Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
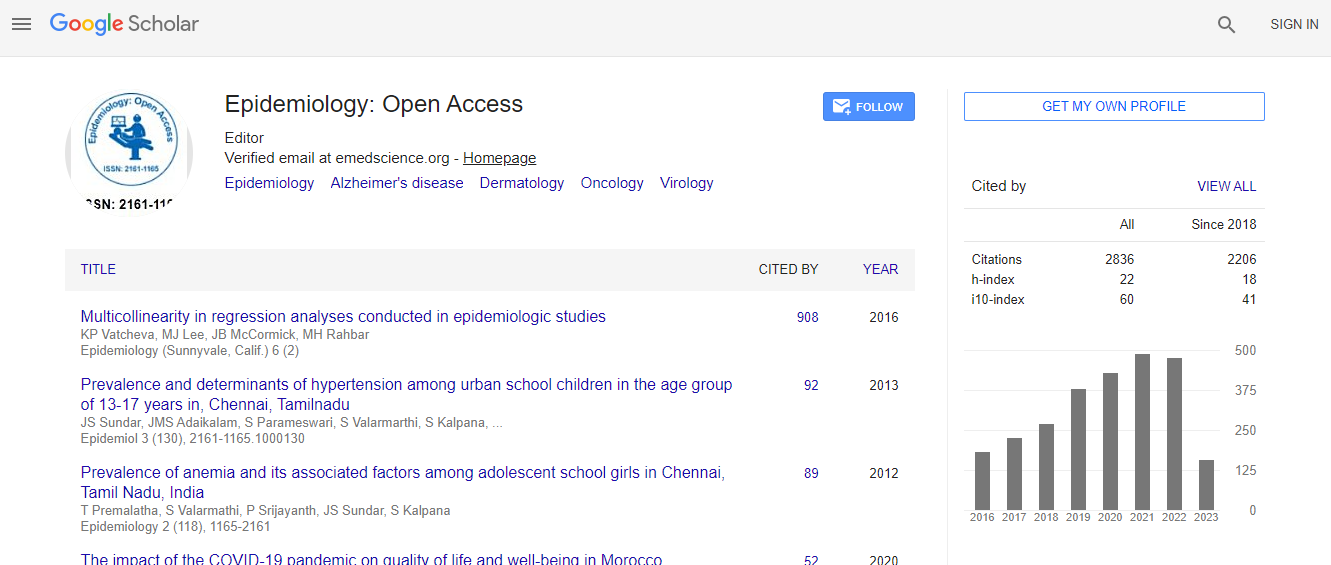
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Prescription claims according to wellness program participation for a large employer in the United States
8th International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Ray M Merrill
Brigham Young University, USA
Keynote: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Worksite wellness programs that include biometric screening and health risk appraisal can identify the need for lifestyle change and prescription medication. Hence, there may be an initial increase cost in prescription medication, but the aim is to prevent more costly health problems in the future, as well as lower absenteeism and presenteeism. The purpose of the current study was to identify the number and total cost of prescription claims and copays for a large US employer according to wellness program participation, age, and sex. A retrospective analysis was conducted of prescription medication use among 6810 workers during 2013-2016. Those completing the wellness program were more likely women (32.5% vs. 22.9%, p < 0.0001) and younger (M=45.5 vs. 48.5, p < 0.0001). Approximately 72.7% (74.4% women and 68.6% men, p < 0.0001) filed a pharmacy claim. In 2013, there was no difference in number of claims filed or total cost between participants and nonparticipants. Mean number of prescriptions changed over the study period, initially increasing but then decreasing for wellness participants. Overall the decrease was 34.7% among wellness participants. The corresponding change for non-participants was an increase of 3.4%. Mean changes in total costs showed similar patterns. In 2016, program participants filed nearly 3 fewer claims, with total cost about $329 less, on average. Approximately 96.5% of employees filing a pharmacy claim made a copayment. Overall, copays consist of 6.4% of total insurance and employee expenditure on pharmacy claims. In conclusion, the biometric screening and health risk appraisal components of the wellness program resulted in an initial increase in number and total cost of pharmacy medication. However, over the four-year study period, the number of claims and total cost of pharmacy medication significantly decreased. Recent Publications 1. Merrill RM, Frutos A. Reduced lung cancer mortality with lower atmospheric pressure. Dose Response. 2018; 16 (2):1559325818769484. 2. Merrill RM. Conditional relative survival among female breast cancer patients in the United States. Breast J. 2017; Epub ahead of print. 3. Merrill RM, Johnson E. Benefits of marriage on relative and conditional relative cancer survival differ between males and females in the USA. J Cancer Surviv. 2017; 11 (5):578-589. 4. LeCheminant J, Merrill RM, Masterson TD. Changes in behaviors and outcomes among school-based employees in a wellness program. Health Promot Pract. 2017; 18 (6):895-901. 5. Merrill RM, LeCheminant JD. Medical cost analysis of a school district worksite wellness program. Prev Med Rep. 2016; 3: 159-165. 6. Merrill RM, Thygerson SM, Palmer CA. Risk of injury according to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, comorbid mental illness, and medical therapy. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2016; 49(2):45-50.Biography
Ray Merrill’s expertise is in biostatistics and epidemiology. His research interests include analysis and modeling of trends in chronic disease incidence, mortality, and survival data; investigation of the impact of chronic disease treatment advances and increased utilization of screening tests on population disease statistics; methodologic investigations into new chronic disease measures, the relationships between incidence, mortality, and survival, and the impact of various biases on chronic disease statistics.
E-mail: Ray _Merrill@byu.edu

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi