Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
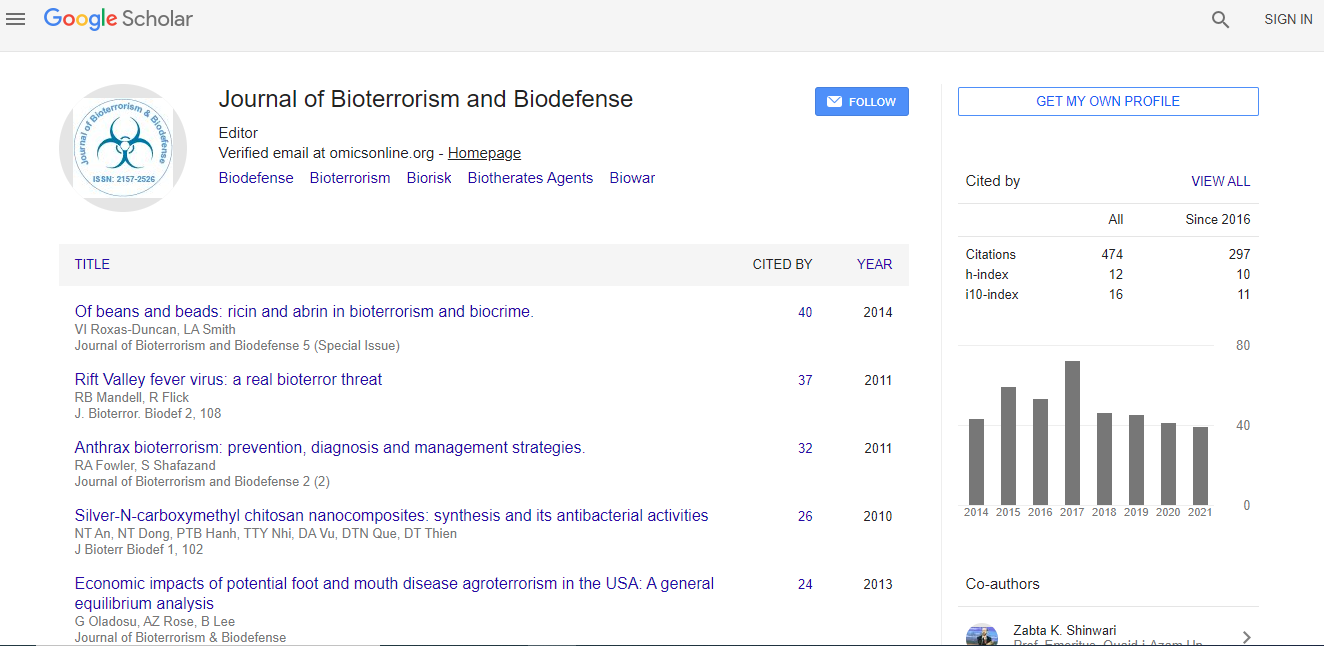
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1129
Journal of Bioterrorism & Biodefense received 1129 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- JournalTOCs
- ResearchBible
- China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- SWB online catalog
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Potential and limits of mobile health (mHealth)
International Conference on Biothreats & Biodefense
Syed A. Hashsham
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Bioterr Biodef
Abstract
Diagnostic tools based on cellphones and mobile devices (broadly known as mHealth) have the potential to significantly reduce the economic burden of global health. By 2015 the number of cellphone users will reach 1.4 billion and at least 500 million of them will have used mHealth. Currently, more than 17,000 mHealth apps are available on various platforms. However, their ability to carry out genetic assays is yet to be harnessed. Out of the more than 2,500 genetic assays available, perhaps none are available on a mobile platform (GeneTests: www.genetests.org/). If the more commonly needed genetic tests are made available on mobile devices at lower cost, a much larger number of persons will benefit from the genomic revolution. The �mobility� and �distributed� nature of these platforms makes them an ideal platform to tackle the challenges ahead which are simply staggering. �The global economic impact of the five leading chronic diseases -- cancer, diabetes, mental illness, heart disease, and respiratory disease -- could reach $47 trillion over the next 20 years, according to a study by the World Economic Forum.� (Reuters, September 18, 2011). Currently, 36 million people die each year from these five non-communicable diseases. By 2030, this number could reach 56 million a year, according to World Health Organization. The high healthcare cost in the US is well known with total healthcare spending of $2.5T in 2010 and average per capita spending of over $7,500. This is three-fold higher than the average for the 34 Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) countries. If the power of cellphones and wireless networks could be harnessed efficiently, these platforms have the ability to make a significant impact. This presentation will present selected developments taking place in the area of mobile health with a focus on diagnostics. It will also highlight the challengesof developing solutions on such platforms and itslimitations.Biography
Syed A. Hashsham is Professor of Environmental Engineering at Michigan State University. A native of Siddhartha Nagar, U.P., India, he studied Civil Engineering at Aligarh Muslim University, India, and completed his Masters in Environmental Engineering at IIT, Mumbai. He then moved to the United States, where he obtained his Ph.D. in Environmental Engineering from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. During his postdoctoral work at Michigan State and at Stanford University, he studied ecological principles governing bioreactor communities and on environmental genomics. In 2000, he joined Michigan State University as Assistant Professor. Since then has been working in the areas of environmental genomics, development of hand-held genetic analysis systems using low-cost microfluidic systems, and interactions of environmental contaminants to gut microbiome and human health. His research interests lie at the intersection of engineering, genomics, and microbial ecology.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi