropharyngeal abscess treated in the past 10 years, the disease predominantly presented with fever and pain in throat with dysphagia, poor oral intake, neck pain and sore throat. Respiratory distress was seen in a few cases. Surgery was not performed in all the cases and in milder forms and in cases where patients refused for surgery, conservative management was done. Patients were investigated by X-ray and CT scan and ultrasonography and once the diagnosis of retropharyngeal abscess was established, they were managed by drainage/aspiration under general anesthesia along with intravenous antibiotics. Early diagnosis is the key to management of these conditions to avoid morbidity and mortality. Some interesting observations like incidence of Koch�s lesions and type of surgical intervention chosen along with possibility of recurrence will be presented in detail.Biography
Email: entsumit@rediffmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi