Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
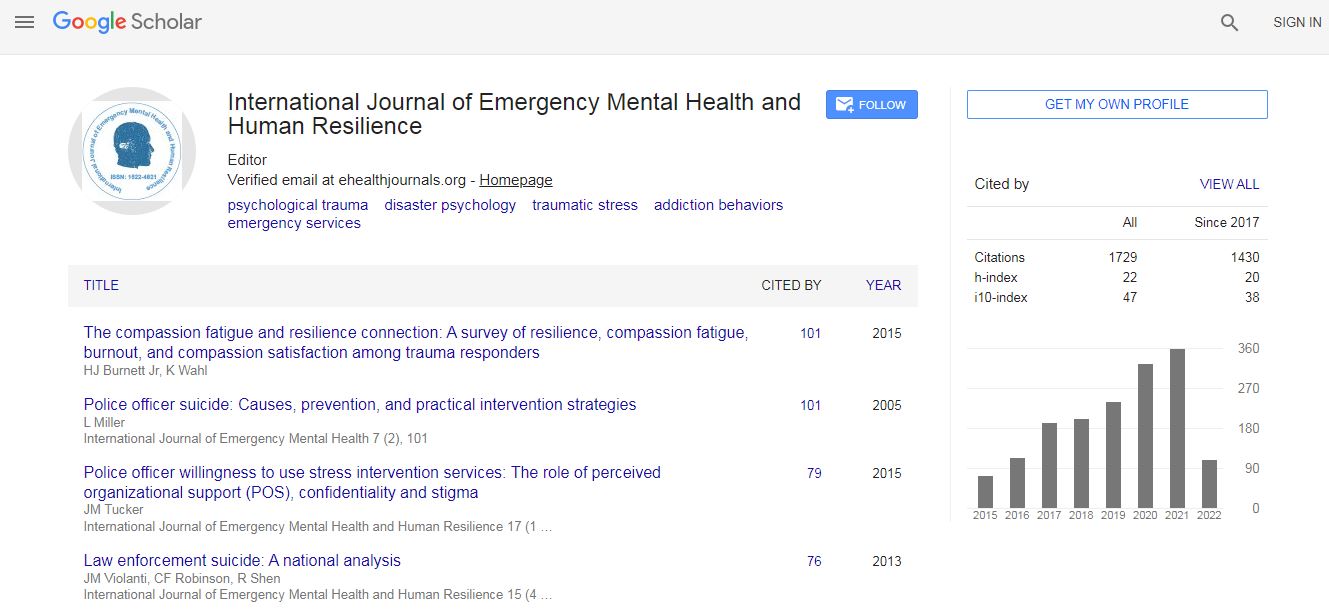
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 4948
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- Publons
- Pubmed
- science Gate
- scispace
- world cat
Useful Links
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Preliminary analysis of self-efficacy, coping styles, competitive greatness & nursing students
Joint Event on 14th World Congress on Psychiatric & Mental Health Nursing & 5th World Congress on Mental Health and Wellbeing
Dale Hilty
Mount Carmel College of Nursing, USA
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: IJEMHHR
Abstract
The purpose of this educational intervention study was to explore the relationship among Wooden's Competitive Greatness (Hilty, 2018) construct (i.e., being the best you can be when your best is needed, continuous self-improvement, appreciating difficult challenges), Self-Efficacy (Schwarzer & Jerusaslem, 1995), and Greenglass' et al. (1999) Proactive Coping, Reflective Coping, Strategic Planning, Emotional Support Seeking scales. Since 43% of new RNs leave their first job within three years (Goodman, 2016), exploring these variables may provide insight into turnover rates. BSN (N=68) traditional nursing students were divided into two groups using competitive greatness. Hypothesis: There would be a difference between competitive greatness high and low scoring groups when the two groups were compared using an Independent t-test on Self-Efficacy, Proactive Coping, Reflective Coping, Strategic Planning, Emotional Support Seeking scales ESS scales. Using SPSS 25, the coefficient alpha were Self-Efficacy (.957), Proactive Coping (.816), Reflective Coping (.909), Strategic Planning (.866), and Emotional Support Seeking (.854). Independent t-test (N=68) analysis found significant differences between the two participant groups for the Self-Efficacy (p=.002), Proactive Coping (p=.001), Reflective Coping (p=.008), Strategic Planning (p=.004), and Emotional Support Seeking (p=.028) scales.Biography
Dale M. Hilty, Associate Professor, received his PhD in counseling psychology from Department of Psychology at the Ohio State University. He has published studies in the areas of psychology, sociology, and religion. Between April 2017 and April 2018, his ten research teams published 55 posters at local, state, regional, national, and international nursing conferences.
E-mail: dhilty@mccn.edu

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi