Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
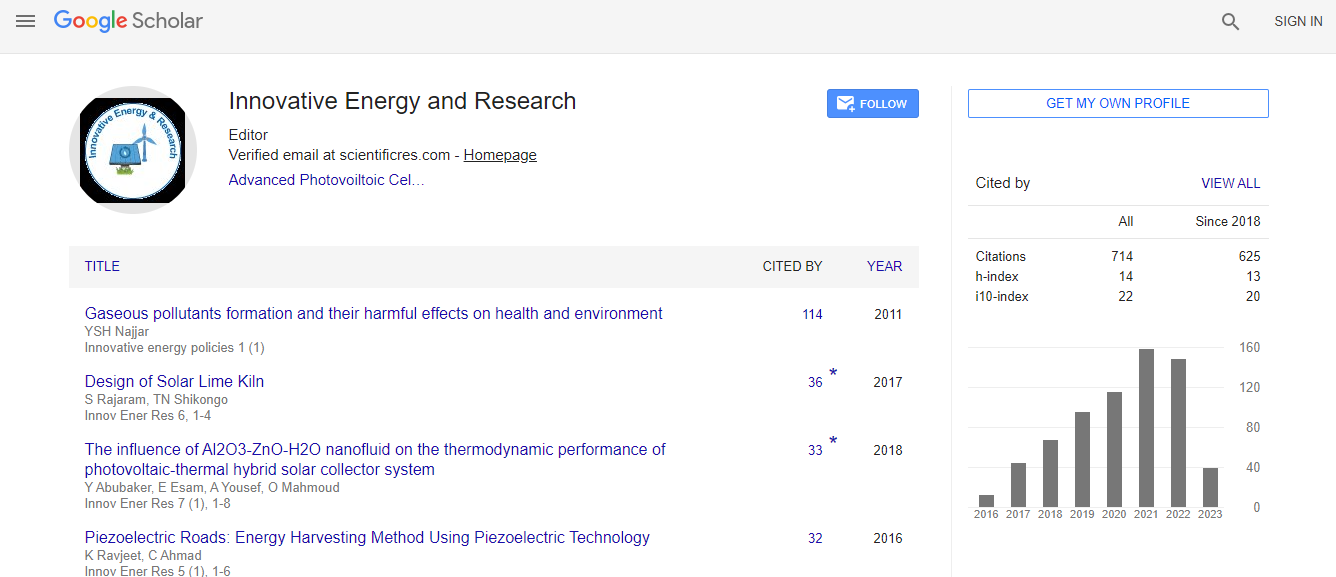
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 712
Innovative Energy & Research received 712 citations as per Google Scholar report
Innovative Energy & Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Recent progressive of two-dimensional materials for terahertz detection
20th International Conference on Advanced Energy Materials and Research
Lin Wang, Xiaoshuang Chen and Wei Lu
Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics - Chinese Academy of Sciences, ChinaUniversity of Science and Technology of China, China
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Innov Ener Res
Abstract
Recent years, layered van der Waals (vdW) crystals consist of individual atomic planes weakly coupled by vdW interaction have attracted great interests due to their intriguing physical properties, such as superconductivity, high carrier mobility, topologically protected surface states and among many others. An ambitious practical goal is to exploit planes of vdW crystals as building blocks of more complex optoelectronic application, especially in the terahertz band. The pursuit of twodimensional materials for terahertz detection is promoted by the unique properties beyond traditional system, such as good CMOS-compatibility, easy for fabrication and fast response. Especially, graphene can support terahertz plasmon which can lead to enhanced THz absorption. Graphene-based terahertz detectors rely on the photo thermoelectric and self-mixing effects both of these effects depends on the near-field or the decay of plasmons. Also, other two-dimensional materials such as black phosphorus, topological insulator exhibit exotic THz optoelectronic properties, such as anisotropic band structure in black phosphorus (BP), interplay between surface states and bulk states such as in Bi2Se3 exhibiting the unique THz spectral profile. Initial characterization has demonstrated the excellent interaction between THz photons and two dimensional materials. However, convent absorbed photons into electricity with high efficiency is still a big challenge. In typically, self-mixing process for direct detection require materials with both high mobility and moderated bandgap, and is usually wipe out/disrupted by the coexisting mechanism such as thermoelectric process. In this work, we present a new route toward manipulation of hot electrons within high mobility materials such as BP and graphene. Due their moderated bandgap, the hot electrons in atomic plane can be extensively excited and randomized. The unilateral flow of excess hot electrons can be facilitated by exploring both the electromagnetic engineering and electrostatic tuning. Intriguingly, the hot electrons effect changes the resistance via nonequilibrium carrier diffusion, leading to the high photoelectric gain under electrical bias. The present results and the novel hot electron mechanism allow for realistic exploitation of two-dimensional materials for large area, fast imaging. Recent Publications: 1. L Vicarelli, M S Vitiello, D Coquillat, A Lombardo, A C Ferrari, W Knap, M Polini, V Pellegrini and A Tredicucci (2012) Graphene field-effect transistors as room-temperature terahertz detectors. Nature Materials 11:865-871. 2. Lin Wang, Changlong Liu, Xiaoshuang Chen, Jing Zhou, Weida Hu, Xiaofang Wang, Jinhua Li, Weiwei Tang, Anqi Yu and Shao Wei Wang (2017) Toward sensitive room-temperature broadband detection from infrared to terahertz with antenna-integrated black phosphorus photoconductor. Advanced Functional Materials 27(7):1604414. 3. Changlong Liu, Lin Wang, Xiaoshuang Chen, Jing Zhou, Weida Hu, Xinran Wang, Jinhua Li, Zhiming Huang, Wei Zhou, Weiwei Tang, Gangyi Xu, Shao-Wei Wang and Wei Lu (2018) Room-temperature photoconduction assisted by hot- carriers in graphene for sub-terahertz detection. Carbon 130:233-240. 4. Weiwei Tang, Antonio Politano, Cheng Guo, Wanlong Guo, Changlong Liu, Lin Wang, Xiaoshuang Chen and Wei Lu (2018) Ultra-sensitive room-temperature terahertz direct detection based on bismuth selenide topological insulator. Advanced Functional Materials DOI:10.1002/adfm.201801786. 5. Changlong Liu, Lin Wang, Xiaoshuang Chen, Jing Zhou, Weiwei Tang, Wanlong Guo, Jin Wang and Wei Lu (2018) Top-gated black phosphorus phototransistor for sensitive broadband detection. Nanoscale 10(13):5852-5858.Biography
Lin Wang is currently an Associate Professor in Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Science. He has been awarded many prizes including special prize of president scholarship for distinguished postgraduate student. He received the outstanding achievement award in Shanghai. He has authored or coauthored more than 40 technical journal papers and delievered more than 10 invited conference presentations, seving as a journal peer-reviewer in Advanced Functional Materials, ACS Nano, APL, etc. His current research interests include plasma wave detection of terahertz/infrared radiation using graphene and III-V, plasmonic nanomaterials and metamaterials devices, graphene-like two-dimensional optoelectronics.
E-mail: wanglin@mail.sitp.ac.cn

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi